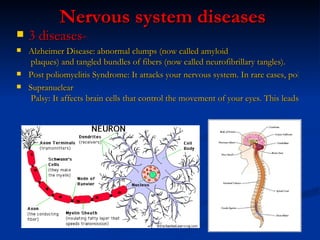
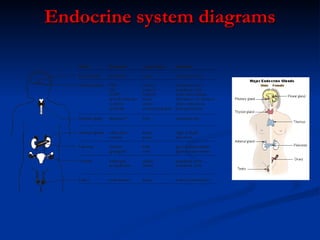
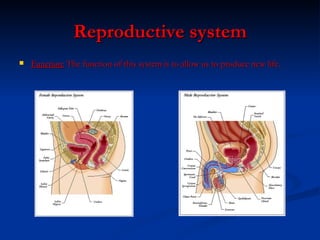
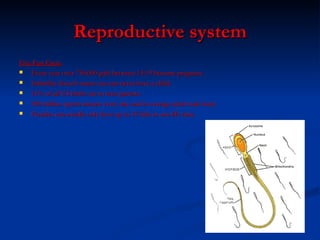
The document provides an overview of the major human body systems, including:
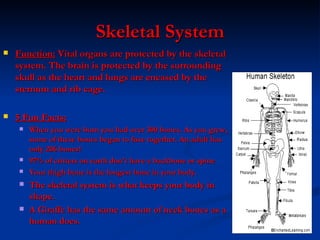
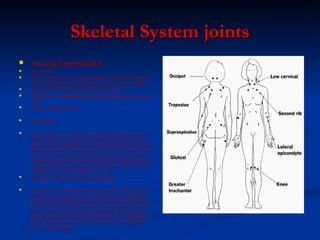
- Skeletal system which protects organs and allows movement via bones and joints
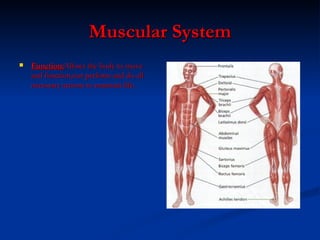
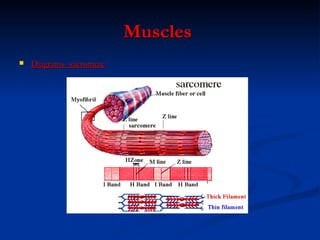
- Muscular system which allows body movement through muscles
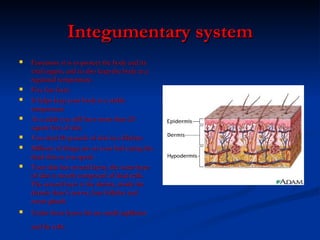
- Integumentary system which protects the body and regulates temperature through skin and hair
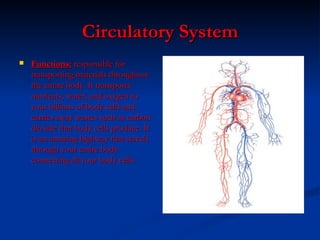
- Circulatory system which transports blood throughout the body carrying oxygen and nutrients and removing wastes
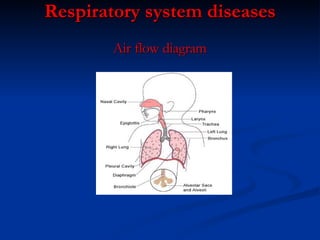
- Respiratory system which intakes oxygen and removes carbon dioxide during breathing