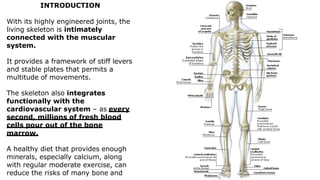
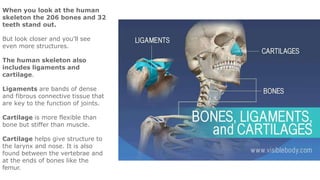
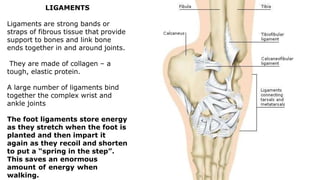
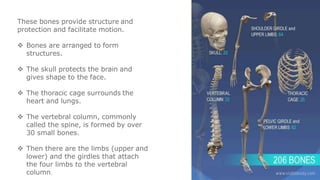
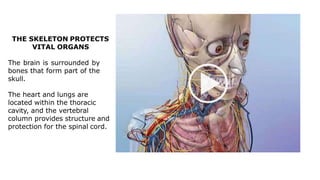
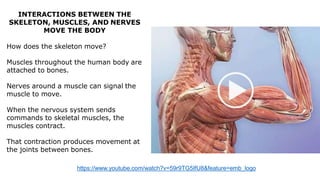
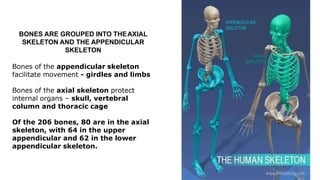
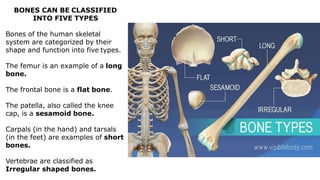
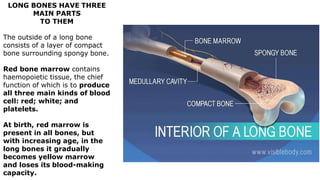
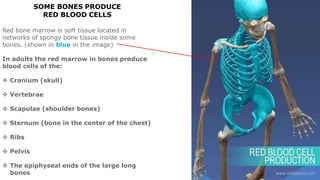
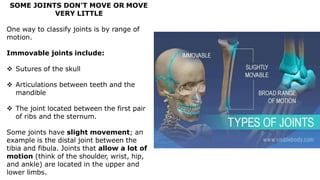
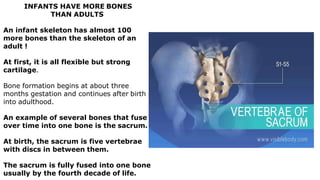
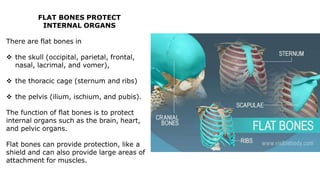
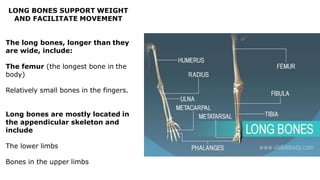
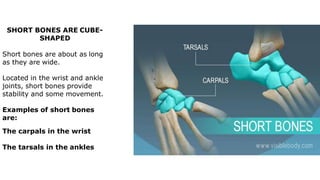
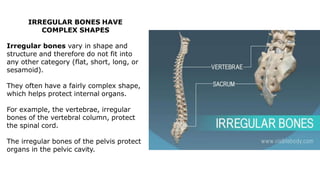
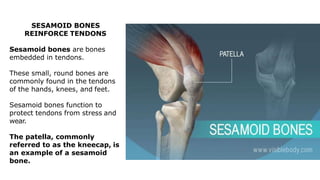
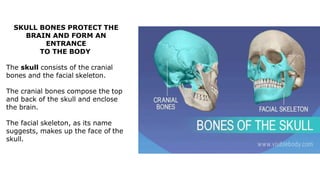
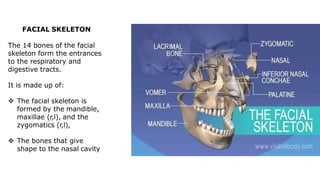
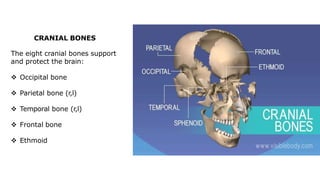
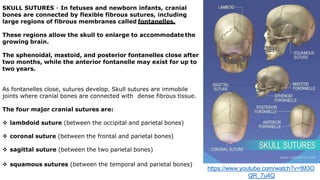
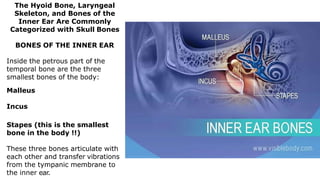
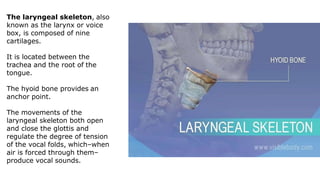
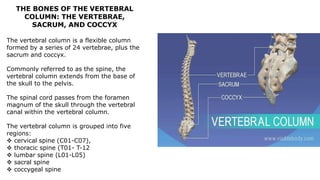
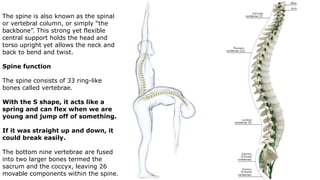
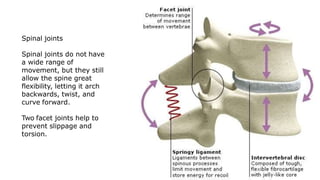
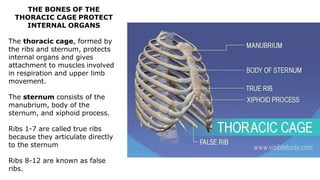
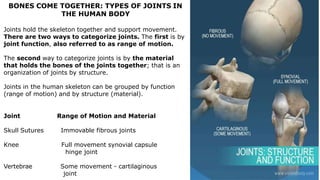
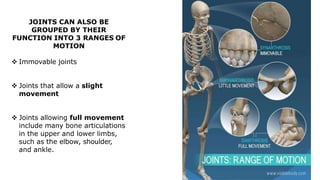
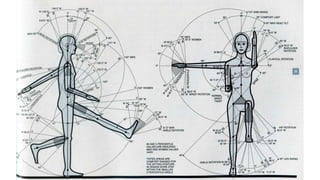
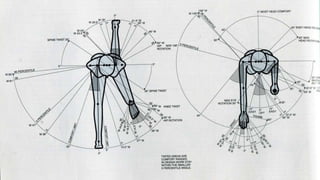
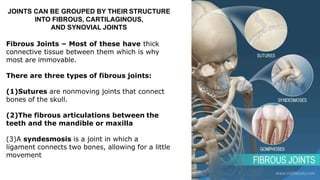
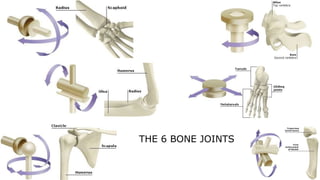
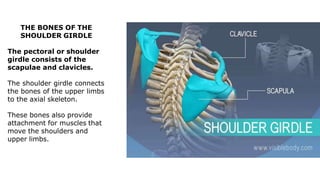
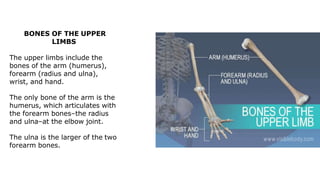
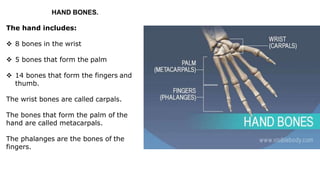
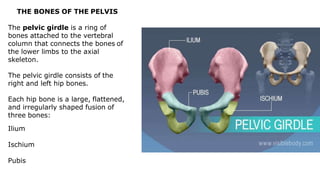
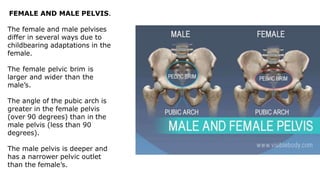
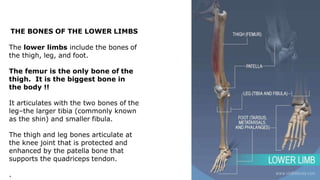
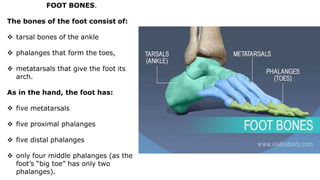
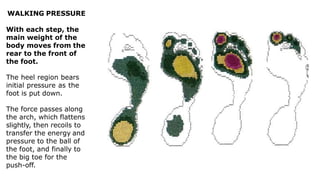
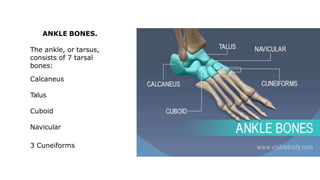
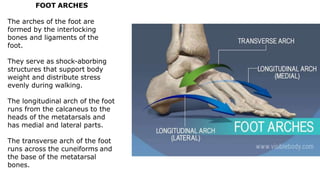
The skeleton is the framework that provides structure to the rest of the body and facilitates movement. It consists of 206 bones that are arranged into the axial skeleton including the skull and vertebral column, and the appendicular skeleton including the limbs. Bones can be classified by their shape as long, short, flat, irregular, or sesamoid. Joints connect bones and allow for varying degrees of movement, and can be categorized by their structure as fibrous, cartilaginous, or synovial joints. The skeleton works with muscles and nerves to enable movement of the body.