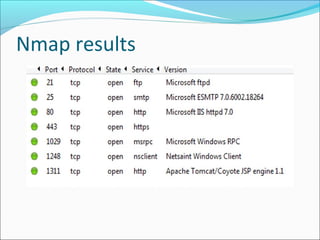
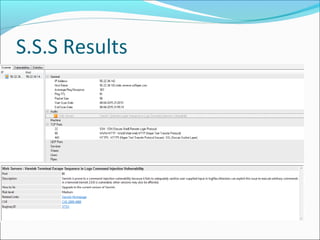
The document discusses port scanning, a technique used by both network administrators and attackers to identify open ports on a server or host. It highlights the differences between defensive and malicious port scanning methods and mentions popular tools like nmap and shadow security scanner, which are used for security assessments. The conclusion emphasizes the importance of implementing robust security measures such as IP spoofing and stateful firewall rules to prevent attacks stemming from port scans.