- Bordetella pertussis is a Gram-negative coccobacillus that causes whooping cough (pertussis). It is highly contagious and affects mostly children.
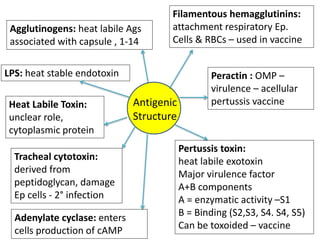
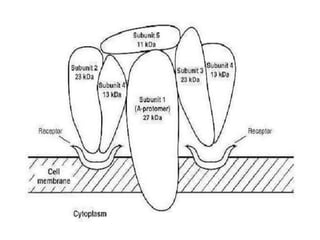
- B. pertussis has various virulence factors like pertussis toxin, adenylate cyclase toxin, and filamentous hemagglutinin that allow it to attach to and damage respiratory epithelial cells.
- Whooping cough presents as a catarrhal stage with maximum infectivity followed by paroxysmal stage with violent coughing spells and characteristic whooping sound when inhaling.
- Laboratory diagnosis involves microscopy, culture on Bordet-Gengou medium, and immunofluorescence or slide ag