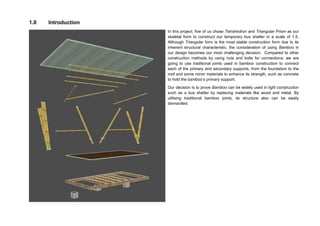
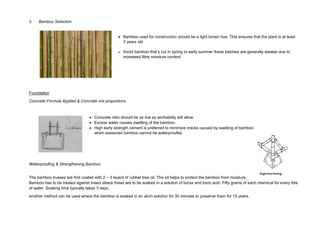
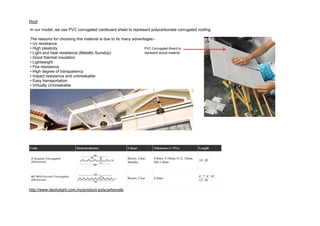
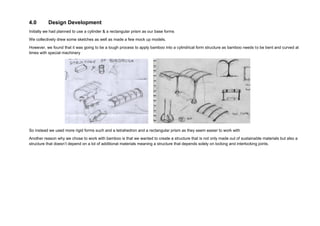
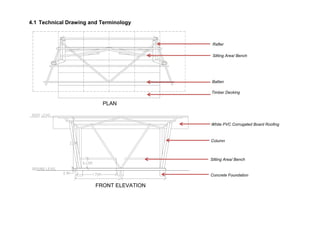
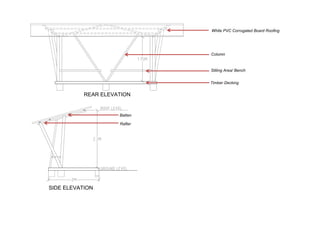
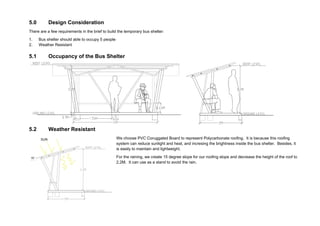
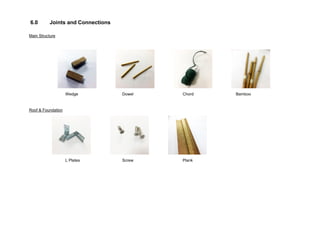
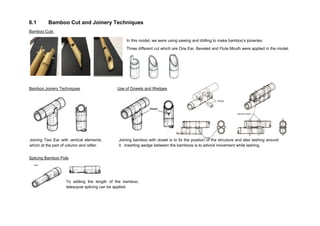
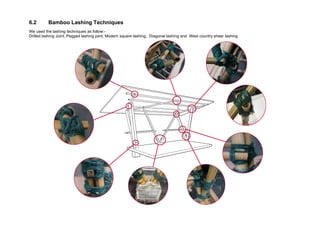
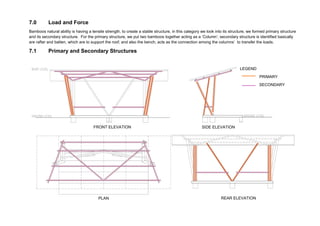
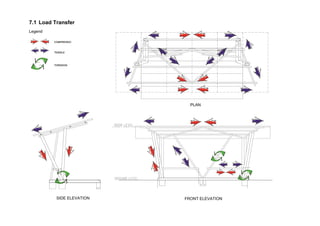
This document outlines a student project to construct a 1:5 scale model of a temporary bus shelter using skeletal bamboo construction. A group of five students chose a tetrahedron and triangular prism shape for the shelter's form due to triangles' inherent structural stability. Bamboo was selected as the primary material to demonstrate its viability for light construction applications. The document discusses the shelter's design analysis, precedent studies, design development process, construction considerations, joint designs, load transfer, and construction steps. Overall, the project aimed to prove that appropriately designed bamboo structures can serve as bus shelters or similar light construction needs.