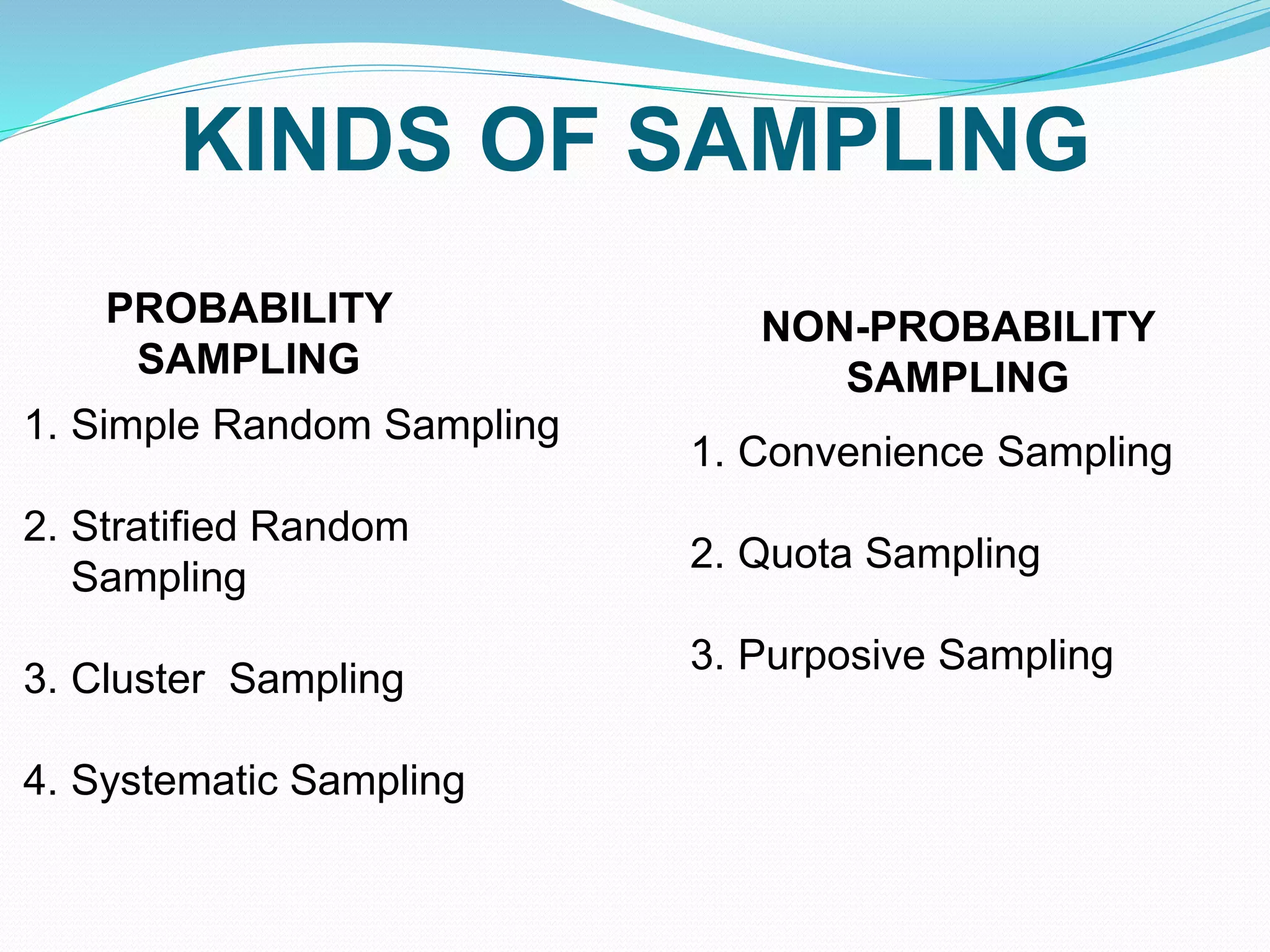
This document discusses different types of sampling methods used in research. It describes probability sampling as methods where all members of the population have an equal chance of being selected, including simple random sampling, stratified sampling, cluster sampling, and systematic sampling. Non-probability sampling methods are also covered, where not all members have a chance of being selected, such as convenience sampling, quota sampling, and purposive sampling. Key factors that influence sample representativeness are the sampling procedure, sample size, and level of participation.