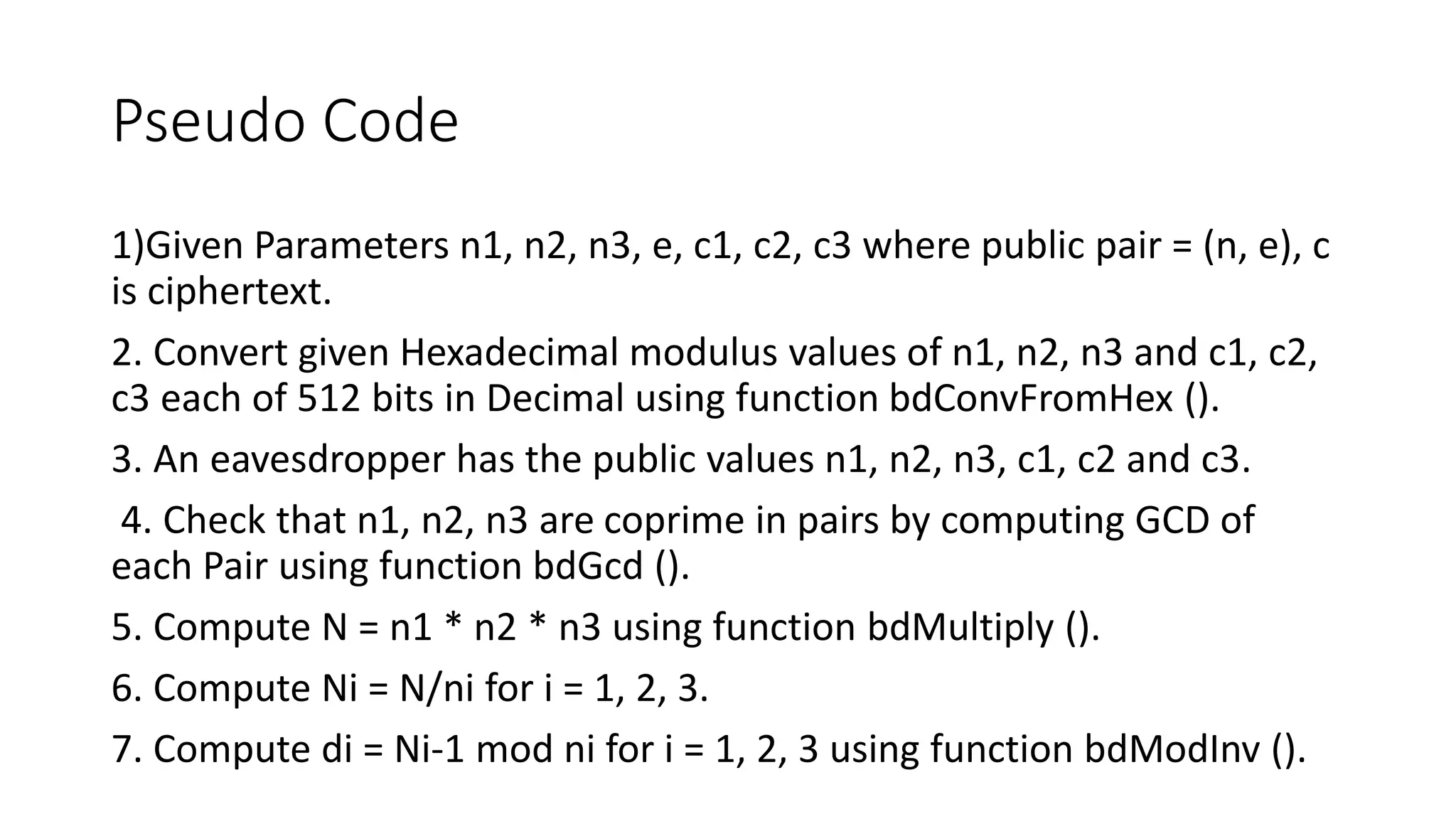
1) The document describes how to decrypt an RSA ciphertext using a Chinese Remainder Theorem attack when the public exponent is small. It involves using the public moduli and exponents from certificates to determine the plaintext.
2) The attack works by using the Chinese Remainder Theorem to determine the plaintext from the ciphertexts modulo the public moduli. This works because the public exponent is small, in this case 3, allowing extraction of the plaintext cube root.
3) Pseudocode is provided showing the steps: using the Chinese Remainder Theorem formula to combine the ciphertexts modulo the public moduli, taking the cube root to obtain the plaintext, which in this example decrypts to a German message about a fixed











![References
• [1] “Applied Cryptanalysis: Breaking Ciphers in the Real World”, Mark
Stamp and Richard M. Low, Wiley-IEEE Press, May 2007.
• [2] “Research and Implementation of RSA Algorithm in Java”, Jiezhao
Peng and Qi Wu, International Conference on Management of e-Commerce
and e-Government.
• [3] “The Handbook of Applied Cryptography”, by A. Menezes, P. van
Oorschot, and S. Vanstone, CRC Press, 1996.
• [4] “An Efficient RSA Public Key Encryption Scheme”, Sattar J Aboud1,
Mohammad A AL-Fayoumi1, 2Mustafa Al-Fayoumi and 3Haidar S Jabbar ,
Fifth International Conference on Information Technology: New
Generations.
• [5] “RSA Problem”, Ronald L. Rivest, and Burt Kaliski, RSA
Laboratories,December](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/broadcastingandlowexponentrsaattack-150923055102-lva1-app6891/75/Broadcasting-and-low-exponent-rsa-attack-13-2048.jpg)