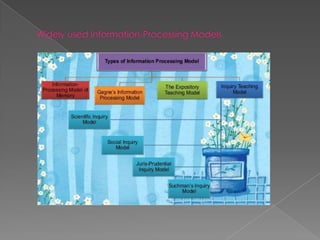
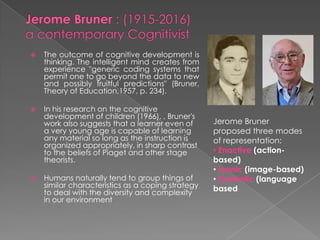
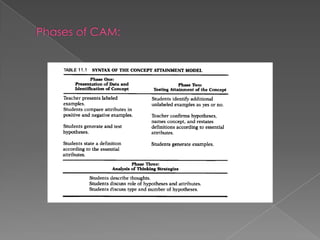
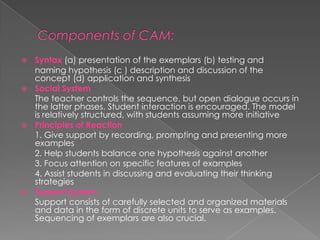
Models of teaching are instructional designs that describe learning environments and interactions to cause specific changes in student behavior. There are several families of models including social, information-processing, personal, and behavioral systems. Models aim to accomplish common educational goals, are research-based, and conform to philosophical orientations. Jerome Bruner's work emphasized that students actively construct knowledge and proposed three stages of representation: enactive, iconic, and symbolic. Bruner also advocated for discovery learning and a spiral curriculum.