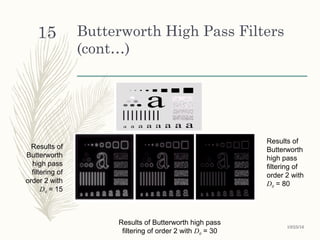
This document discusses frequency domain filtering for image sharpening. It begins by explaining the difference between spatial and frequency domain image enhancement techniques. It then describes the basic steps for filtering in the frequency domain, which involves taking the Fourier transform of an image, multiplying it by a filter function, and taking the inverse Fourier transform. The document discusses sharpening filters specifically, noting that high-pass filters can be used to sharpen by preserving high frequency components that represent edges. It provides examples of ideal low-pass and high-pass filters, and Butterworth and Gaussian filters. Laplacian filters are also introduced as a common sharpening filter that uses an approximation of second derivatives to detect and enhance edges.











![Butterworth High Pass
Filters
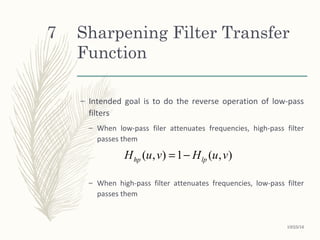
The Butterworth high pass filter is given as:
where n is the order and D0 is the cut off distance as before
n
vuDD
vuH 2
0 )],(/[1
1
),(
+
=
10/25/16
14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/imageenhancement-sharpening-161025103601/85/Image-enhancement-sharpening-14-320.jpg)