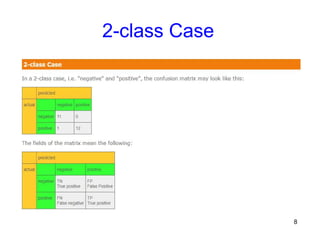
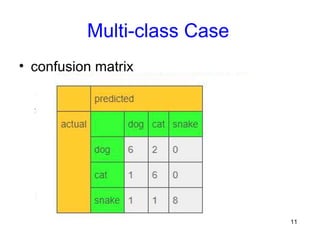
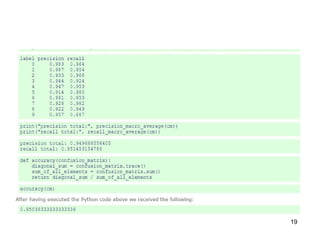
This document discusses confusion matrices, which are used to evaluate machine learning algorithms. A confusion matrix shows the predictions made by a model versus the actual classifications. It allows users to see what types of mistakes or "confusions" are made. The document explains 2-class and multi-class confusion matrices through examples. A multi-class matrix for animal classification is shown, demonstrating how values on the diagonal represent correct predictions while off-diagonal values are errors. Code is also presented to calculate precision, recall, and macro-averaged precision from a confusion matrix in Python.




![6
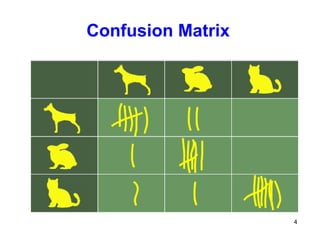
Confusion Matrix
• The name confusion matrix reflects the fact that it
makes it easy for us to see what kind of
confusions occur in our classification algorithms.
• For example the algorithms should have predicted
a sample as Ci because the actual class is Ci, but
the algorithm came out with Cj. In this case of
mislabelling the element cm[i,j] will be incremented
by one, when the confusion matrix is constructed.
• We will define methods to calculate the confusion
matrix, precision and recall in the following class.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/machinelearningbyusingpythonlesson3-190809223342/85/Machine-learning-by-using-python-lesson-3-Confusion-Matrix-By-Professor-Lili-Saghafi-6-320.jpg)