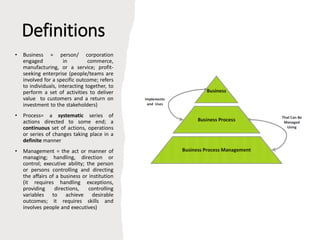
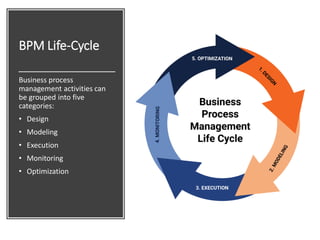
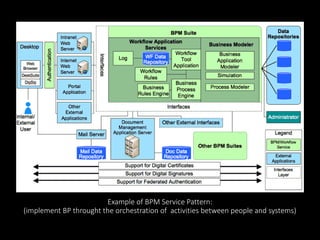
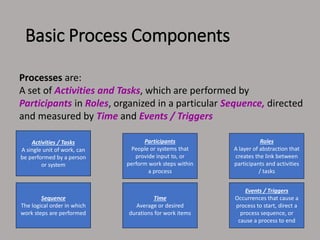
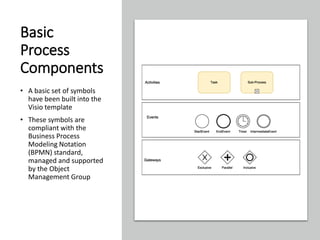
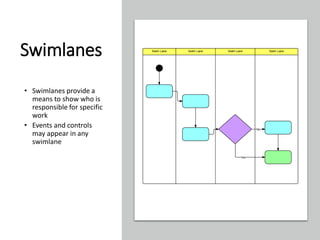
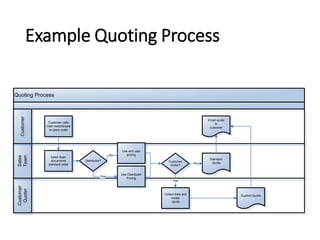
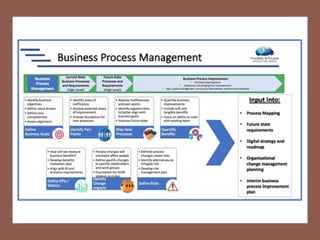
The document profiles Setia A. Wicaksana, an expert in organizational development, business psychology, and human resources. It lists her roles managing consulting firms, associations, and as a professor. The document also summarizes her qualifications, publications, and educational background. It provides an overview of business process management, including definitions, the BPM lifecycle of design, modeling, execution, monitoring and optimization. It gives examples of basic process components and how they are organized in BPMN diagrams.