This document provides an overview of taxation including:
1) It defines taxation as the act of a taxing authority levying taxes and notes that taxation has existed in various forms throughout history, including in ancient India and other parts of the world.
2) It describes the modern definition of a tax as a financial charge imposed by a government and outlines the main types of direct and indirect taxes.
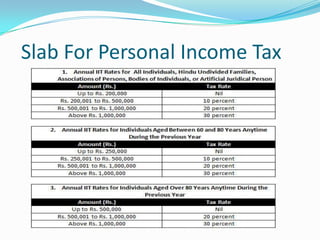
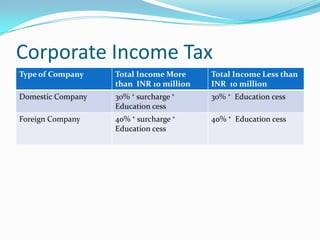
3) It provides examples of different taxes like income tax, corporate tax, customs duty, excise duty, sales tax, service tax, and VAT and summarizes how they work.