The cache is a small amount of fast memory located close to the CPU that stores frequently accessed and nearby data from main memory in order to speed up data access times for the CPU. Without cache, every data request from the CPU would require accessing the slower main memory. Caches exploit the principle of locality of reference, where programs tend to access the same data repeatedly, to improve performance by fulfilling many requests from the faster cache instead of main memory.







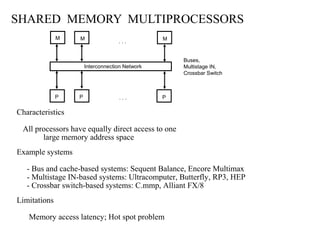

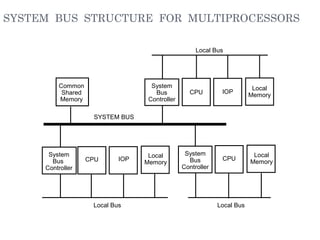
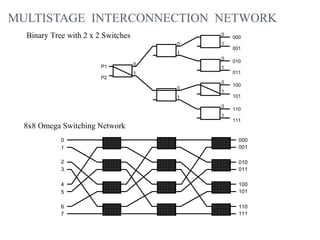
![- A collection of signal lines that carry module-to-module communication
- Data highways connecting several digital system elements
Operations of Bus
Bus
M3 wishes to communicate with S5
[1] M3 sends signals (address) on the bus that causes
S5 to respond
[2] M3 sends data to S5 or S5 sends data to
M3(determined by the command line)
Master Device: Device that initiates and controls the communication
Slave Device: Responding device
Multiple-master buses
-> Bus conflict
-> need bus arbitration
Devices
M3 S7 M6 S5 M4
S2
BUS](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vishalcoa-160830131603/85/Cache-memory-and-cache-12-320.jpg)