1) The document describes a student project to construct a 1:5 scale model of a temporary bus station with a skeletal structure using recycled timber and steel joints.
2) It discusses the design process including mockups, as well as design considerations for weather resistance, ventilation, accessibility, and function.
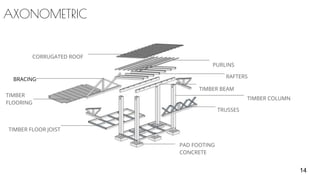
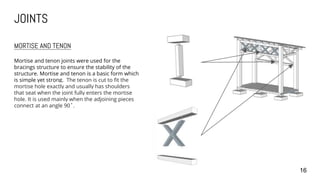
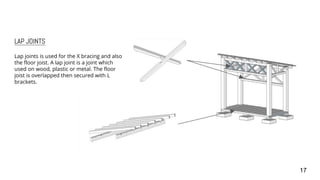
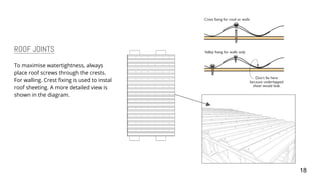
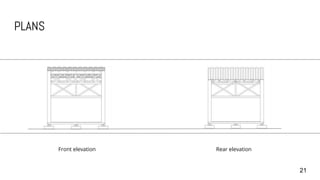
3) Details are provided on the skeletal structure, material selection of timber, corrugated roofing, and concrete pad footing. Construction details like joints, structural strength, and orthographic drawings are also summarized.