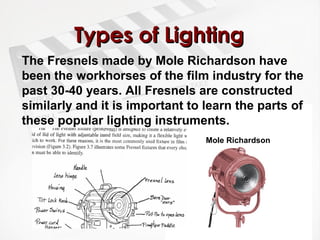
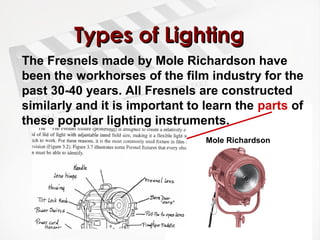
The document provides a comprehensive overview of lighting techniques used in cinematography, focusing primarily on 3-point lighting, which involves key, fill, and back lights. It discusses the types of lighting instruments used, including tungsten, HMI, fluorescent, and LED lights, along with their characteristics and applications. Additionally, it covers important aspects of light such as coherence, color temperature, and intensity, as well as methods for controlling and manipulating light in film production.