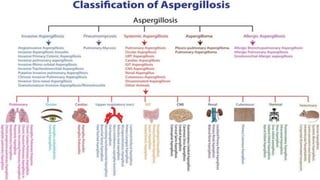
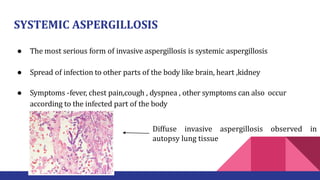
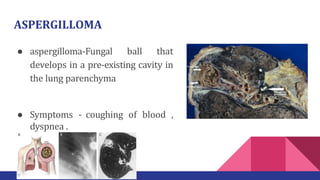
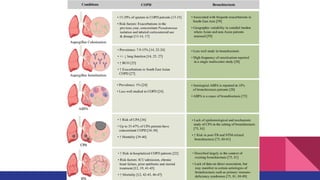
Aspergillosis is a disease caused by the Aspergillus mold, which is common and can be harmful to individuals with weakened immune systems or lung disorders. The document outlines the types, transmission, symptoms, and treatment of aspergillosis, emphasizing the importance of early diagnosis and the use of antifungal therapies like voriconazole. It also provides historical context and morphological details of Aspergillus species.
![ASPERGILLOSIS
VARSHINI, S.
III B.Sc. MICROBIOLOGY
PG & RESEARCH DEPARTMENT OF
BIOTECHNOLOGY AND MICROBIOLOGY,
NATIONAL COLLEGE [AUTONOMOUS]
TIRUCHIRAPPALLI - 620001
TAMIL NADU , INDIA.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/varshinisaspergillosis-210918115757/85/Aspergillosis-1-320.jpg)