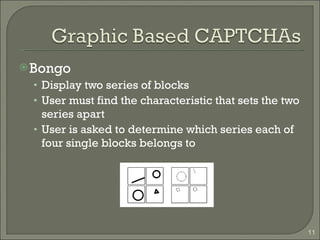
The document discusses CAPTCHAs, which are programs that can distinguish humans from computers by generating tests that are easy for humans but difficult for computers. It provides background on CAPTCHAs, describes common types including text, graphic, and audio CAPTCHAs, and discusses techniques for breaking existing CAPTCHAs. It then proposes a new approach to CAPTCHAs that uses distorted images of concrete objects from Google Images and requires users to identify the object from a list of words to address limitations in other CAPTCHAs.