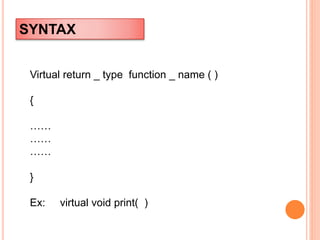
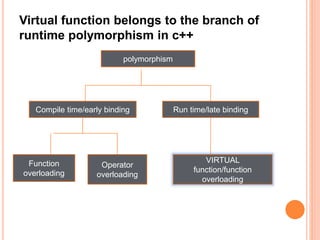
Virtual functions allow functions to be overridden in derived classes. The virtual keyword before a function in the base class specifies that the function can be overridden. When a virtual function is called using a base class pointer, the version from the most derived class will be executed due to late binding. This allows runtime polymorphism where the function call is resolved based on the actual object type rather than the pointer variable type.