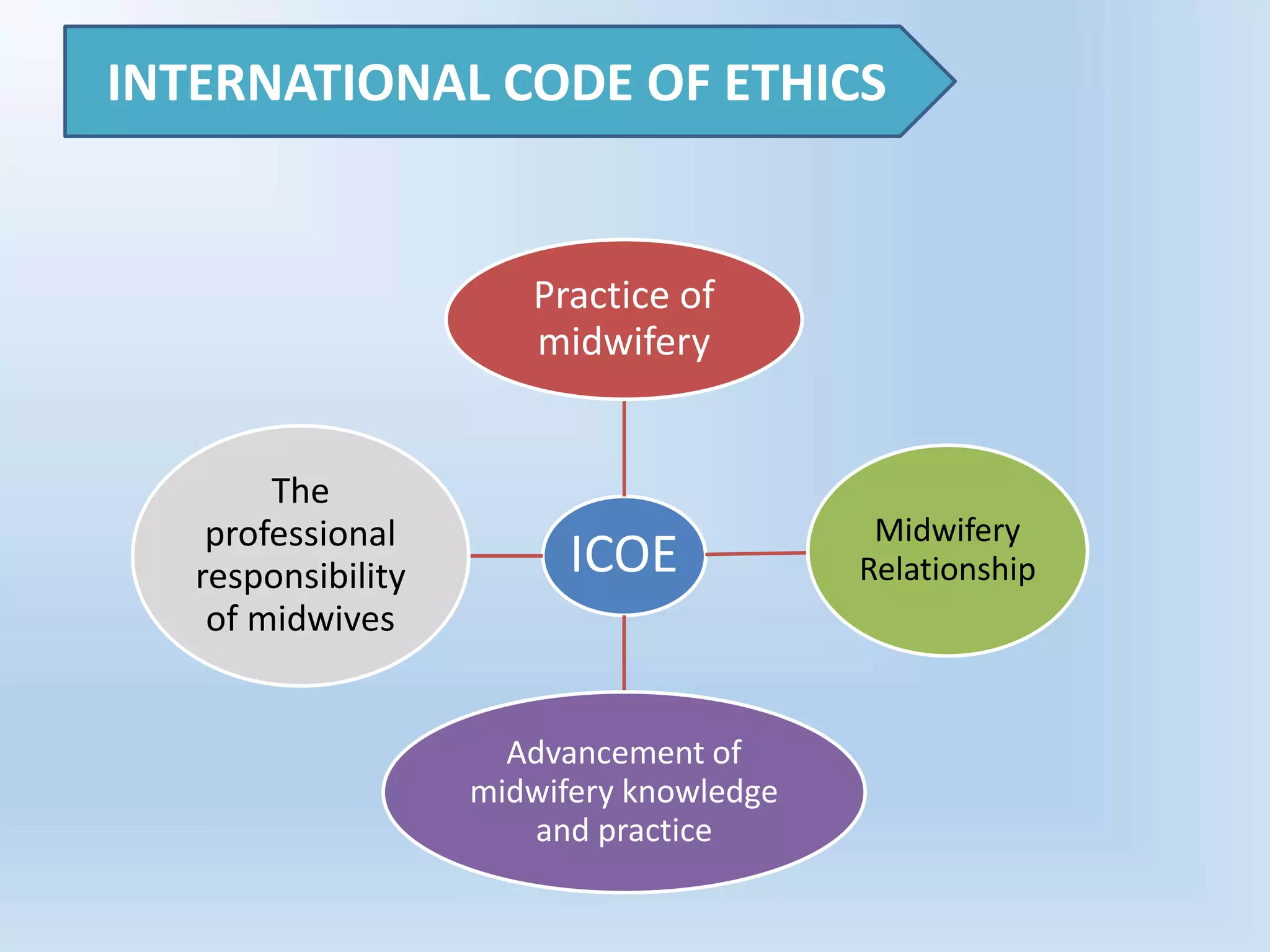
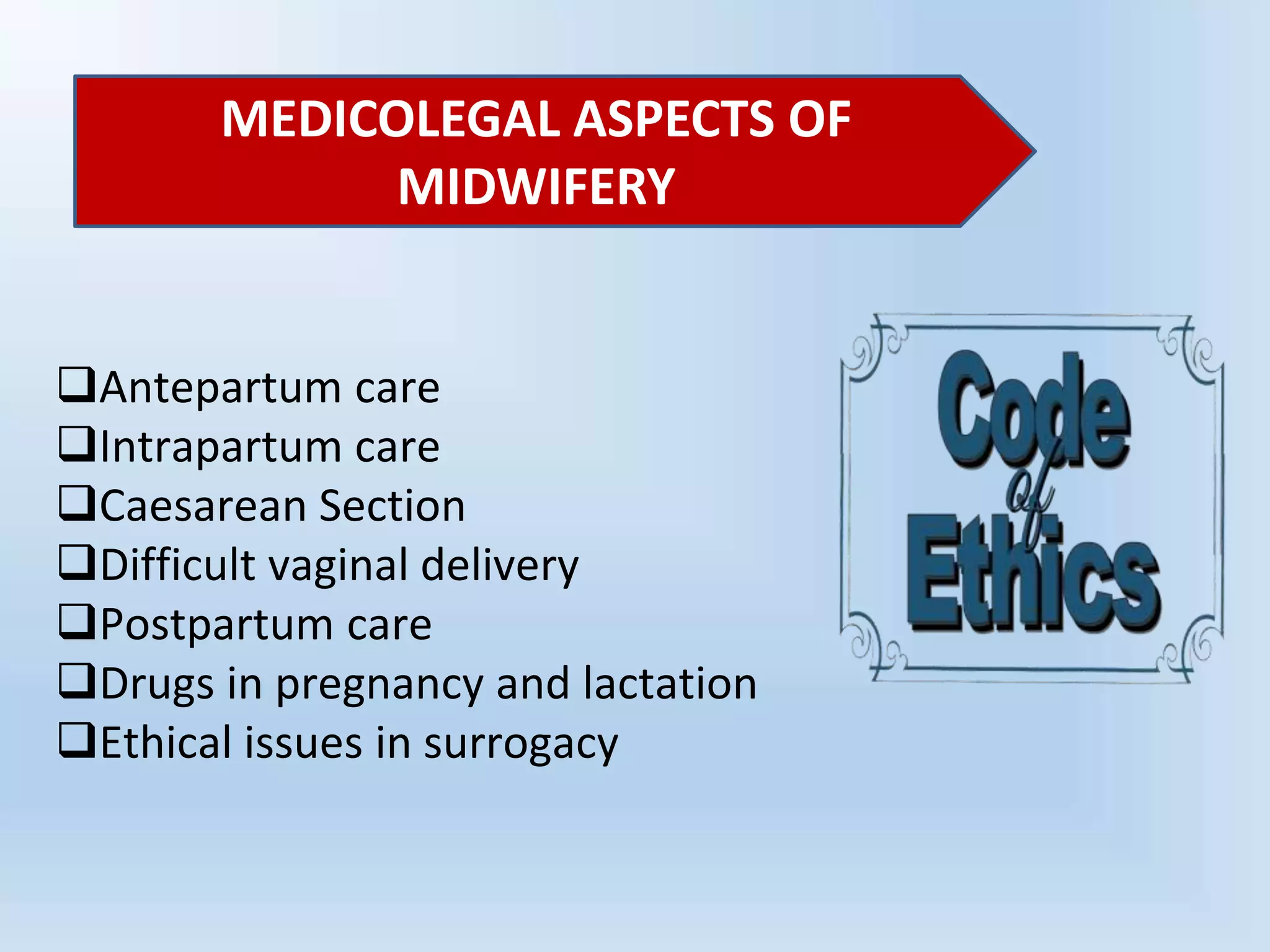
This document discusses legal and ethical issues in midwifery practice. It defines ethics and codes of ethics, outlining their purpose to guide ethical decision making. Key issues in midwifery like informed consent, failure to monitor, and medication errors are described. Standards of midwifery practice emphasize woman-centered care and professional accountability. Standing orders allow nurses to treat patients according to predefined protocols signed by licensed practitioners. Overall the document provides an overview of ethical and legal responsibilities in midwifery.