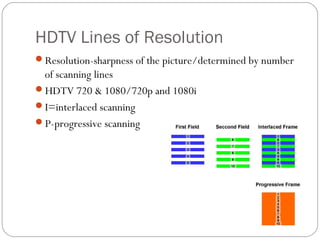
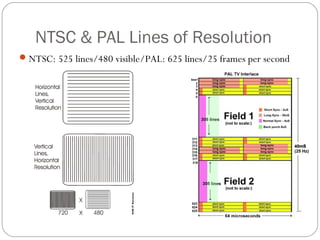
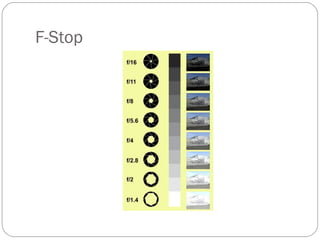
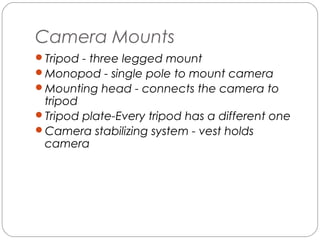
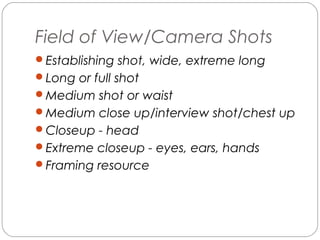
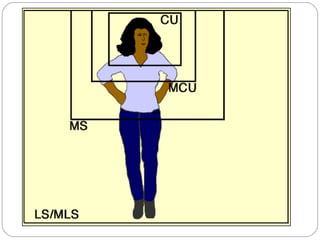
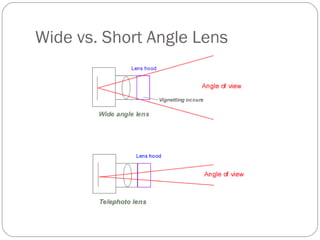
This document provides an overview of key concepts for shooting video, including the main components of a camera, camera functions, lenses, camera shots, lighting, and other technical aspects of video production. It discusses camera components like the lens, sensor, and viewfinder. It also covers topics such as focal length, aperture, depth of field, field of view shots, lighting ratios, and camera mounts and stabilization. The goal is to educate about proper techniques for capturing high-quality video footage.