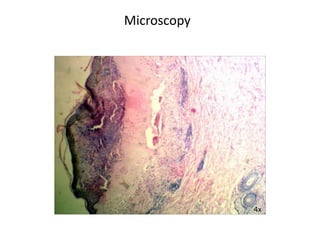
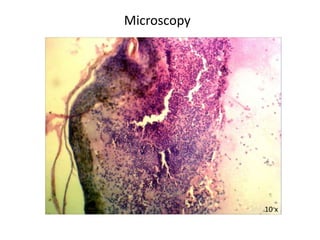
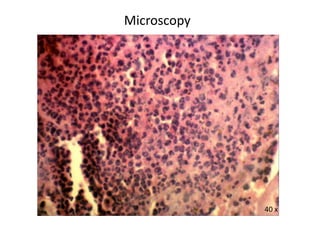
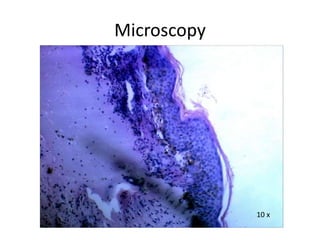
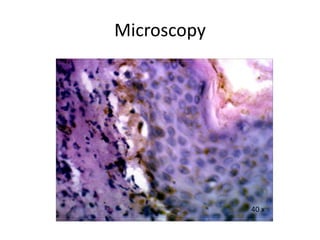
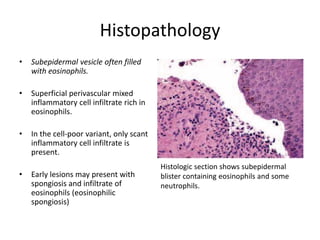
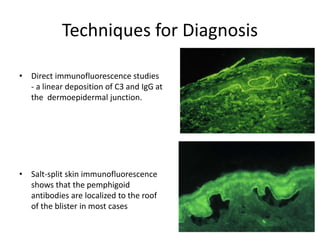
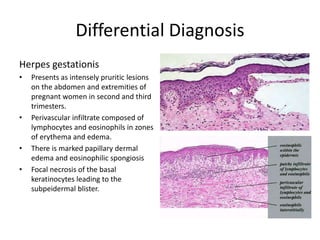
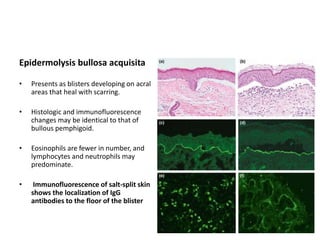
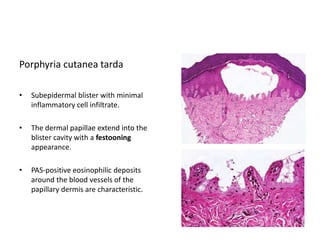
This document describes a biopsy of an 80-year-old female with a clinical diagnosis of bullous pemphigoid. Microscopic examination showed a subepidermal bulla filled with plasma, neutrophils, and eosinophils. The dermis beneath showed a dense perivascular infiltrate of lymphocytes, eosinophils, and plasma cells. These features are consistent with bullous pemphigoid. Bullous pemphigoid is an autoimmune blistering disease that typically affects the elderly and presents as large, tense bullae on the trunk and extremities. Histologically, it shows a subepidermal blister often containing eosinophils and a superficial perivascular mixed inflammatory infiltrate