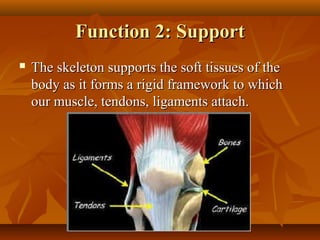
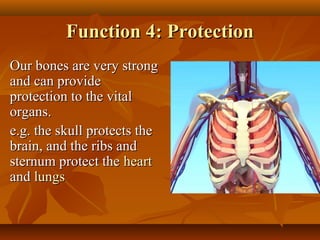
The skeleton provides 5 major functions: shape, support, body movement, protection, and blood cell formation. There are 4 types of bones: long, short, flat, and irregular. Joints allow movement and come in 4 types: ball and socket, hinge, pivot, and gliding. Ligaments connect bones, tendons connect muscles to bones, and cartilage protects joints. Synovial fluid reduces friction in joints. A healthy skeleton requires calcium, phosphorus, weight-bearing exercise, and avoidance of osteoporosis.