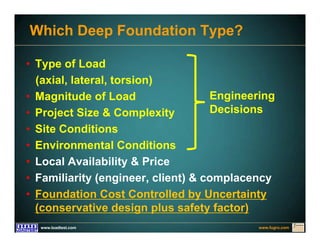
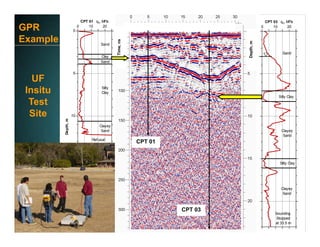
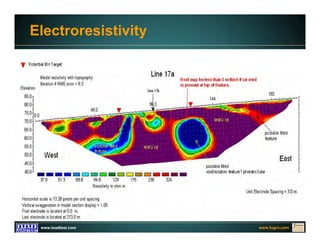
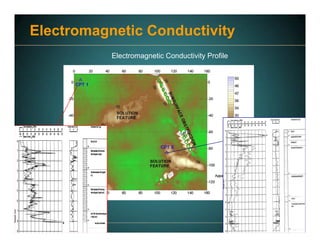
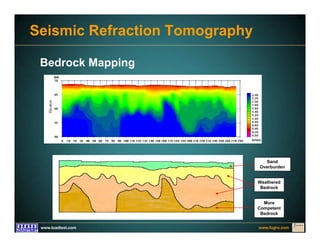
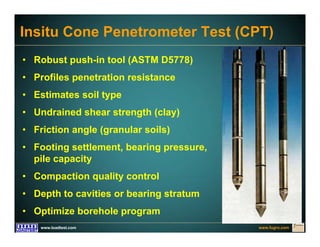
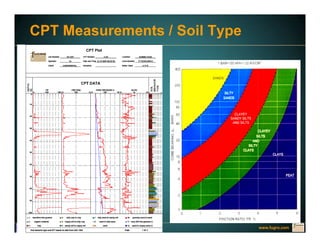
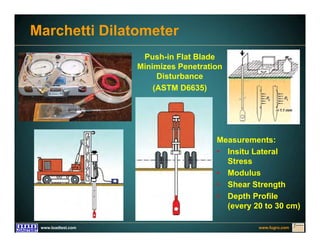
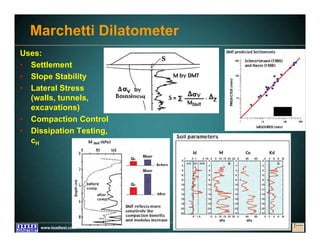
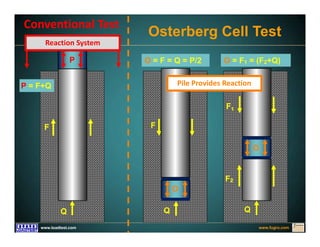
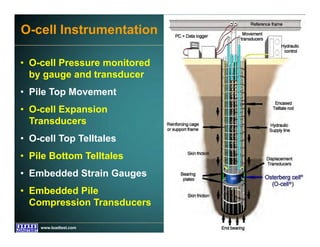
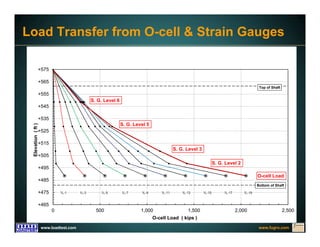
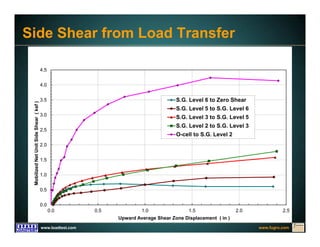
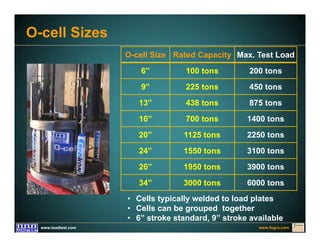
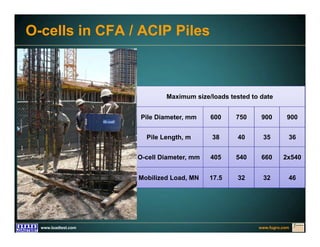
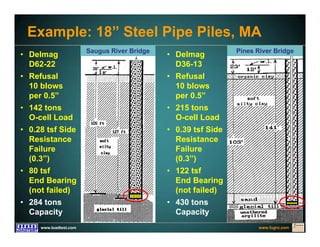
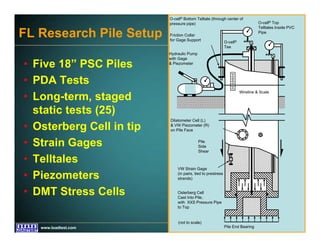
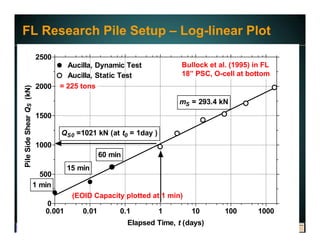
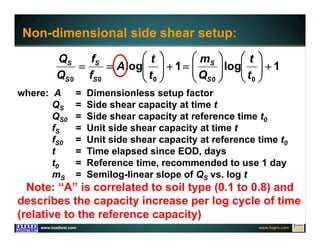
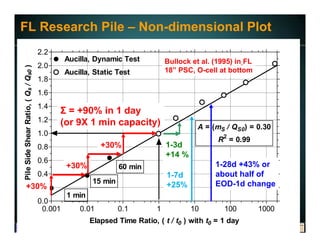
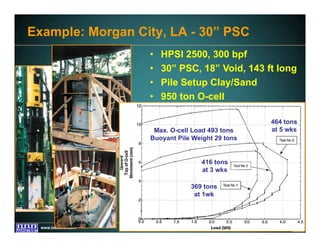
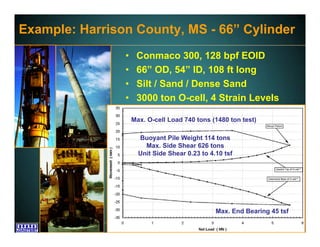
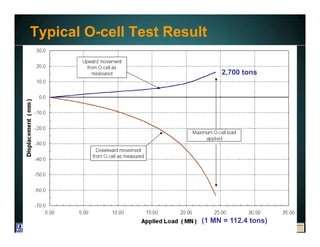
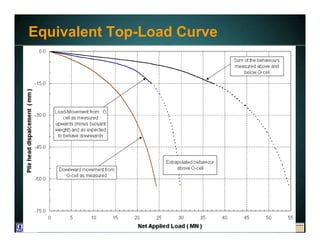
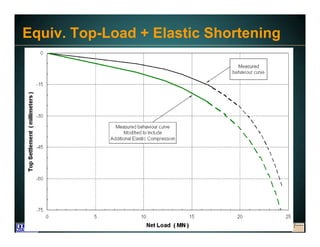
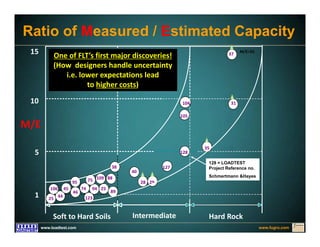
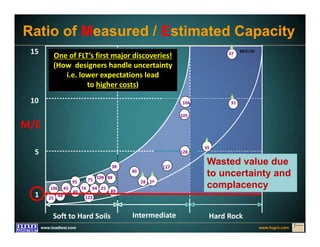
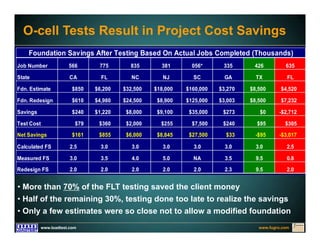
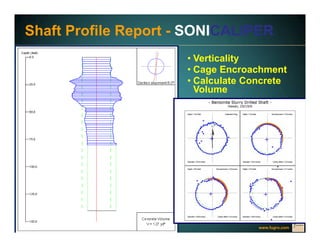
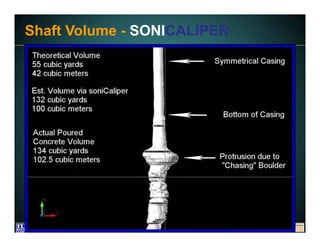
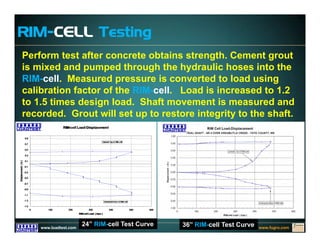
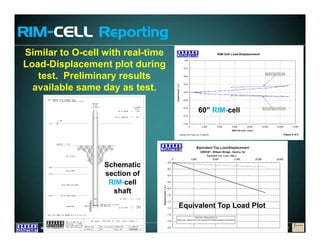
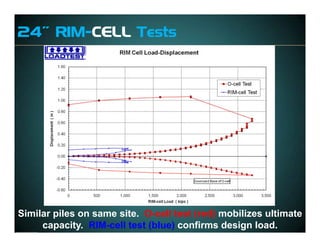
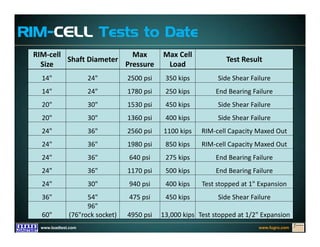
This document discusses deep foundation design and testing. It notes that deep foundation design involves uncertainty due to site variability and limited testing. Integrated site investigations using techniques like geophysics, cone penetration testing, and dilatometer testing can help characterize ground conditions and reduce uncertainty. Load testing using bi-directional Osterberg cells is described as an effective method to verify design assumptions and optimize foundation design. Case studies demonstrate how load testing can reduce costs by 5 times the testing costs through design optimization and reduced safety factors.