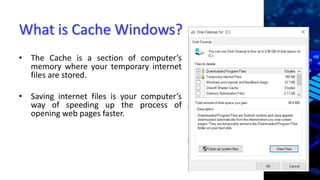
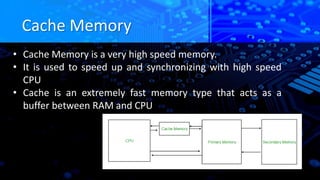
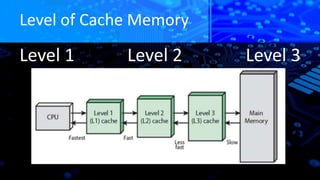
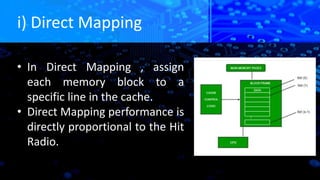
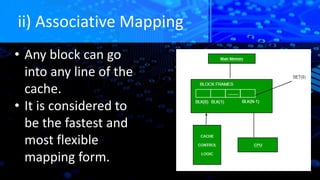
The document explains caching in Windows, detailing its function as a temporary storage to speed up the loading of websites and applications. It describes different levels of cache memory (L1, L2, and L3) and their characteristics, including their speed and integration with the CPU. Additionally, it covers cache mapping techniques, such as direct, associative, and set-associative mapping, and highlights the benefits of cache memory in improving data access efficiency.