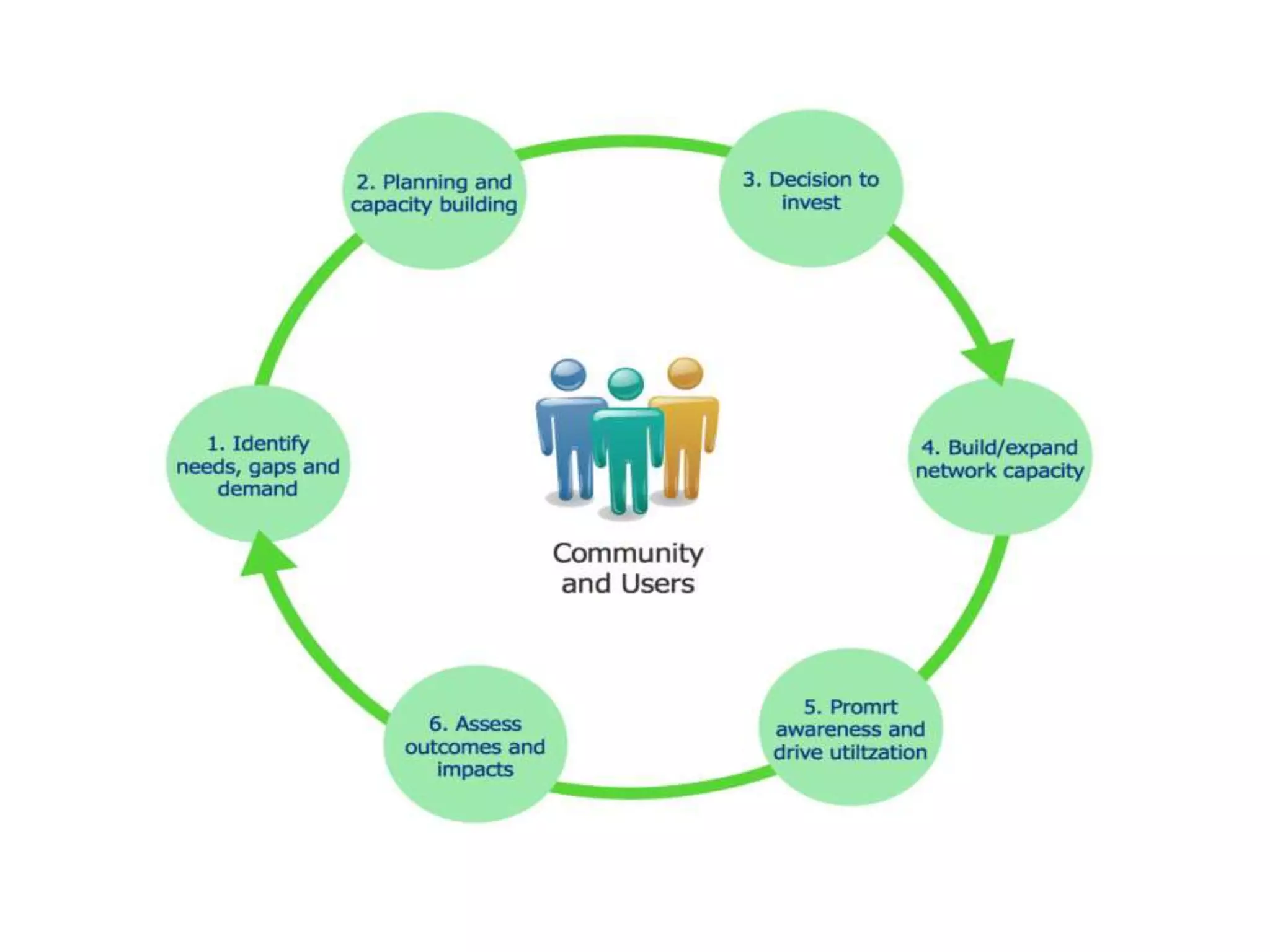
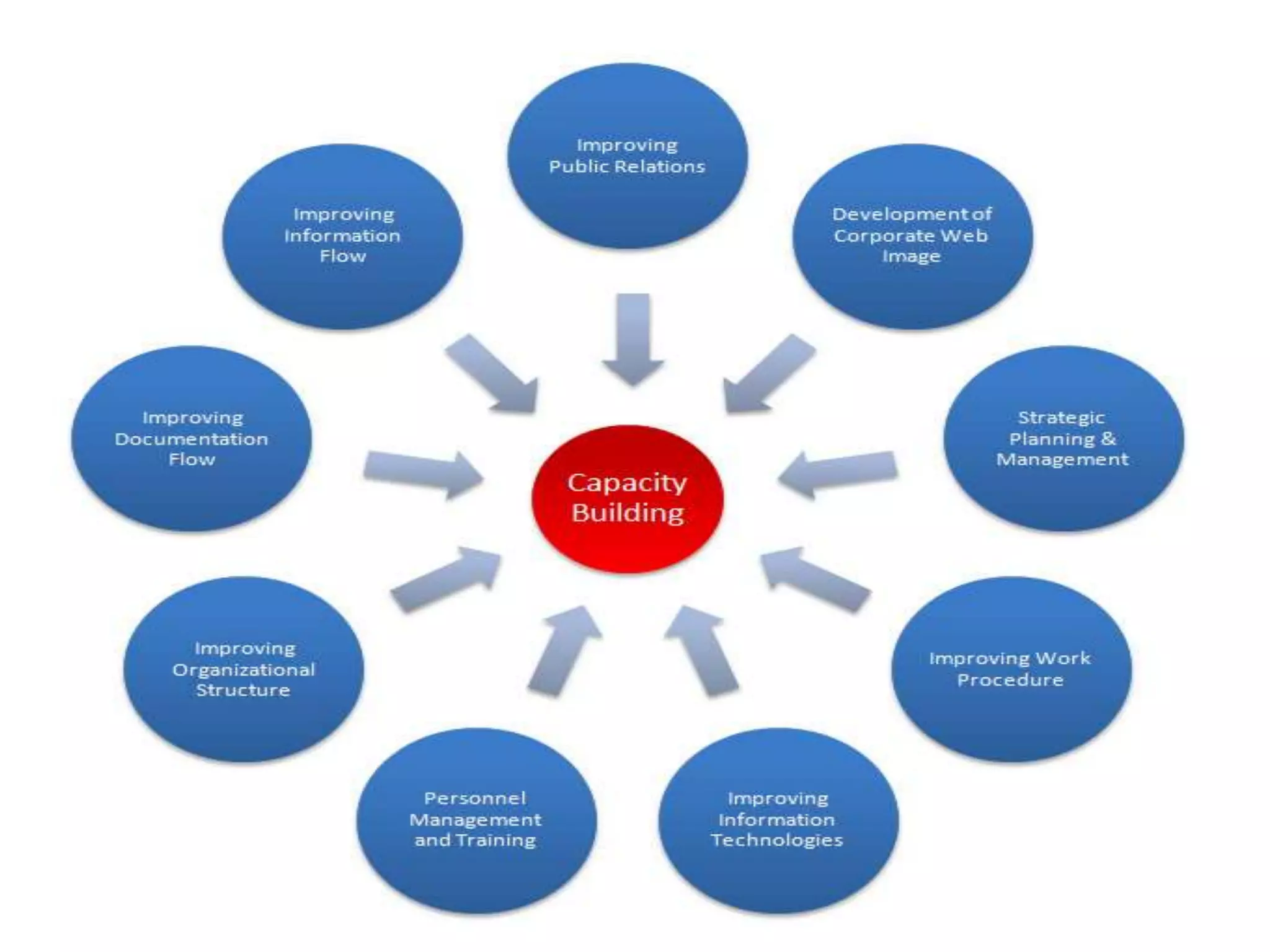
Capacity building in disaster management involves strengthening local skills, resources, and abilities. This includes educating communities about hazards and responses, training volunteers, collaborating with relief agencies, conducting mock drills, and understanding warning messages. Assessing needs, knowledge, and attitudes is important for effective training programs. Involving all stakeholders and mainstreaming disaster risk reduction also builds capacity. Capacity building connects disasters with development and relies on traditional knowledge and participation to improve well-being and ensure organizational success over time.