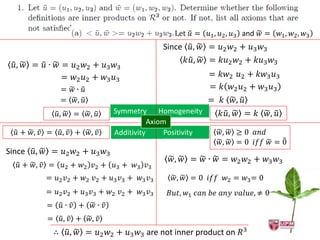
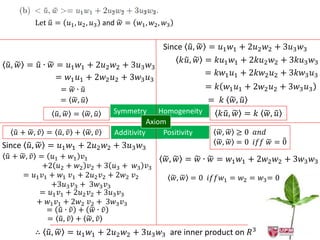
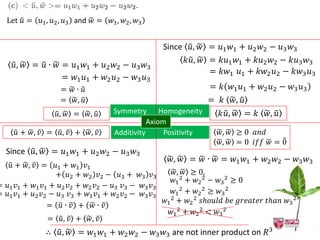
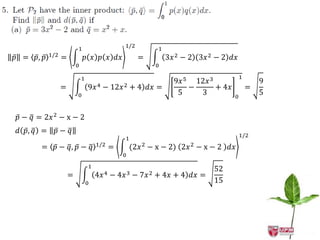
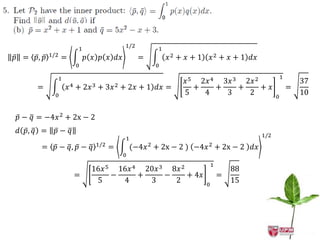
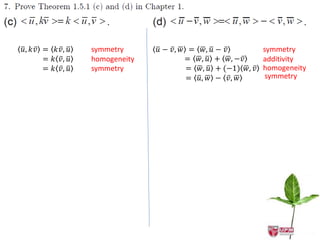
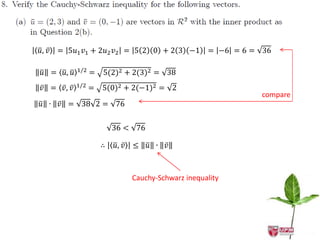
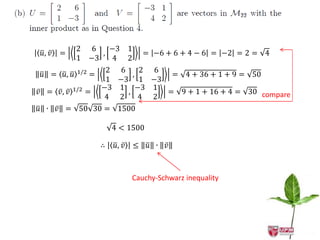
The document discusses inner products and their properties in linear algebra. It provides examples of dot products of vectors in R3 that satisfy the properties of an inner product and those that do not. Specifically, it shows that u1w1 + u2w2 + u3w3 and u1w1 + 2u2w2 + 3u3w3 satisfy the properties, while u1w1 + u2w2 - u3w3 does not always satisfy non-negativity. It also discusses other properties such as symmetry, homogeneity, additivity and positive definiteness.