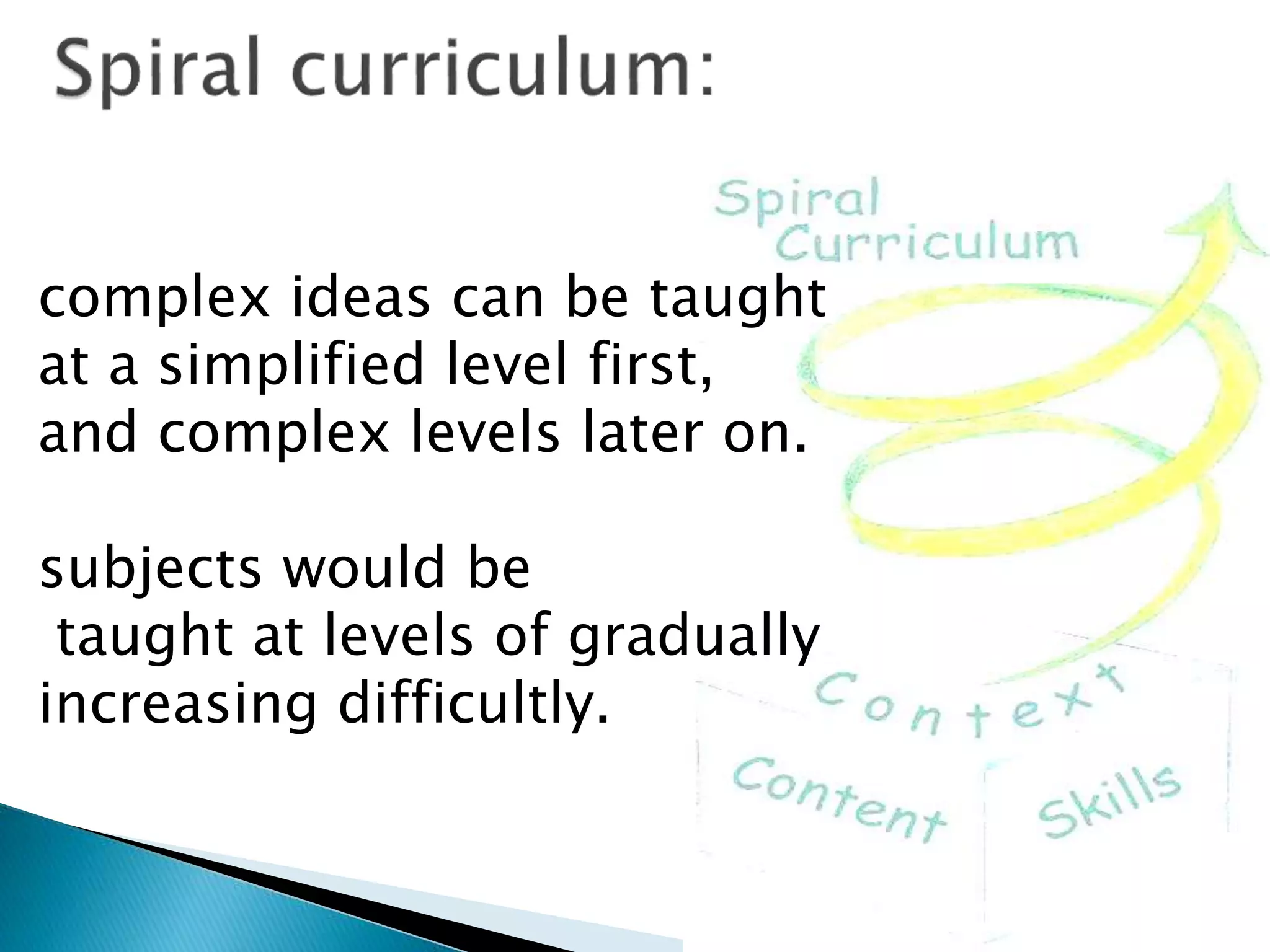
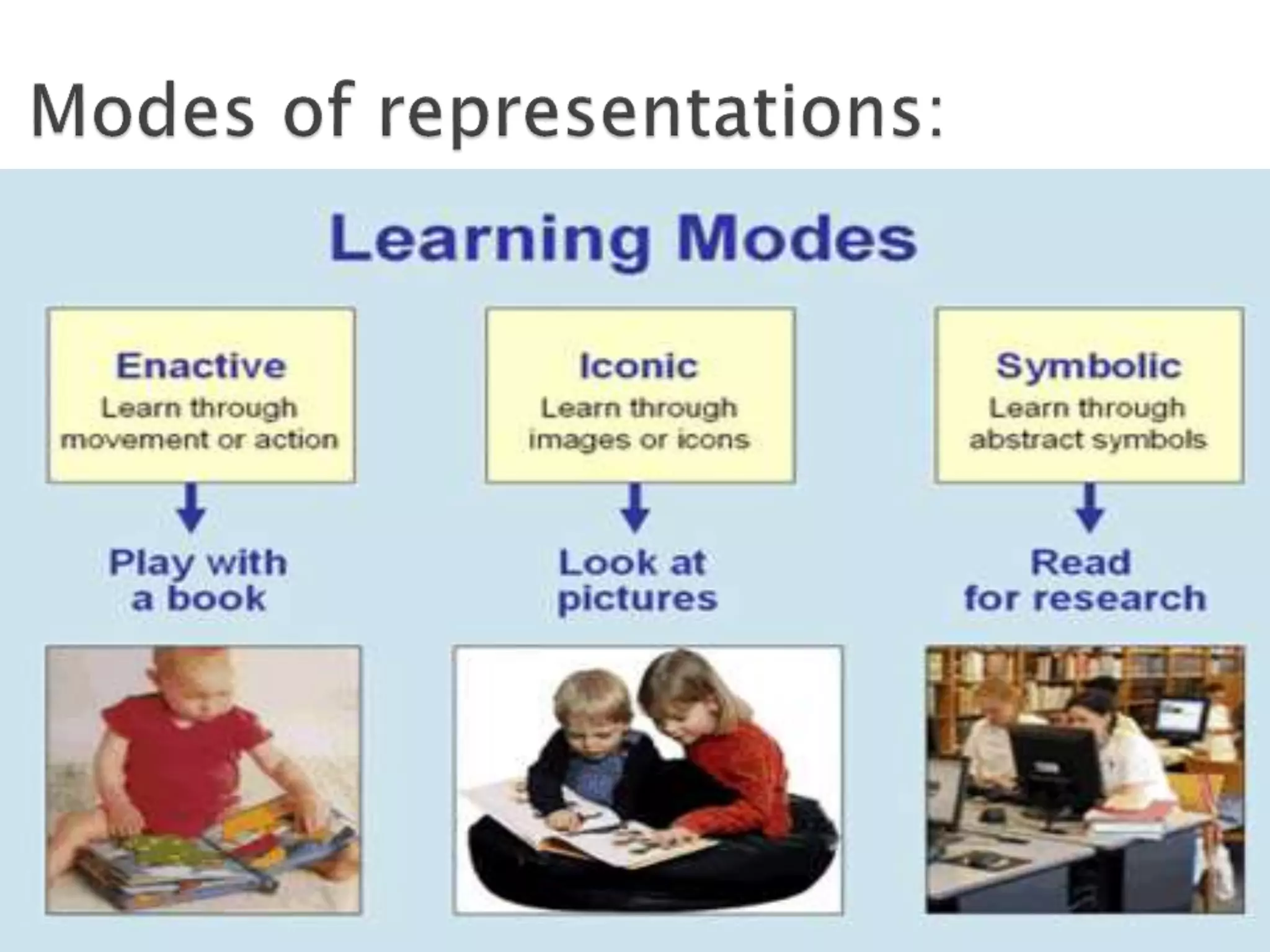
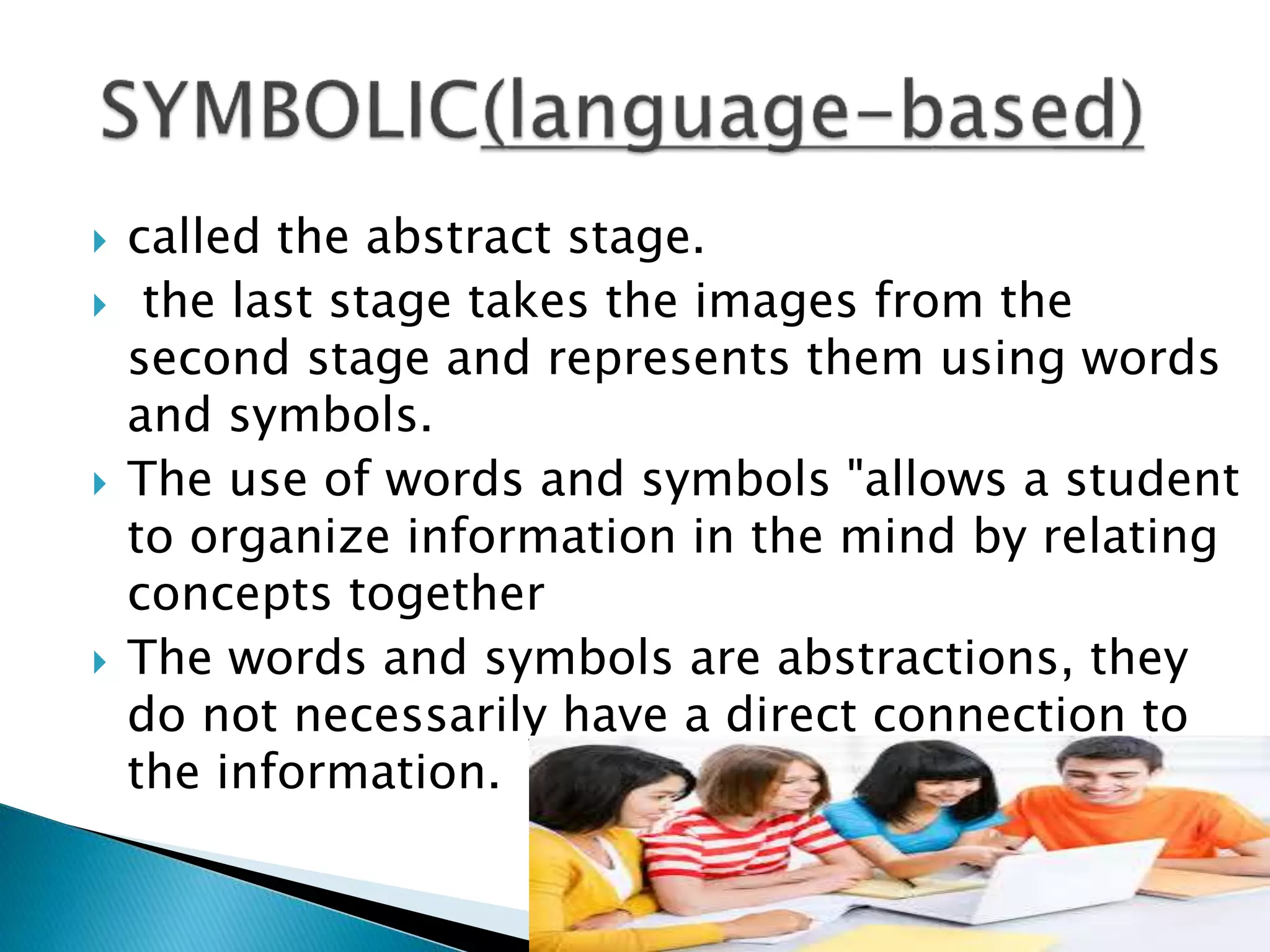
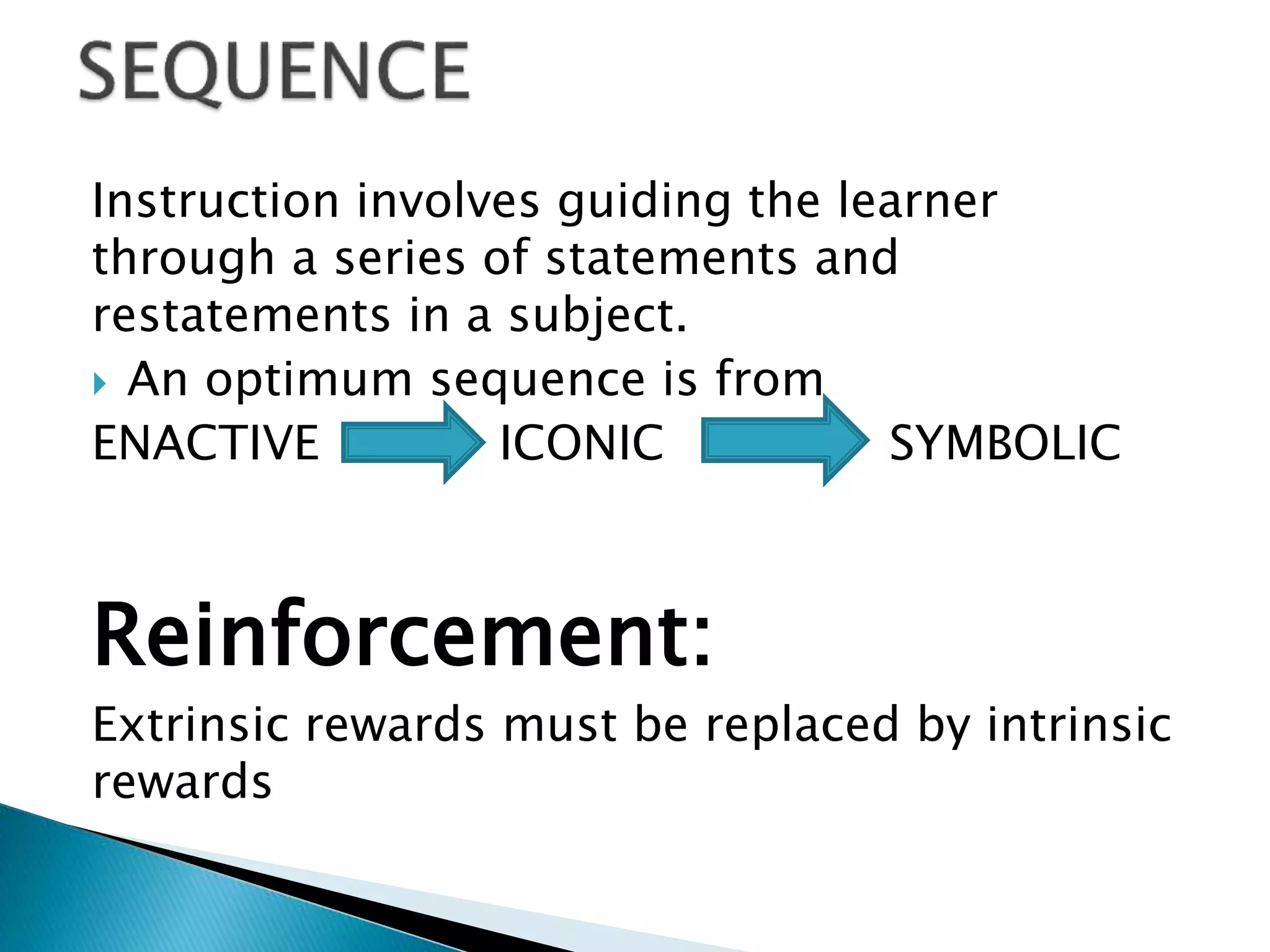
Jerome Bruner was an American psychologist who contributed significantly to cognitive psychology and educational psychology. He was one of the founders of constructivist learning theory. Bruner believed that classroom learning should proceed from the specific to the general, and that concepts are made up of attributes. He argued against Piaget's theory of cognitive development stages, saying that complex ideas can be taught simply at first and made more complex later through a spiral curriculum.