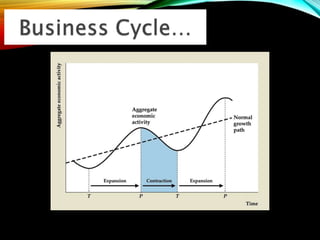
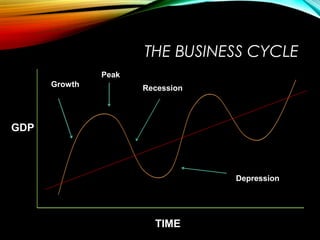
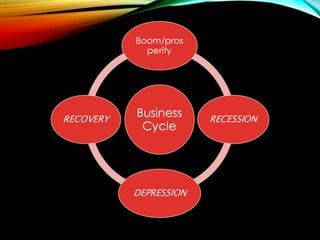
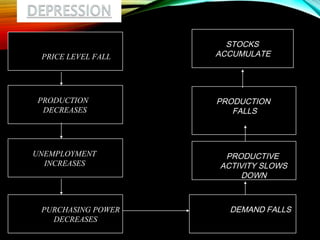
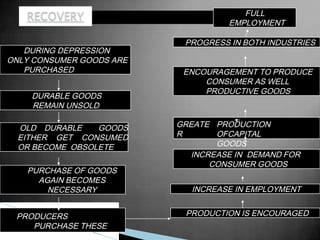
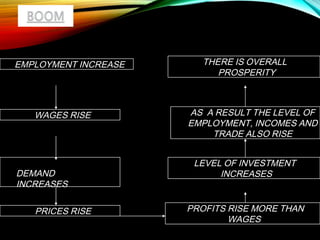
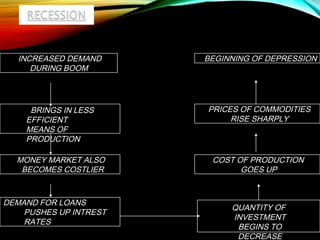
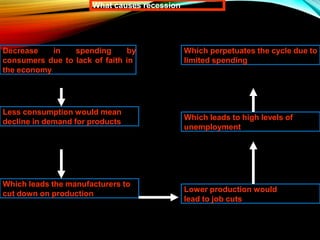
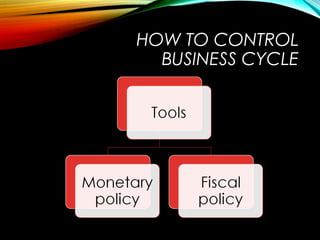
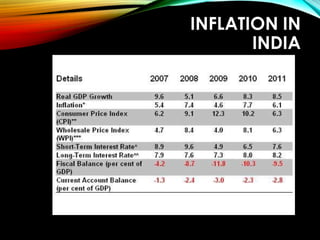
The business cycle refers to periodic fluctuations in economic activity, involving periods of expansion and contraction. A peak marks the end of an expansion period, while a trough marks the end of a contraction period. Business cycles are caused by internal factors like consumption, investment, and government activity, as well as external factors like innovations, wars, and political events. Governments try to control business cycles through monetary and fiscal policies that influence aggregate demand and output.