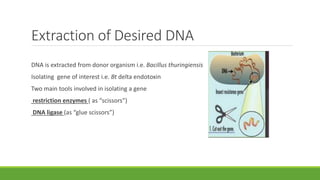
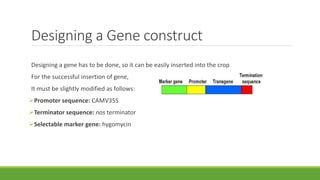
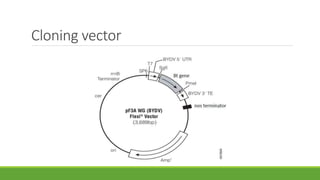
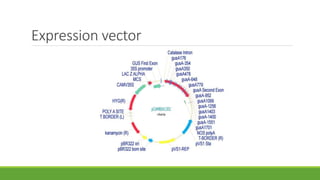
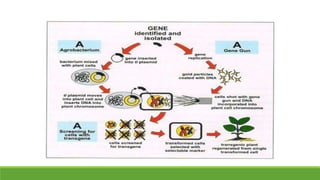
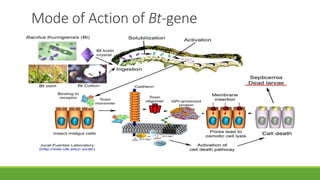
Bt gene insertion in wheat can help address the problem of increasing pest resistance to insecticidal sprays. The Bt gene from Bacillus thuringiensis produces an insecticidal toxin that is inserted into crop plants like cotton, corn, wheat and maize through genetic engineering techniques. This allows the plants to internally produce the toxin, killing insect pests without the need for concentrated insecticidal sprays. The Bt gene is isolated from B. thuringiensis bacteria and modified with a promoter and terminator sequence before being inserted into the plant genome using transformation methods like biolistics or Agrobacterium. Transformed plants are selected and grown in greenhouses before field testing to ensure expression of the Bt toxin and resistance