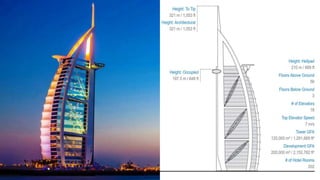
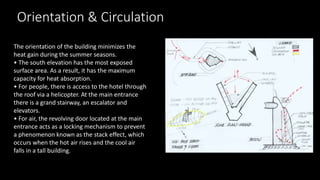
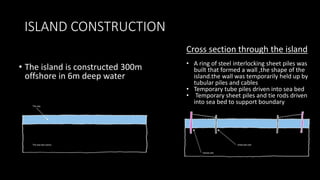
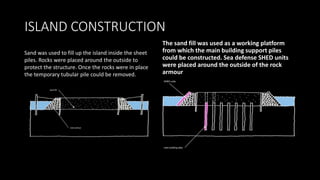
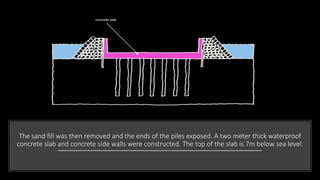
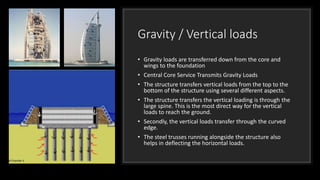
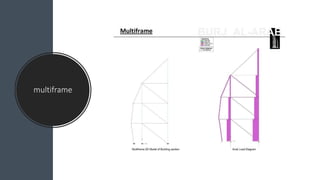
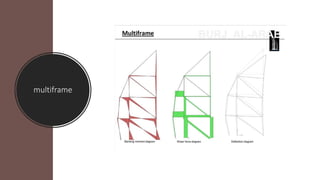
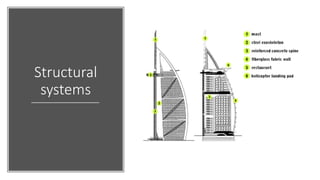
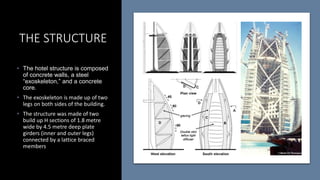
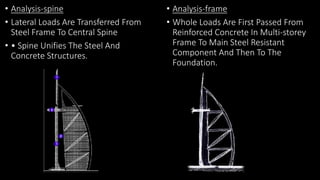
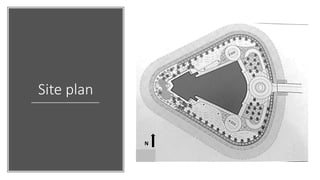
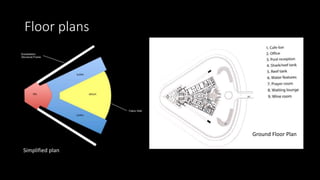
The Burj Al Arab hotel in Dubai is known for its distinctive sail-shaped structure. It was designed by Tom Wright and built from 1994-1999. The hotel sits on an artificial island 280 meters offshore and is supported by 230 deep foundation piles that are 1.5 meters in diameter and 45 meters long. The composite structure uses a steel exoskeleton with bracing and a central concrete core to support the hotel and withstand high wind loads in the area.