Embed presentation
Downloaded 16 times
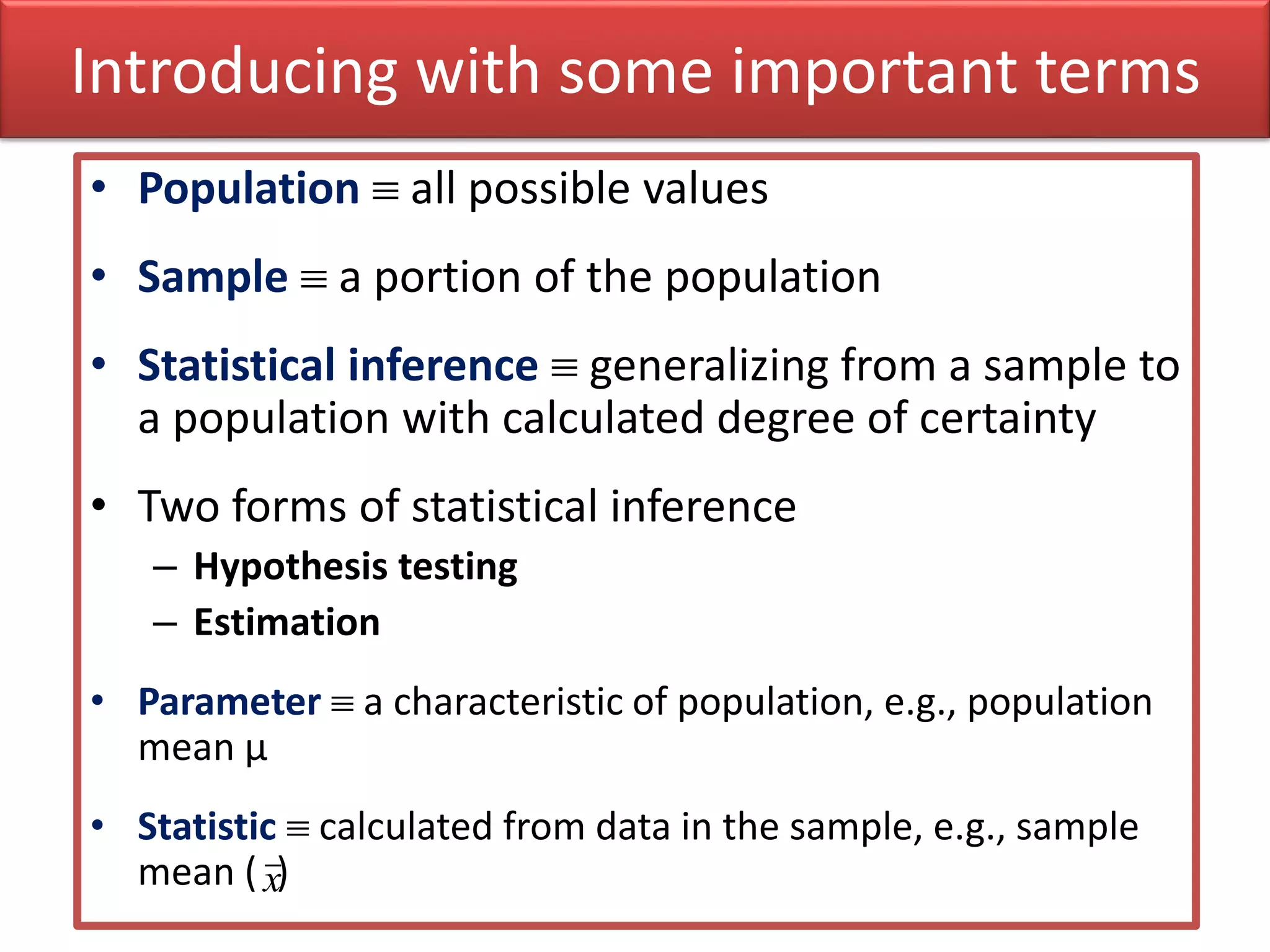
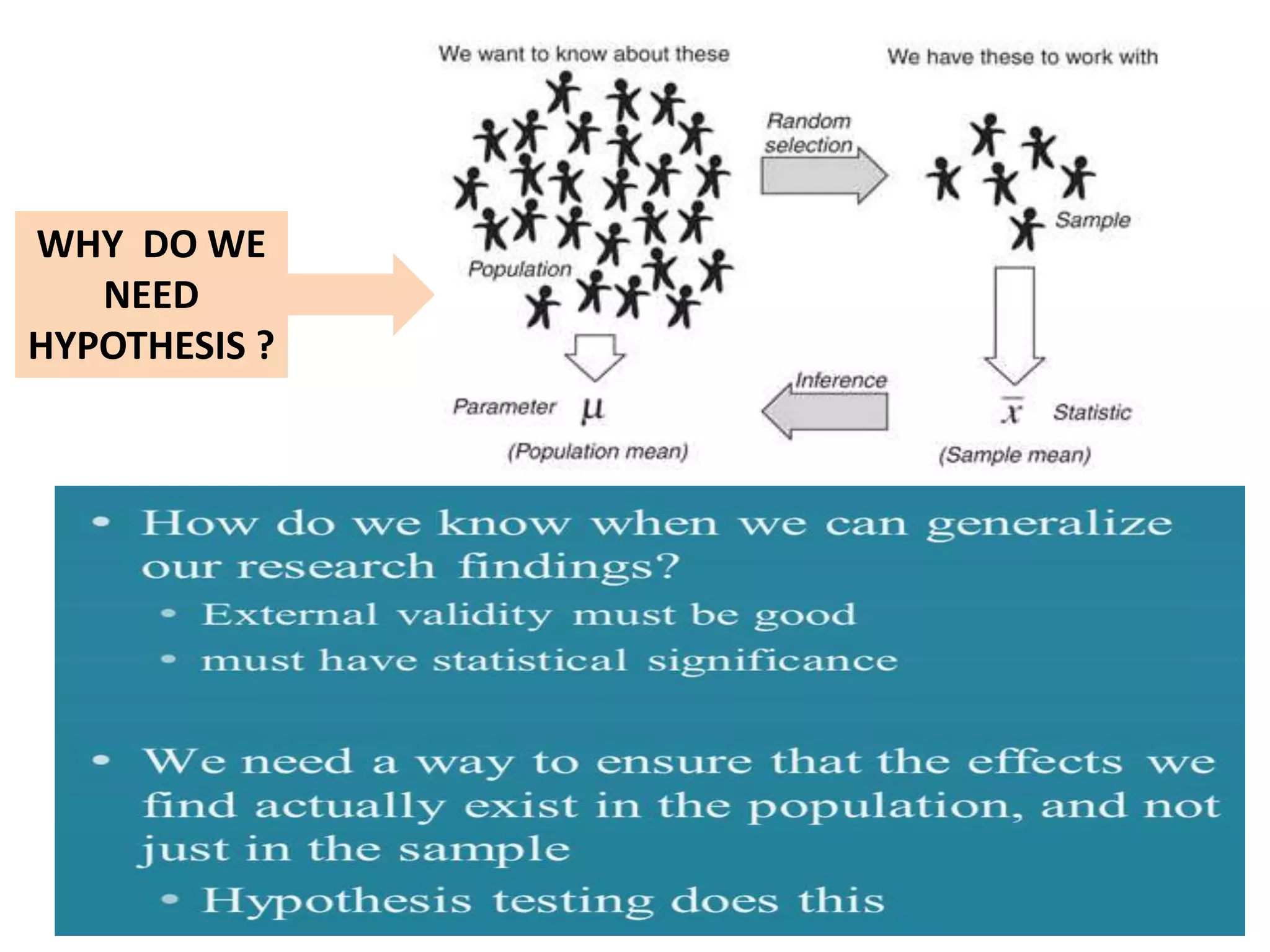
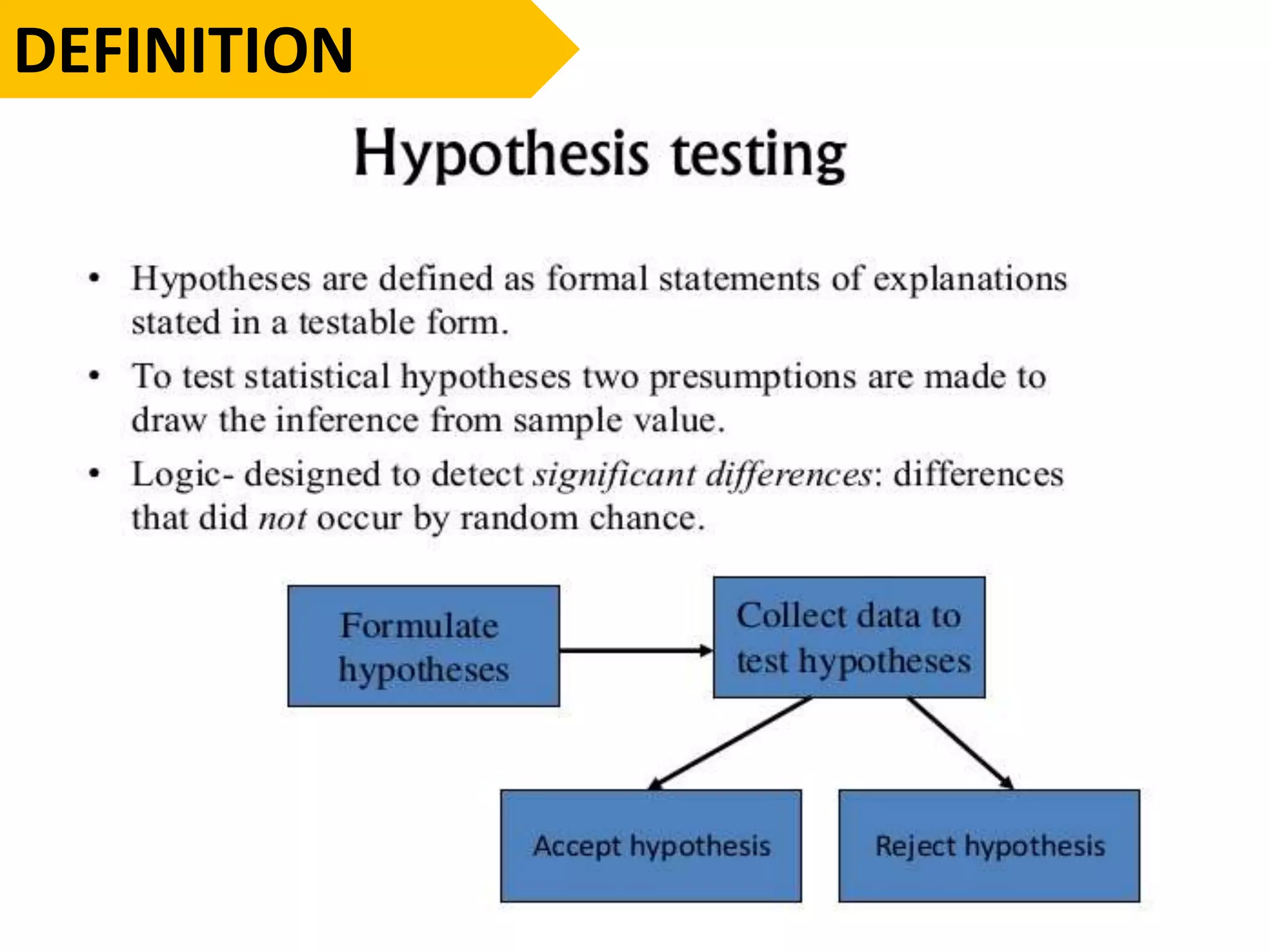
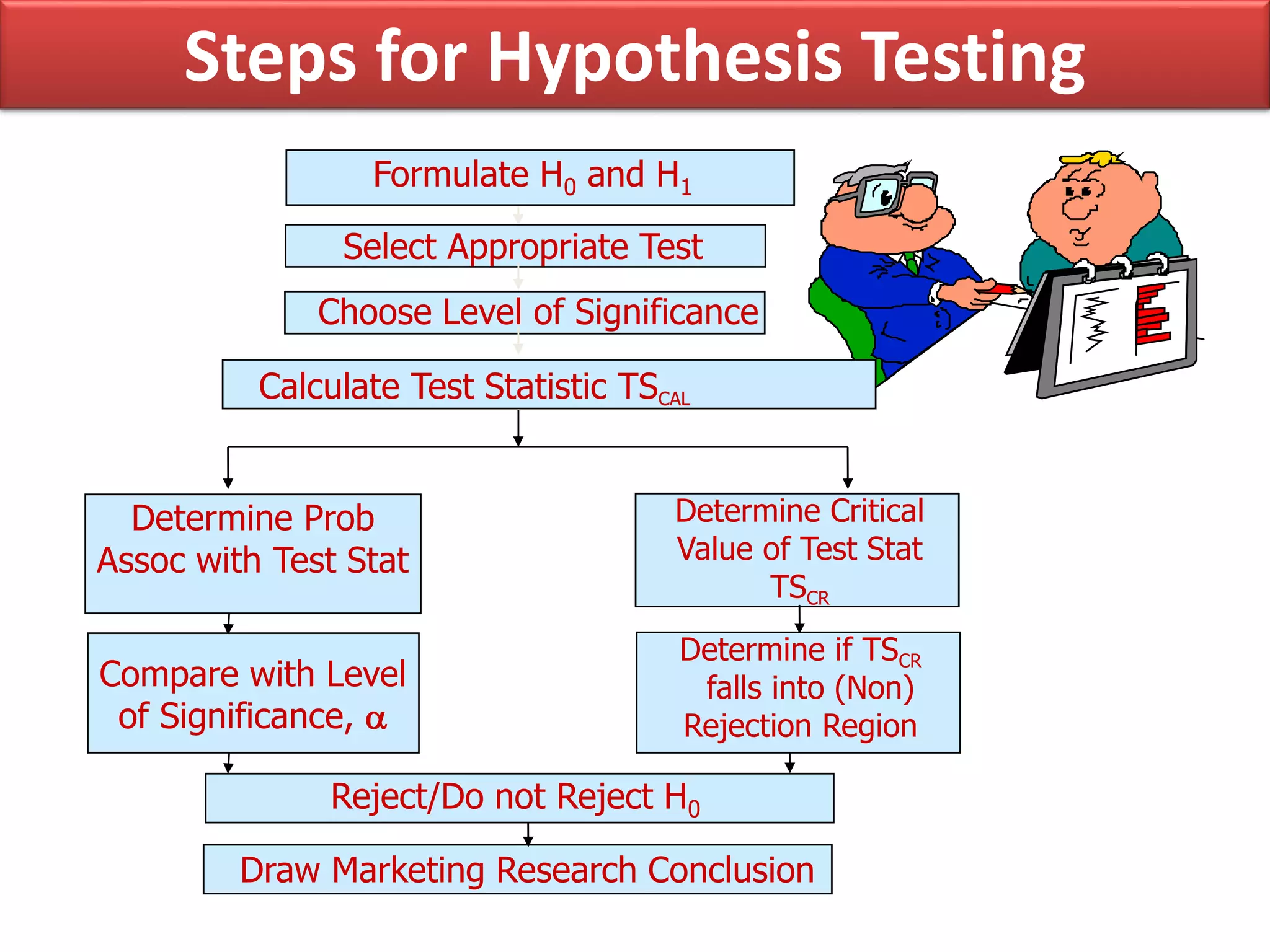
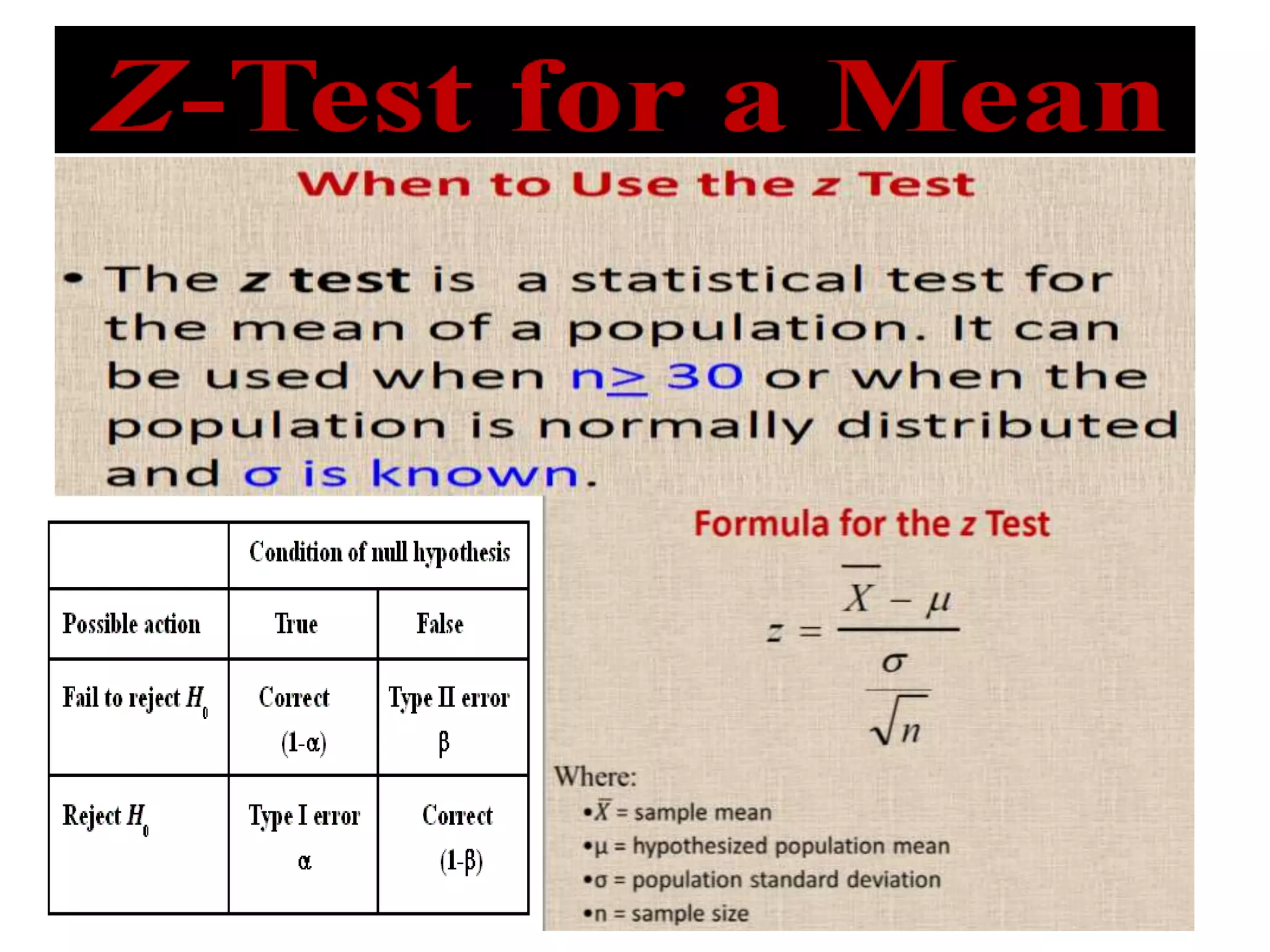
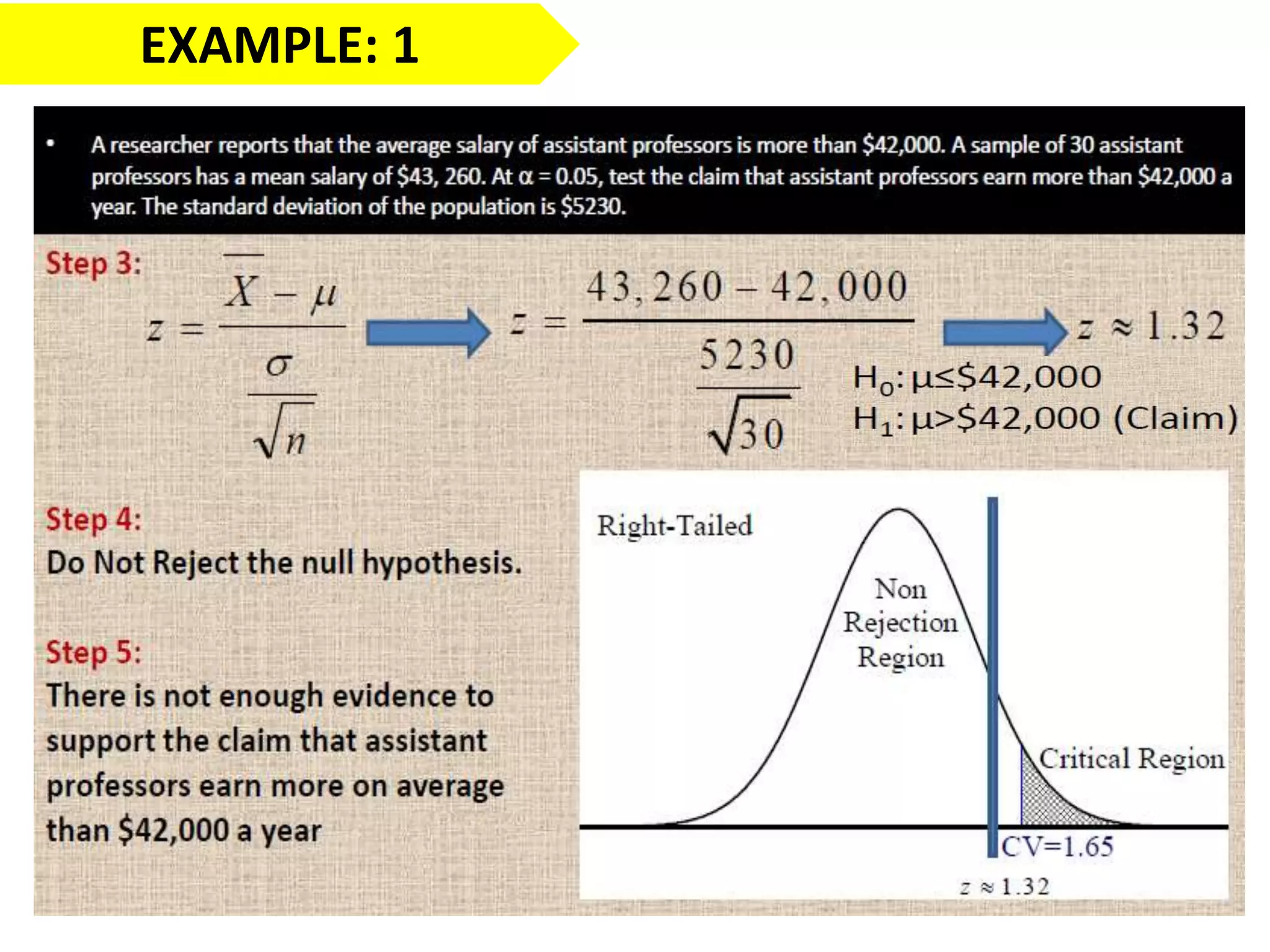
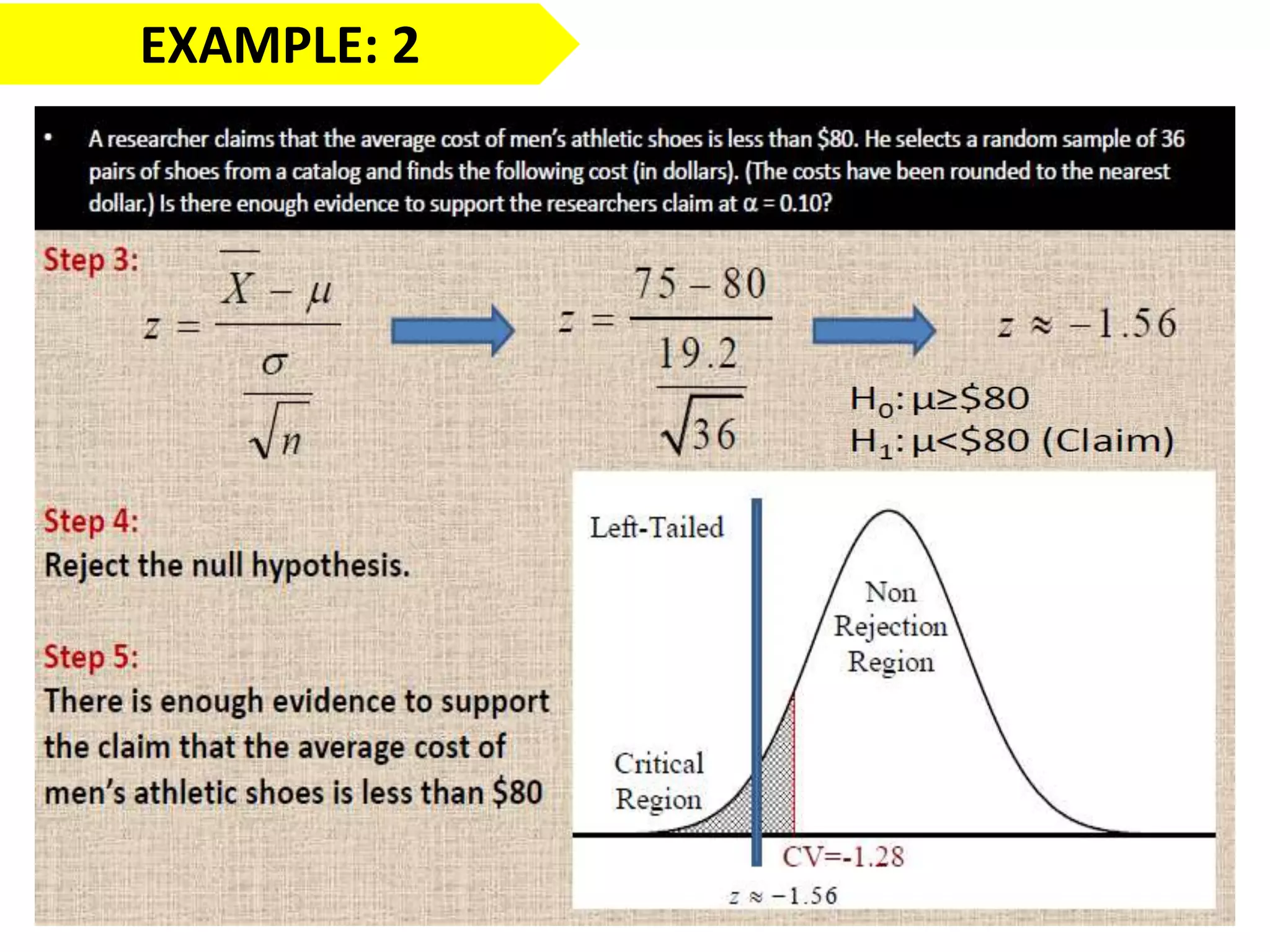
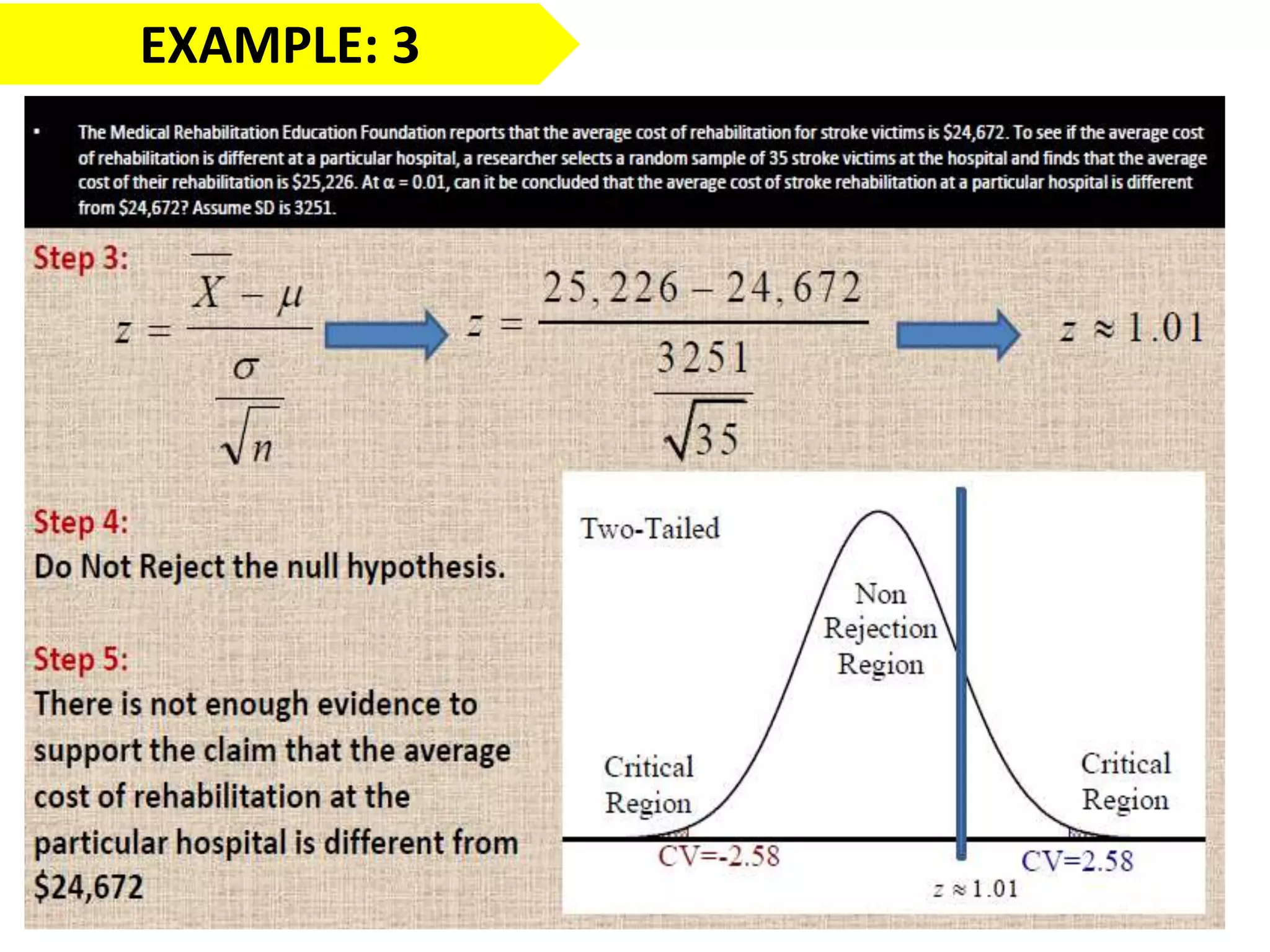
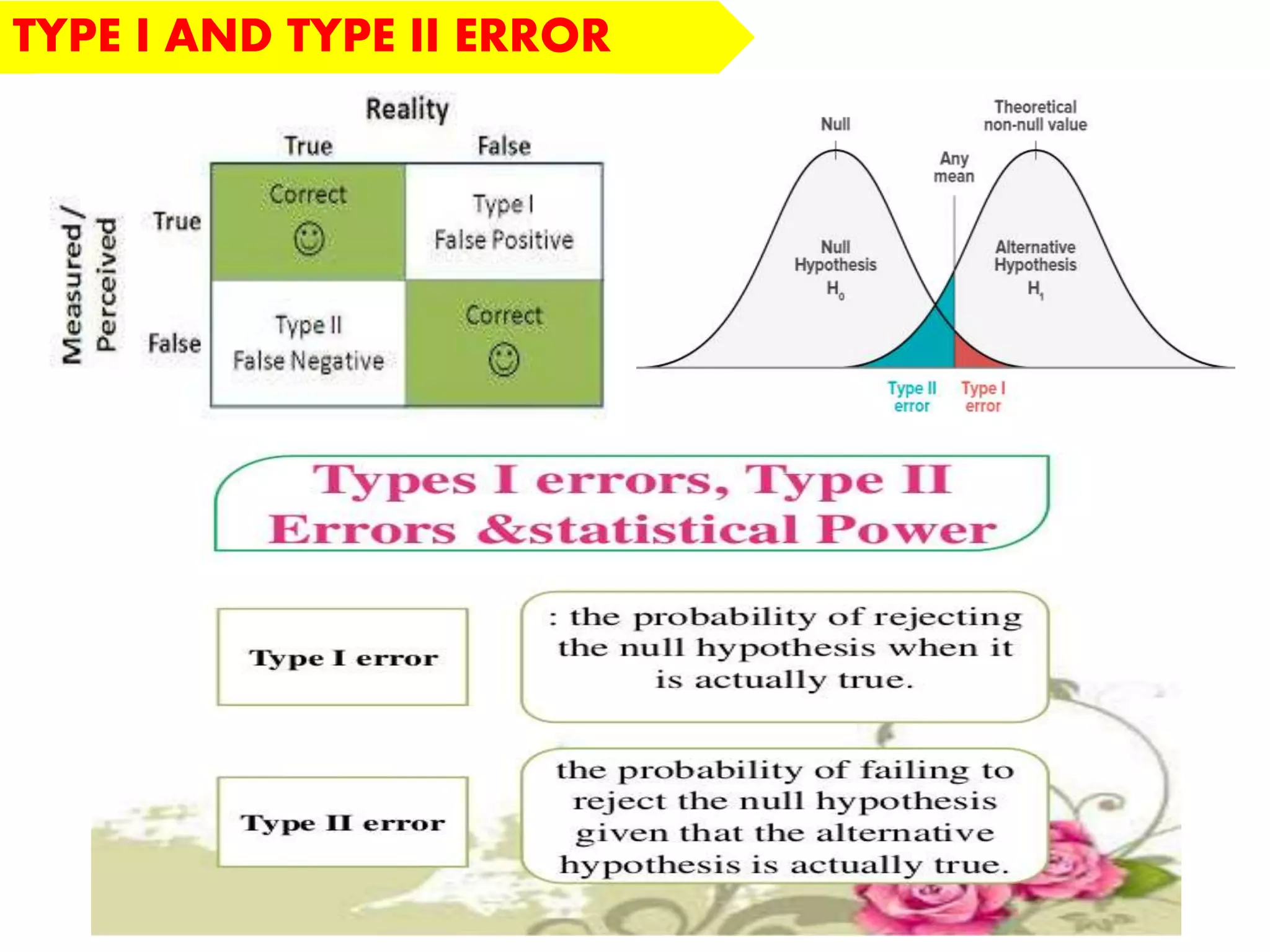

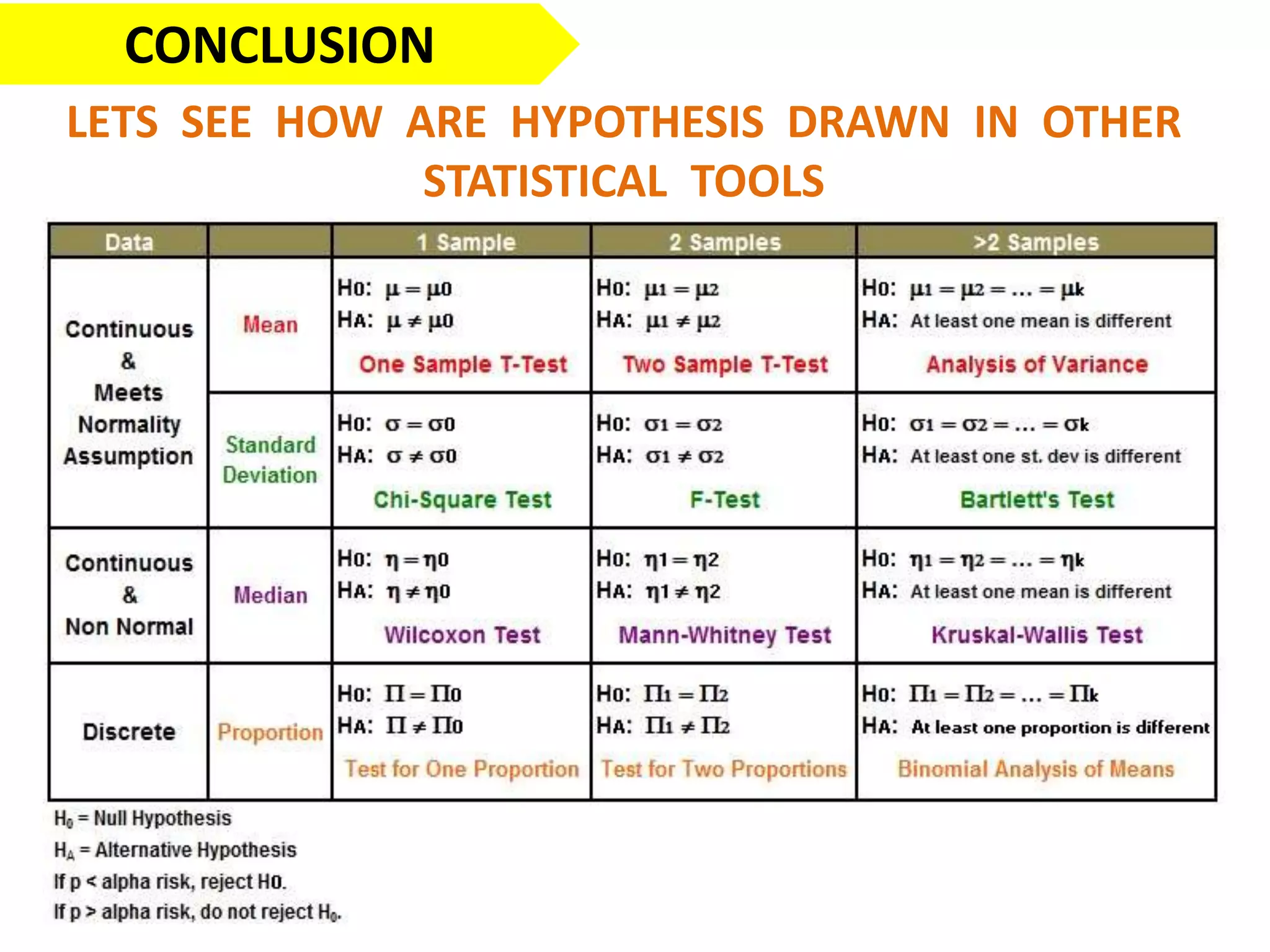

This document discusses the fundamentals of hypothesis testing. It introduces important terms like population, sample, statistical inference, parameters, and statistics. It explains that hypothesis testing is a form of statistical inference used to generalize from a sample to a population. The document outlines the steps for hypothesis testing, including formulating the null and alternative hypotheses, selecting an appropriate test, determining critical values, and deciding whether to reject or not reject the null hypothesis. It provides examples and discusses type I and type II errors.












