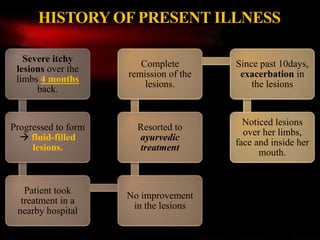
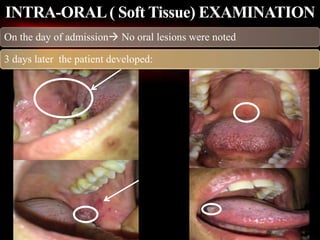
1) The patient, a 45-year-old female, presented with multiple fluid-filled itchy lesions over her limbs and face for the past week and developed oral lesions 3 days after admission.
2) A clinical diagnosis of bullous pemphigoid was made based on tense fluid-filled cutaneous lesions, involvement of oral mucosa, histopathology showing subepidermal blistering, and direct immunofluorescence demonstrating linear deposition of IgG and C3 along the basement membrane zone.
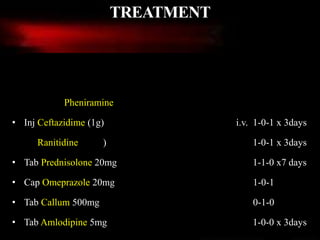
3) The patient was treated with systemic corticosteroids and immunosuppressants along with topical corticosteroids for oral lesions and advised long-term follow-up to manage the chronic autoimmune condition.