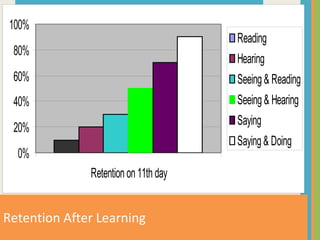
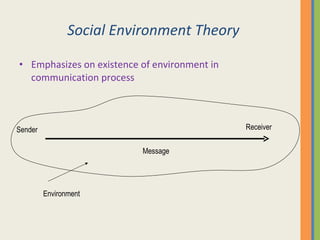
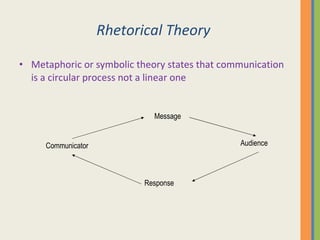
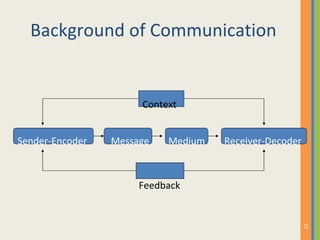
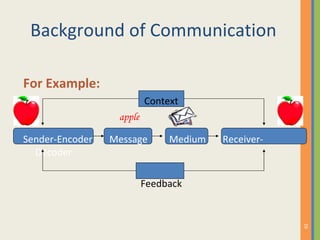
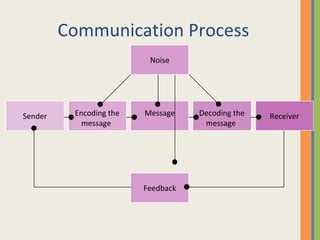
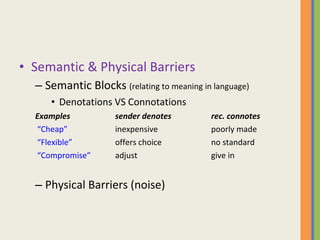
This document discusses various aspects of business communication, including retention rates of different learning methods, common elements of communication, the importance of communication, challenges in global communication, communication theories, barriers to communication, and nonverbal communication. It notes that people generally retain 10% of what they read, 20% of what they hear, 30% of what they see, 50% of what they see and hear, and 90% of what they say and do. Communication involves a sender, message, medium, receiver, feedback, and can be impacted by psychological, semantic, physical and nonverbal barriers.