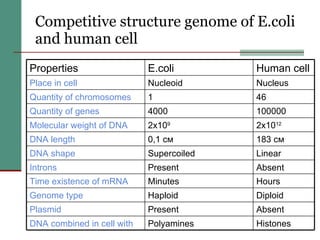
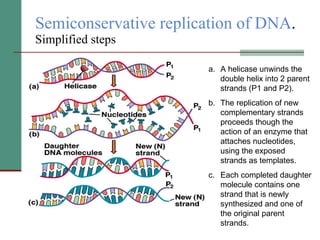
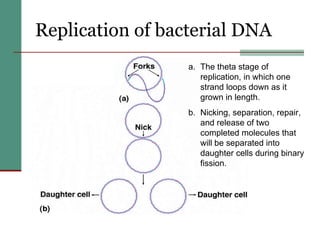
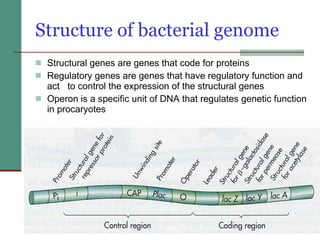
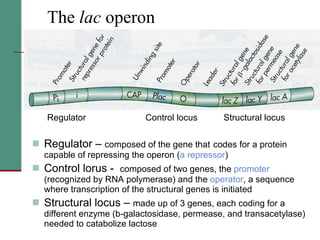
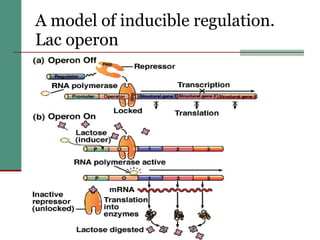
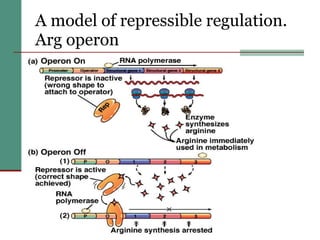
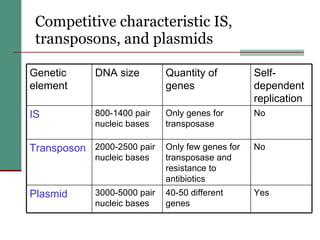
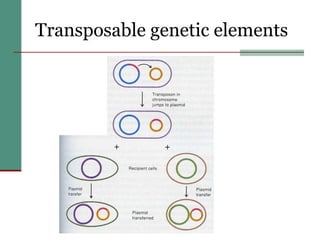
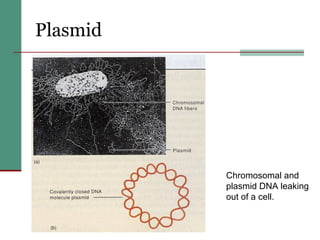
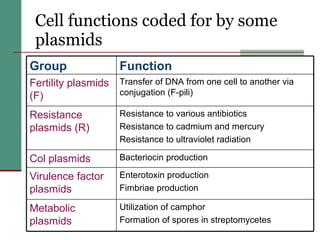
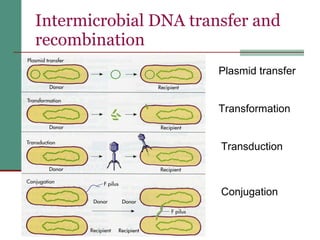
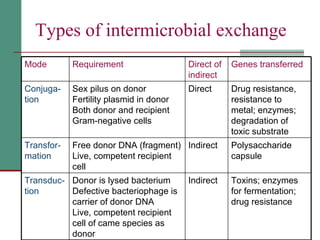
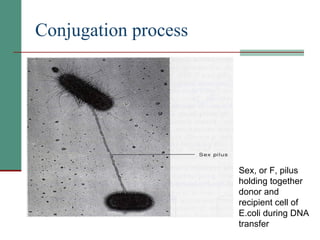
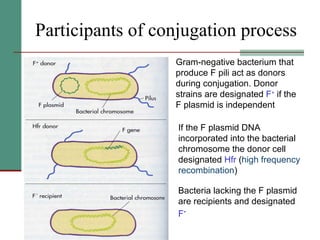
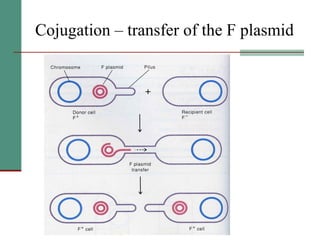
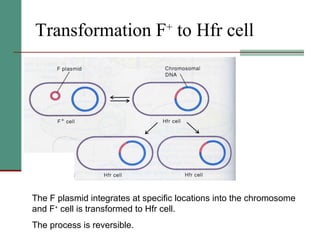
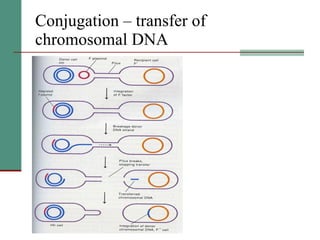
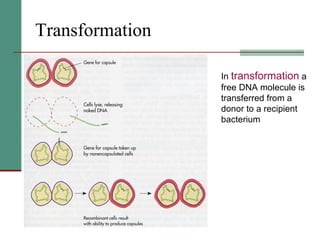
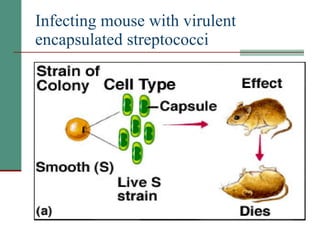
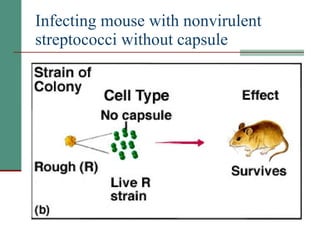
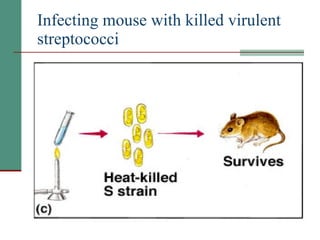
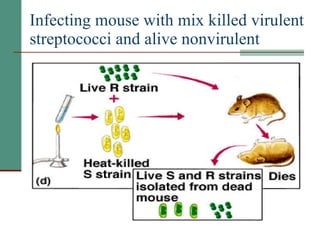
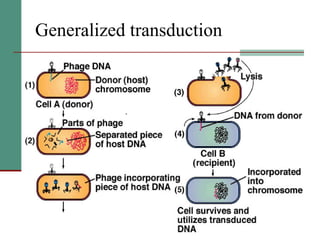
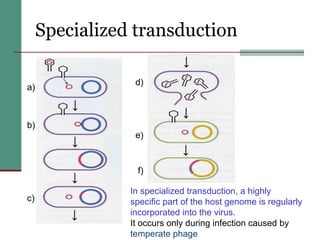
Genetic of microorganisms provides advantages for genetic research due to their simple genome structures, universal gene code, lack of diploid chromosomes and dominant genes, ease of cultivation, rapid reproduction, genetic population heterogeneity, and accessibility of modern genetic analysis methods. Bacteria like E. coli have smaller, supercoiled DNA compared to human cells. Bacterial genomes contain structural and regulatory genes organized into operons that control gene expression. The lac and arg operons demonstrate inducible and repressible gene regulation through repressor proteins and substrate/product binding. Mutation, recombination, and mobile genetic elements allow for genetic variation and horizontal gene transfer between microorganisms.