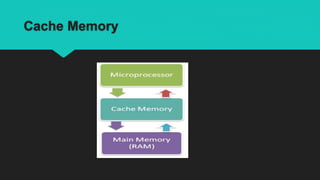
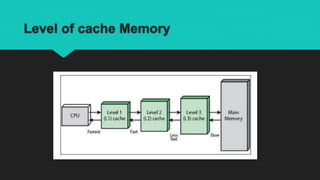
Cache memory is a small, fast memory located close to the CPU that stores copies of frequently used data from main memory. It comes in three levels - L1 cache is built into the CPU and fastest, L2 cache is larger but slower, and L3 cache is located on the motherboard between the CPU and main memory. Cache memory speeds up system performance by allowing the CPU to access needed data and instructions faster than from main memory.