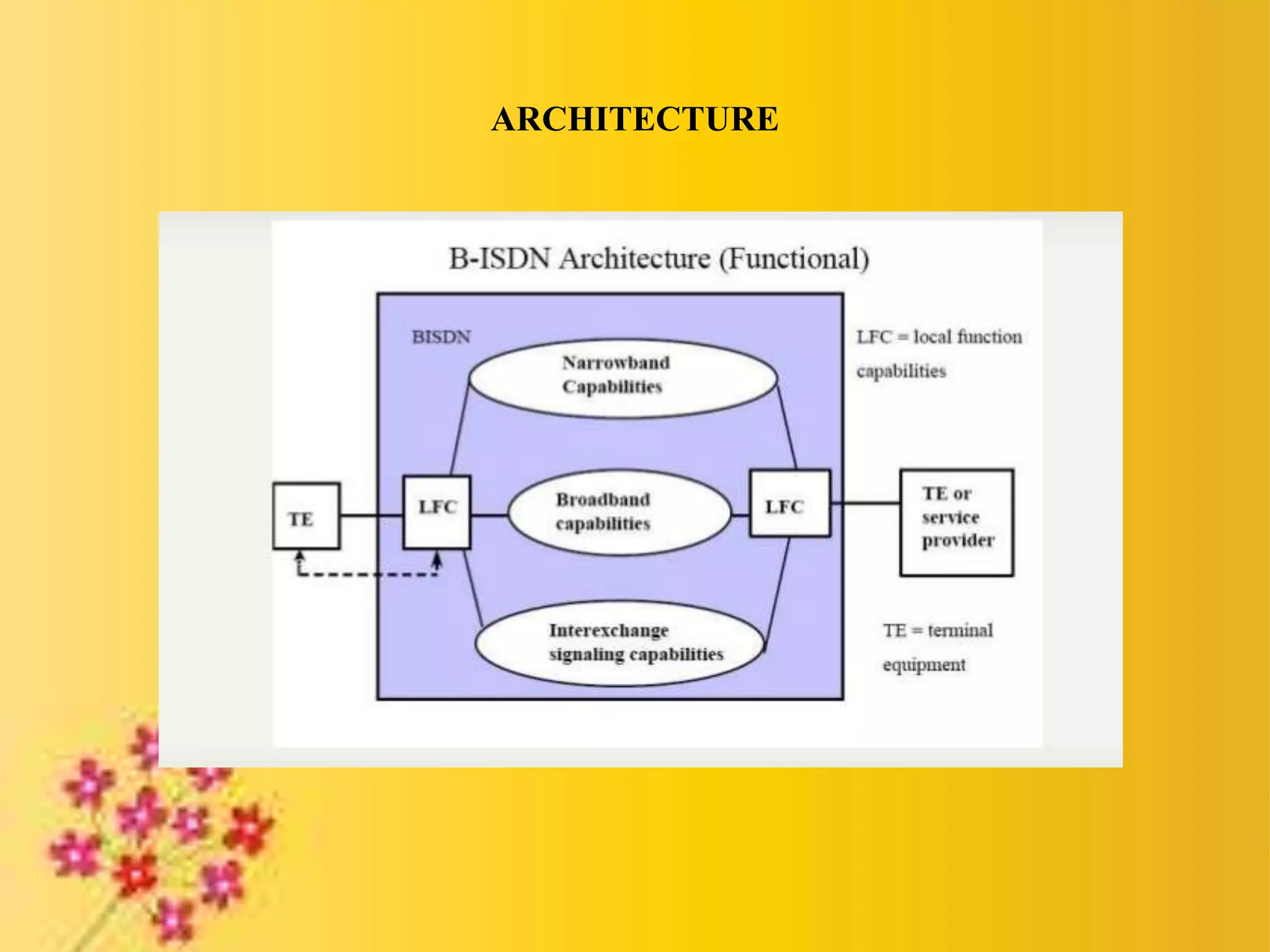
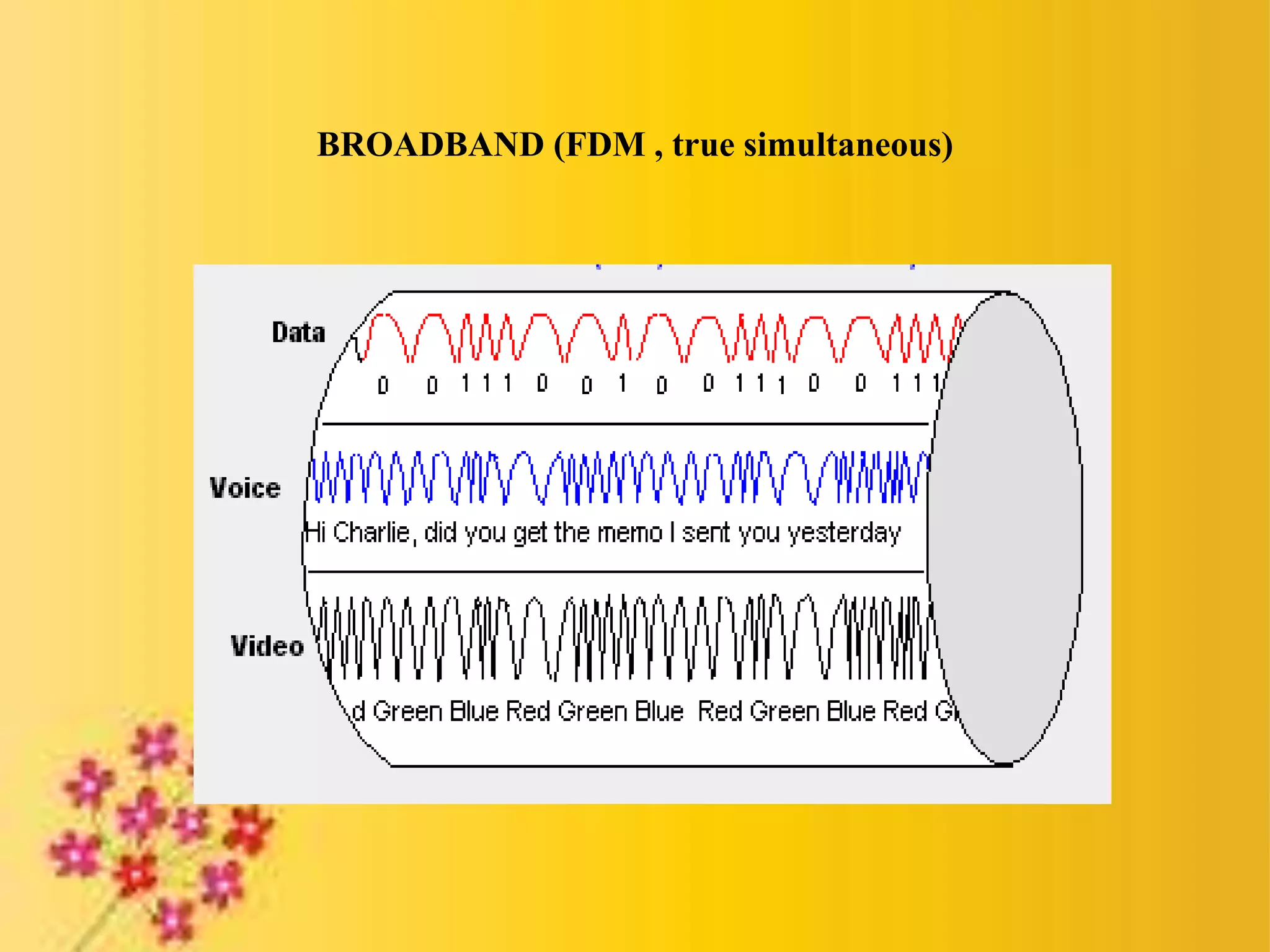
Broadband ISDN (B-ISDN) is an extension of ISDN that provides both narrowband and broadband capabilities over digital networks. It supports interactive and distributive services using Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM), which transmits data in small, fixed-size cells. ATM provides either permanent or switched virtual connections and uses small, constant cell sizes to transmit video, audio, and computer data over the same network.