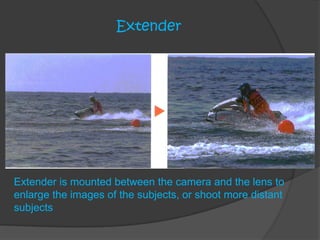
The document provides information about Rajanish Kumawat's practical training at Doordarshan Kendra in Jaipur. It discusses key details about Doordarshan, including that it is India's public service broadcaster, it was established in 1959, and currently operates 21 TV channels. It also provides specifics about DD Rajasthan, the state-owned channel broadcast from Doordarshan Kendra Rajasthan, including that it covers 79% of the state's population. The document then covers technical aspects of television cameras, lenses, apertures, and other camera functions.