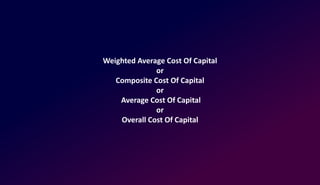
This document discusses capital structure and cost of capital. It defines capital structure as the mix of long-term sources of funds used by a firm, including equity, preference shares, debt, and retained earnings. The goals of capital structure decisions are to minimize cost of capital, reduce risks, provide flexibility, and maximize firm value. Cost of capital is the required rate of return for investments in order to increase the firm's market value. The document then discusses types of cost of capital such as historical vs future, specific vs composite, average vs marginal, and explicit vs implicit. It also provides formulas for calculating the costs of equity, preferred shares, debt, and retained earnings, and defines weighted average cost of capital (WACC) as