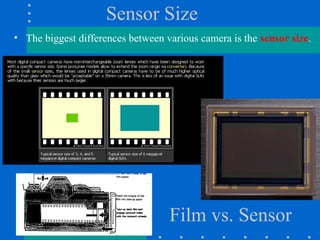
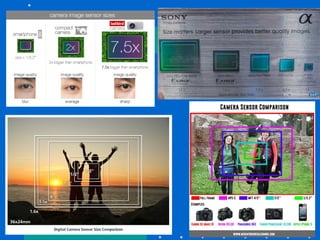
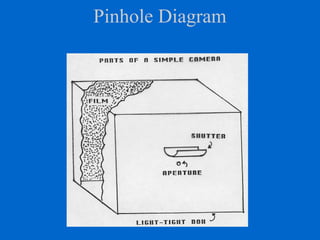
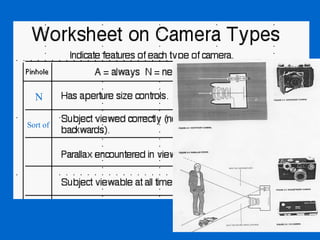
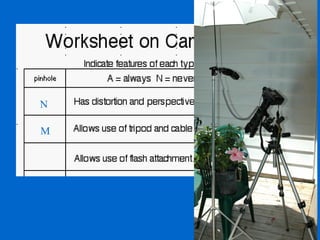
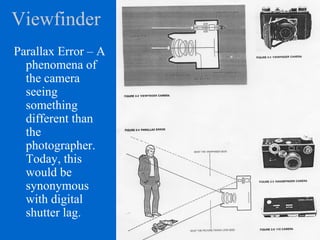
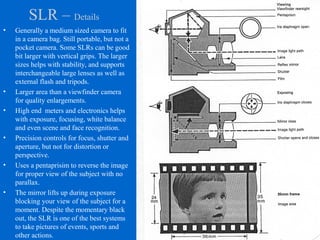
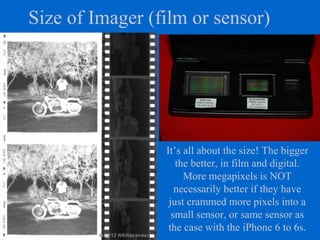
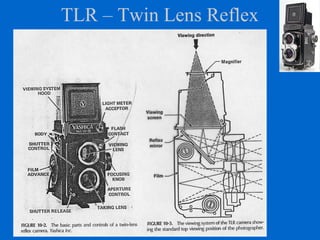
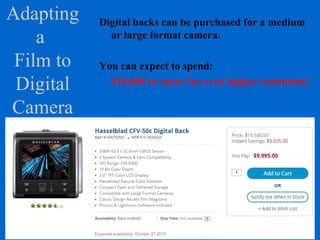
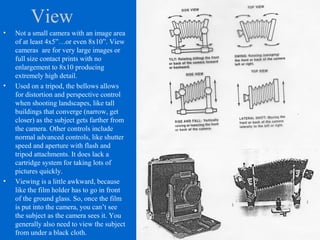
The document provides an overview of various types of cameras, including pinhole, single lens reflex (SLR), twin lens reflex (TLR), and large format view cameras. It discusses the advantages and disadvantages of each type, highlighting differences in features, image quality, and usability. Additionally, it touches on the evolution of digital cameras and the impact of technological advancements on their design and functionality.