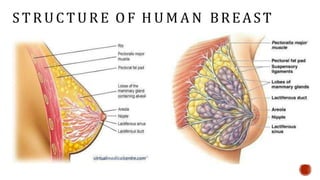
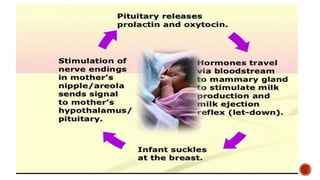
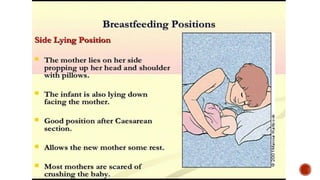
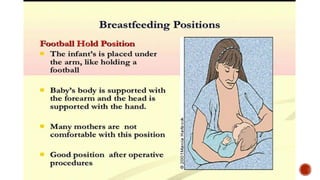
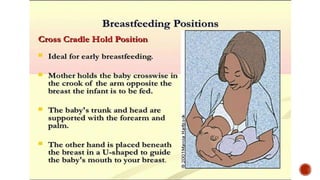
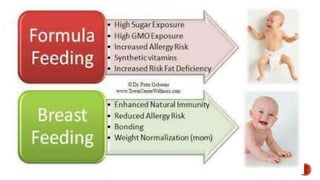
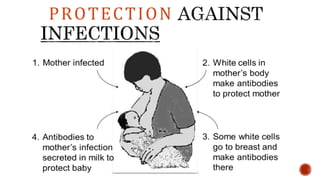
This document discusses breastfeeding and the benefits of exclusive breastfeeding for the first 6 months. It outlines that breast milk provides all essential nutrients for an infant's growth and development. The World Health Organization recommends exclusive breastfeeding for the first 6 months and continued breastfeeding for at least 12 months. The document also describes the structure of the human breast and production of milk, as well as the Baby Friendly Hospital Initiative and its Ten Steps to promote breastfeeding.