Embed presentation
Downloaded 93 times
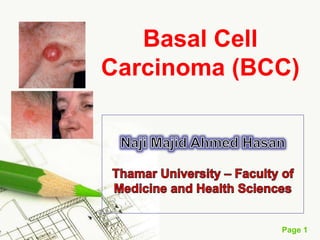
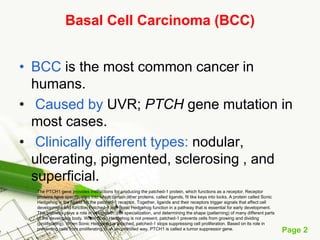







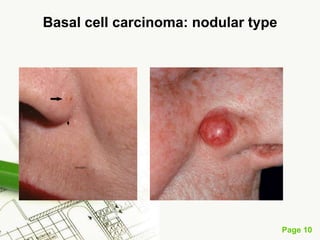
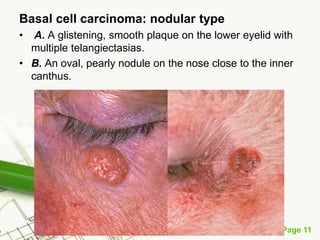
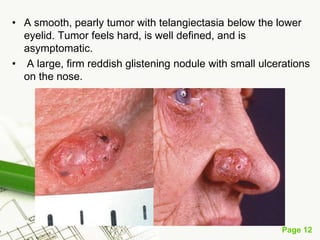
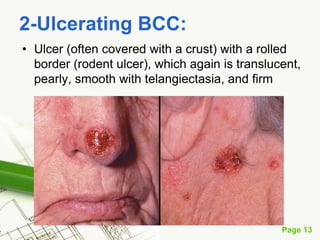
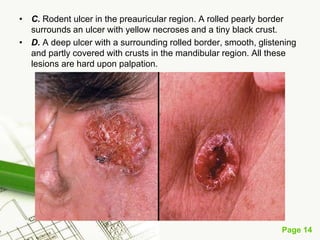
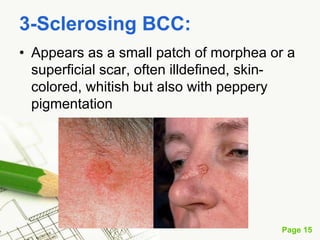
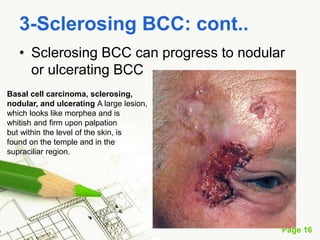
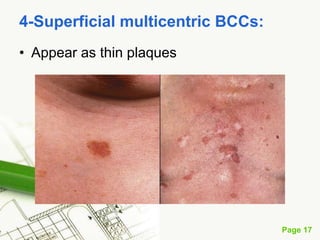
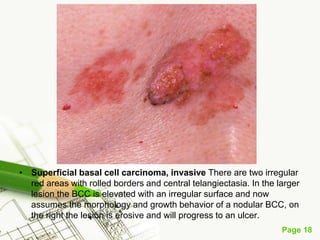


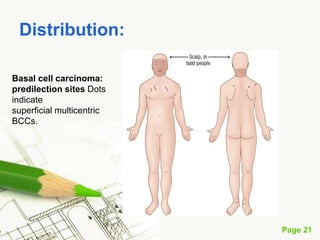
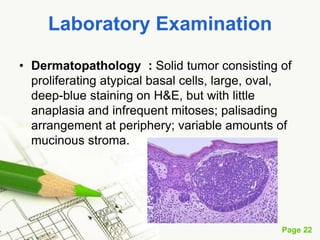
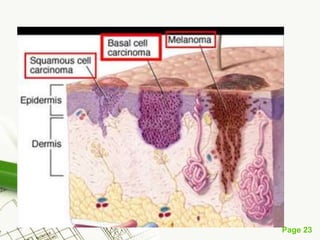





Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is the most common cancer in humans, primarily caused by UV radiation and mutations in the PTCH gene, leading to various types such as nodular and ulcerating BCC. It is locally invasive but rarely metastasizes, with common treatment methods including surgical excision and Mohs micrographic surgery. Predisposing factors for BCC include skin type, history of heavy sun exposure, and previous X-ray therapy, with the majority of cases occurring in individuals over 40 years of age.


























