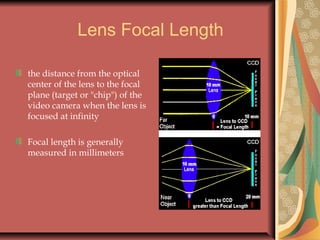
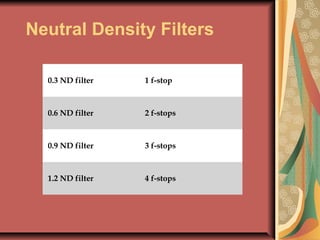
The document discusses various components and techniques used in camera work including lenses, imaging devices, focal lengths, angles of view, shot types, focus, lighting levels, depth of field, white balancing, shutter speeds, camera mounts, filters, and more. It provides information on technical specifications and how different settings and equipment impact the look and quality of recorded video.