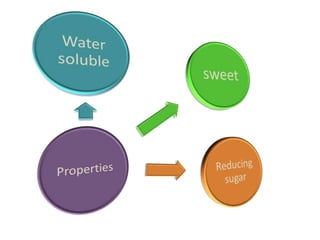
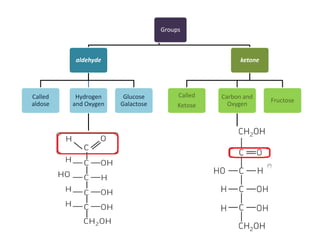
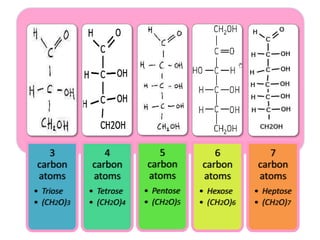
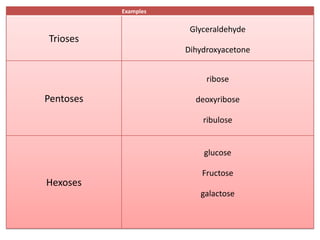
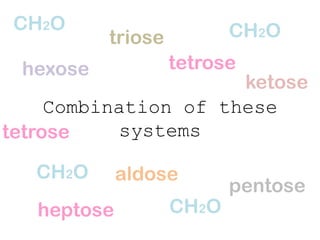
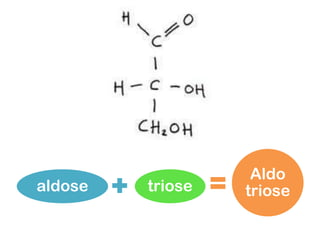
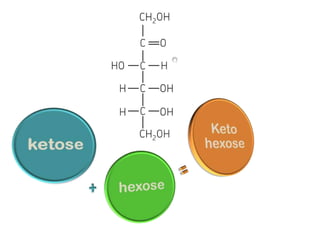
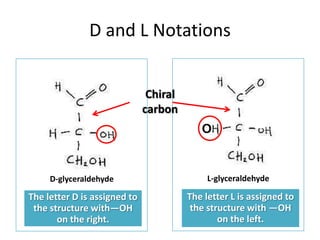
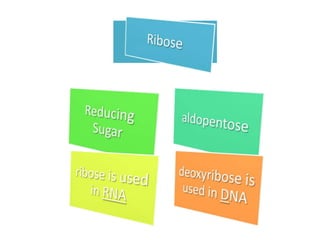
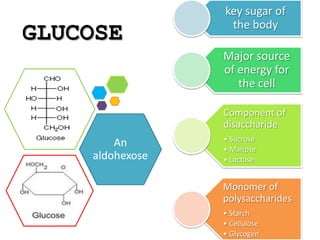
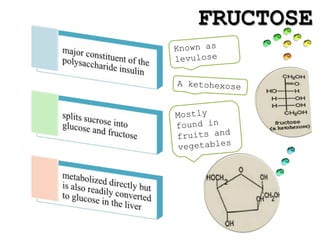
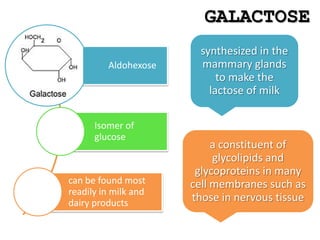
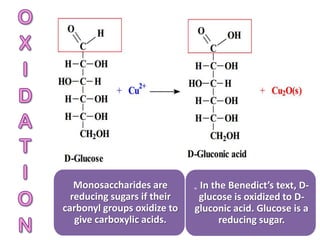
Monosaccharides are the simplest type of carbohydrate that cannot be broken down further. They typically have 3-7 carbon atoms and have the formula (CH2O)n. Common monosaccharides include glucose, fructose, and ribose. Glucose is a six-carbon aldohexose that is the major source of energy for cells. It is also a component of important disaccharides and polysaccharides like starch, cellulose, and glycogen. Fructose is a ketose found in fruits, while galactose is found in milk and dairy and is involved in glycolipids and glycoproteins. Monosaccharides can undergo oxidation reactions where the carbonyl group is oxidized, or reduction