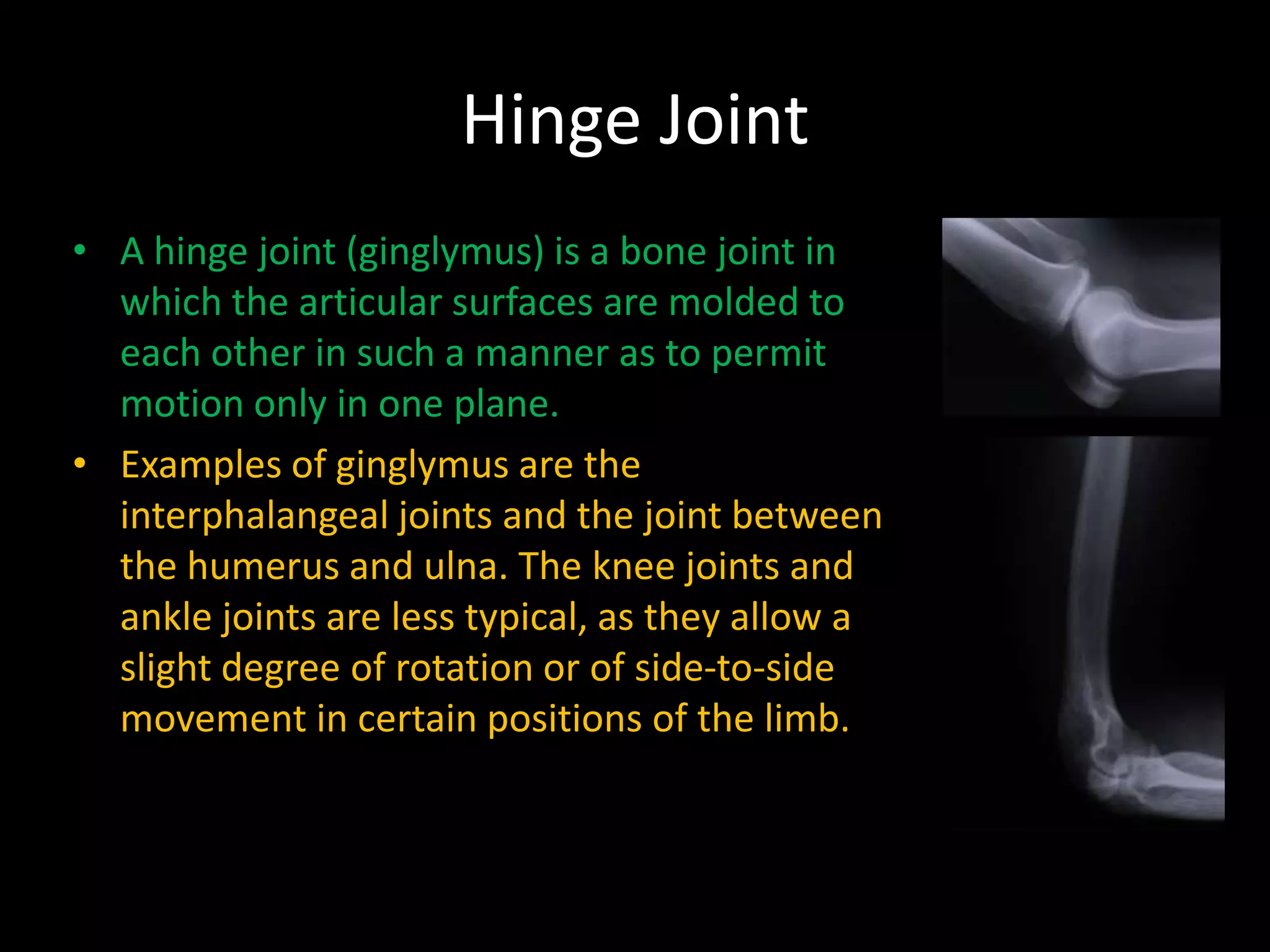
The document explains the functions of bones in the human body, which include support, protection of organs, production of blood cells, and mineral storage. It describes various types of joints, such as ball and socket, hinge, pivot, gliding, and fixed joints, along with their characteristics and examples. Additionally, the document answers several questions regarding body functions, cartilage, joints, bone marrow, and differences between various skeletal structures.