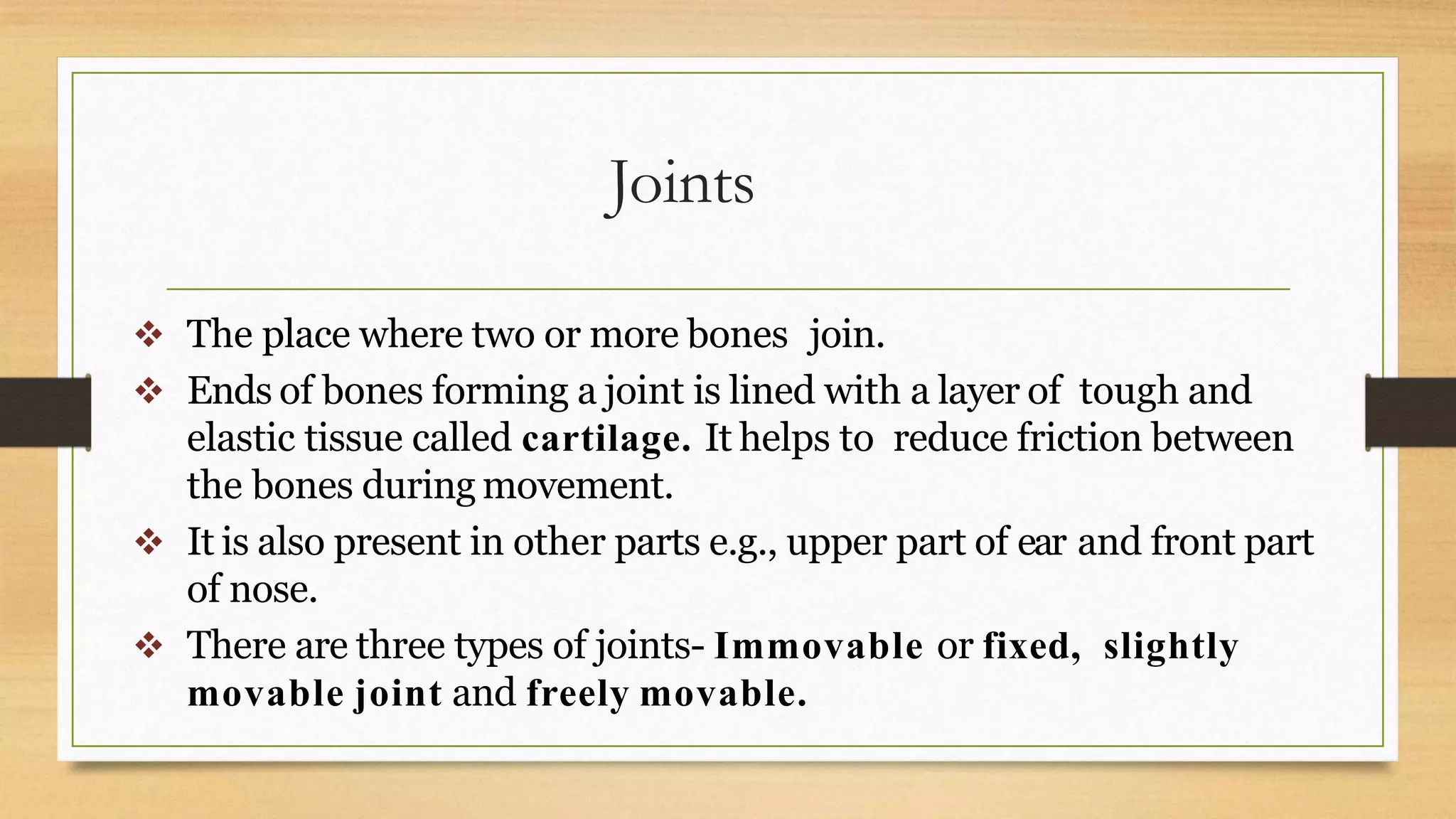
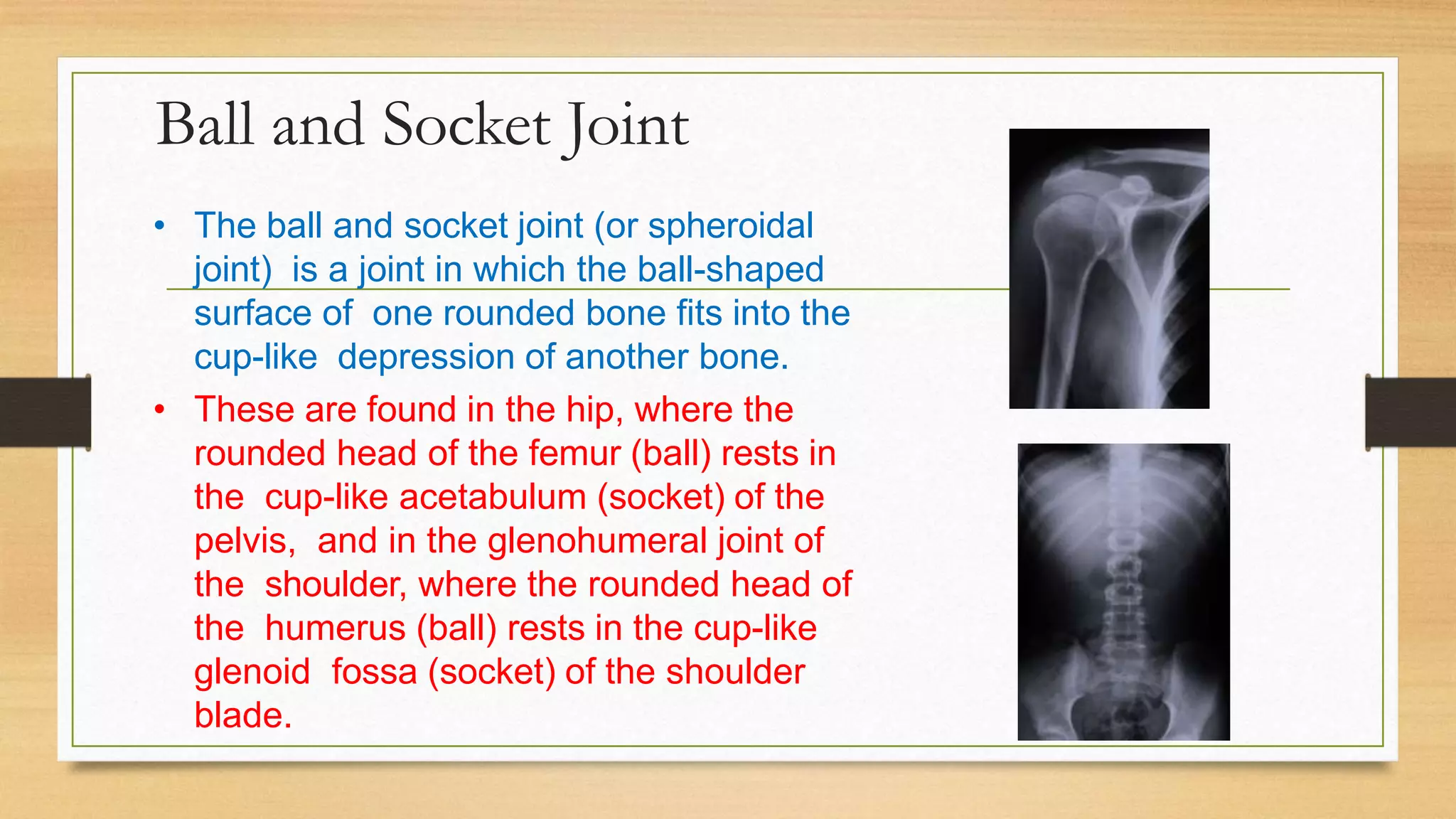
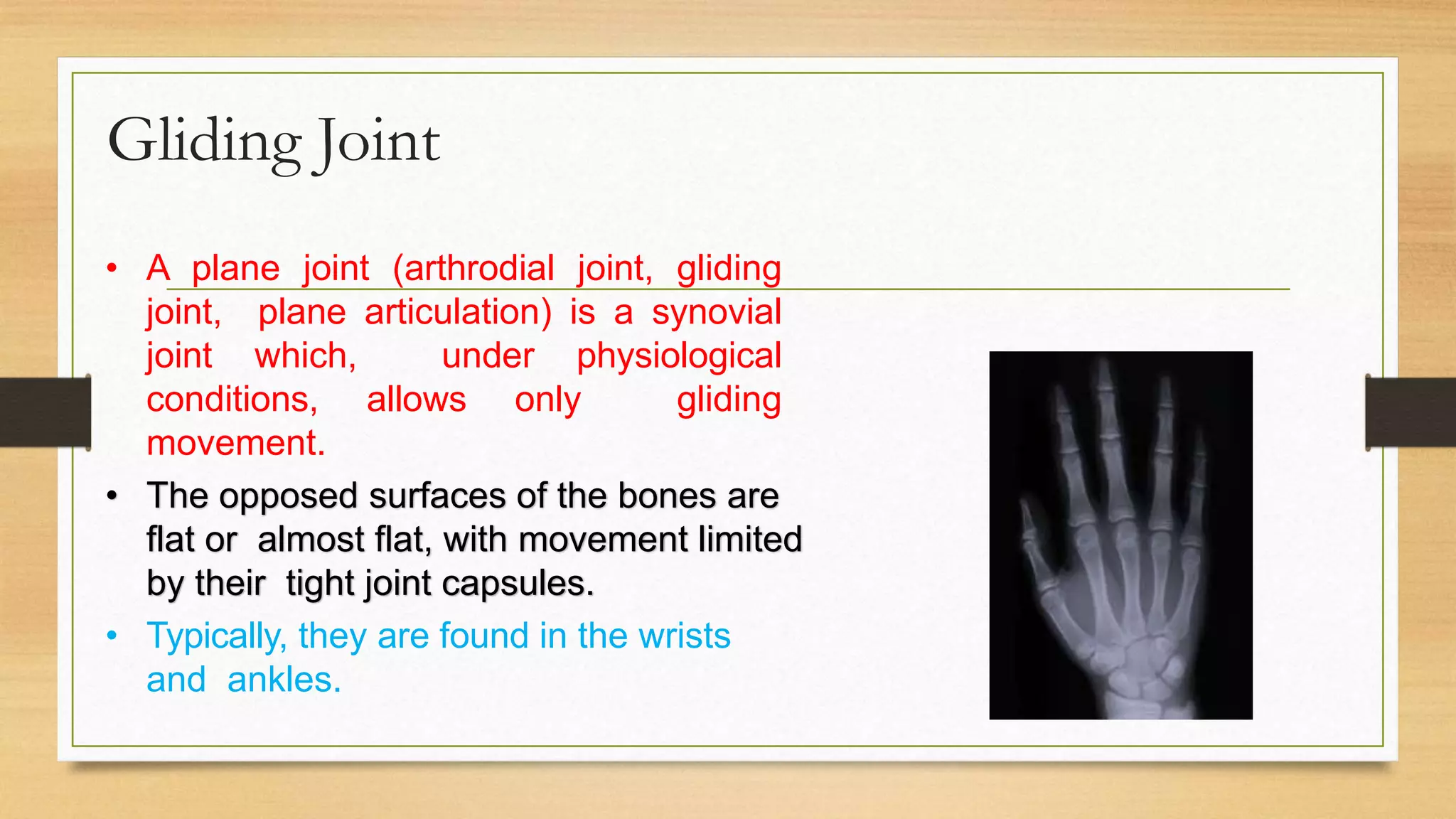
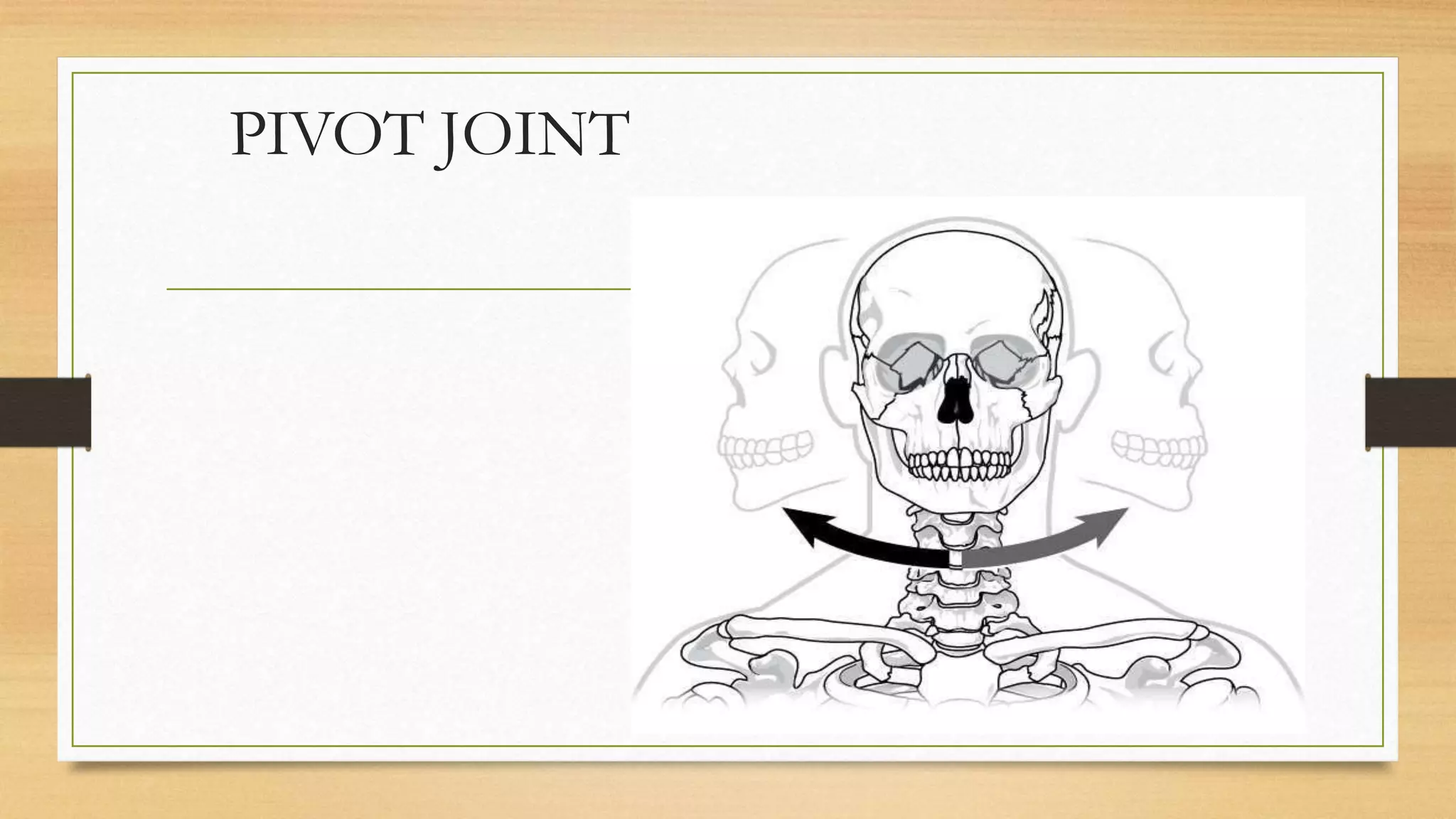
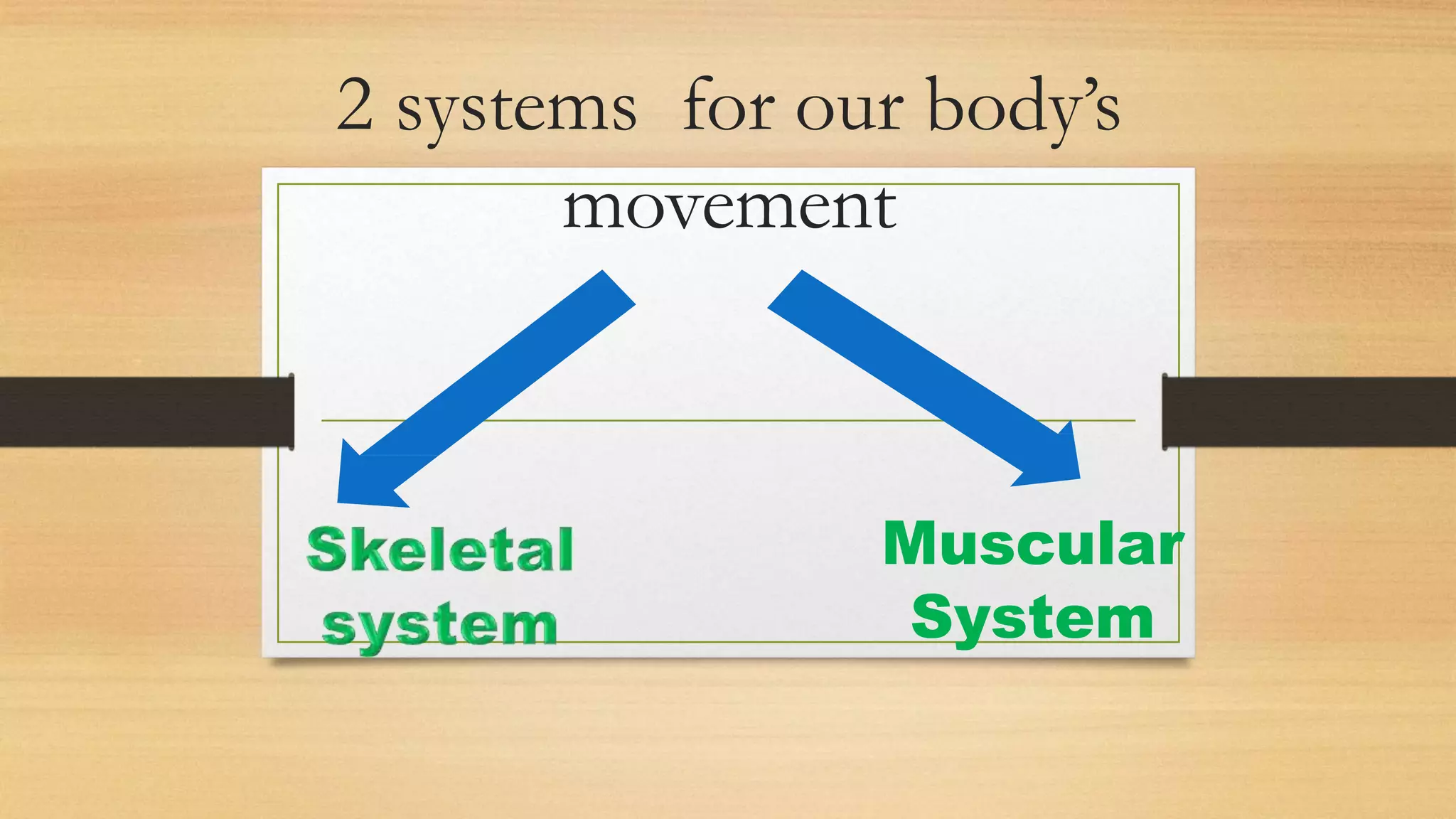
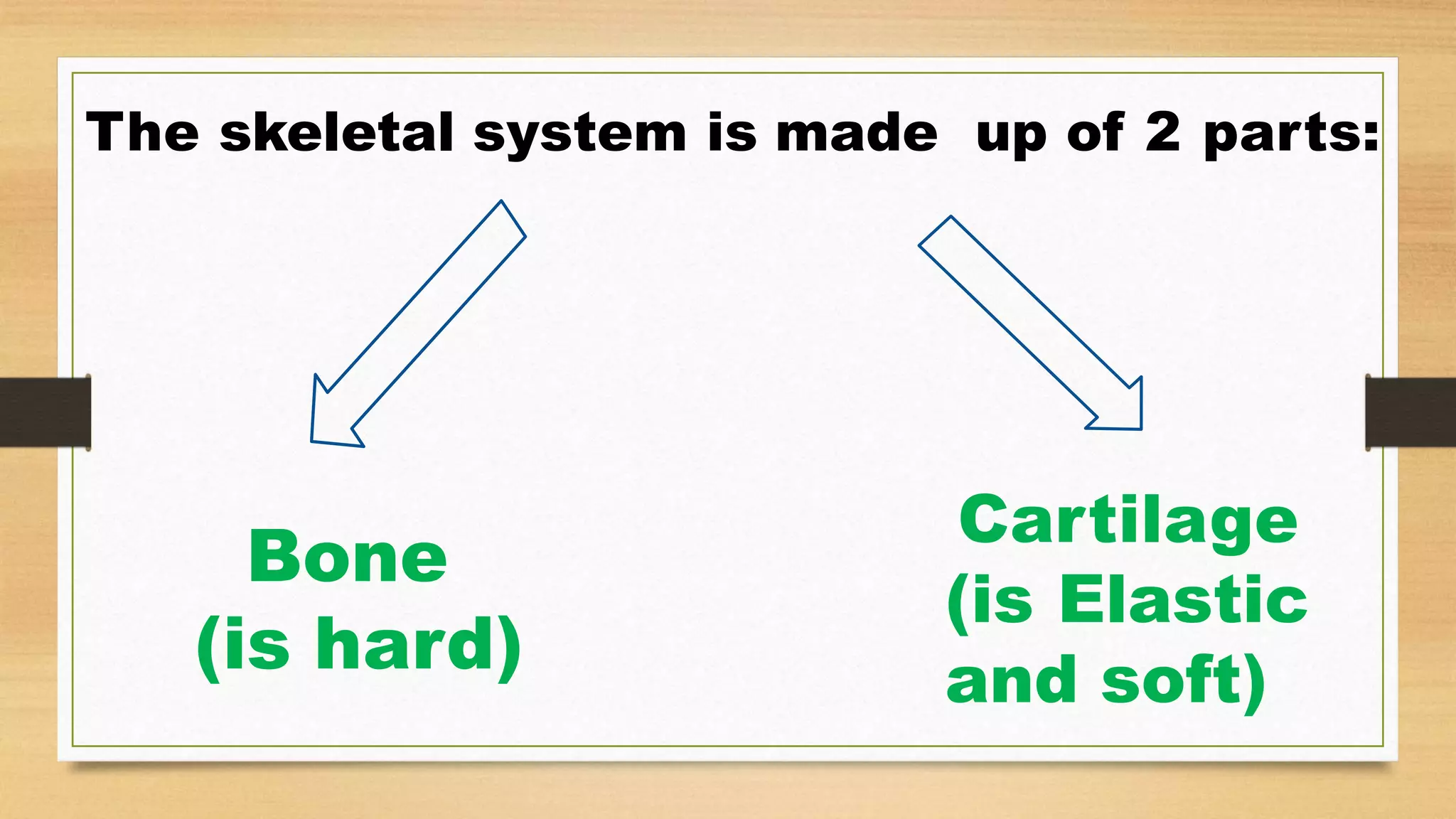
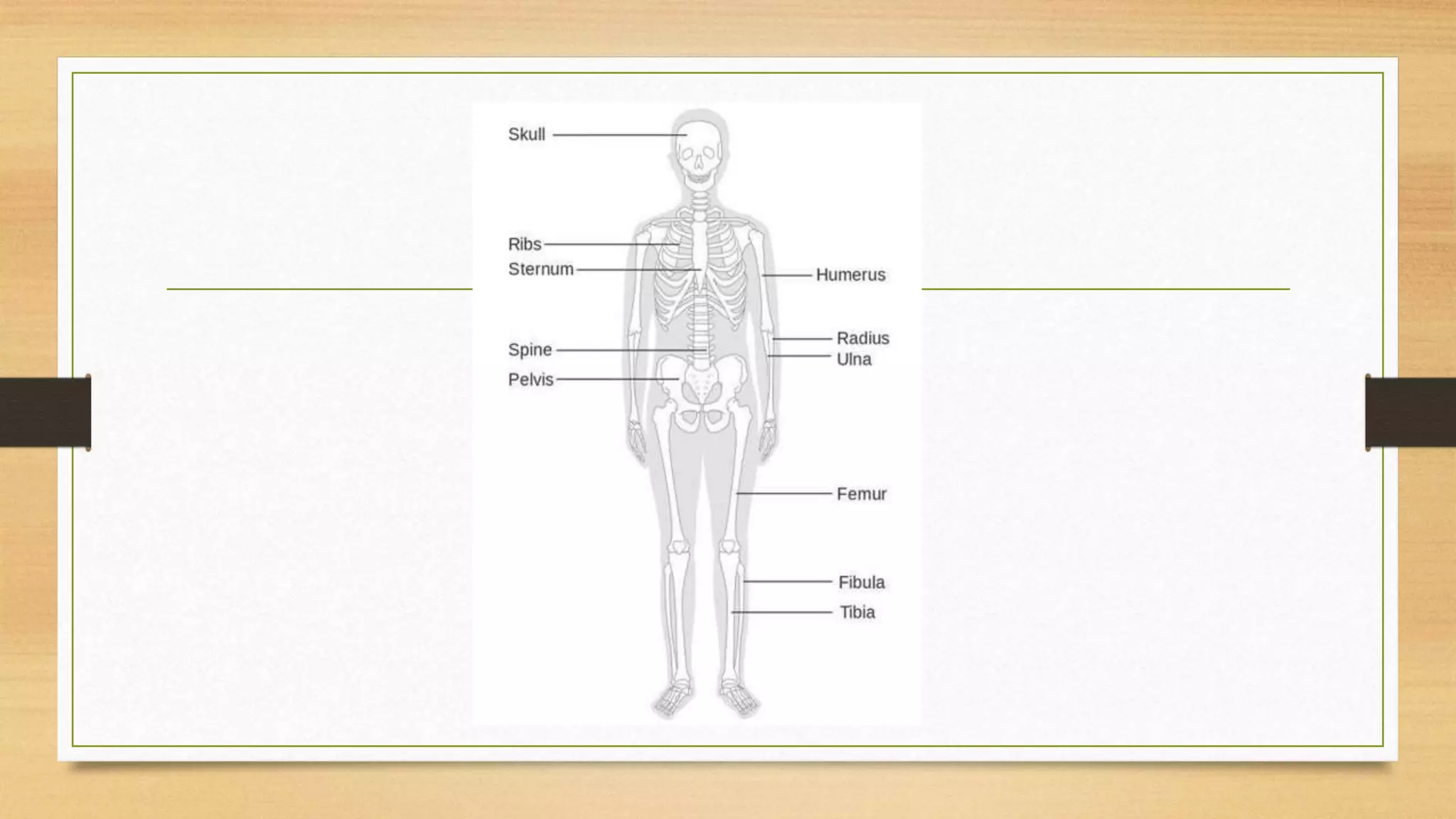
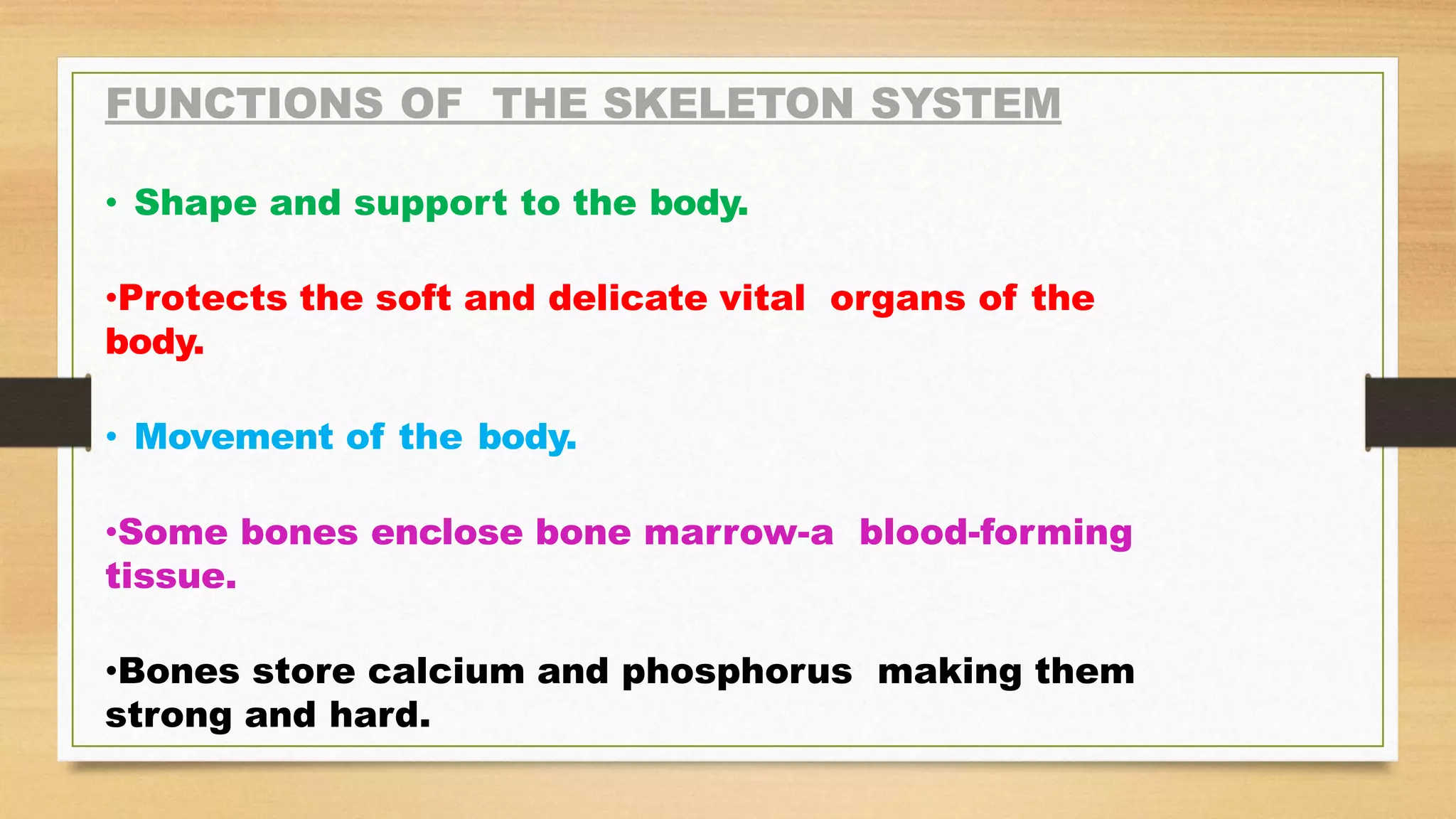
The document discusses locomotion and the skeletal and muscular systems that enable movement. It describes the three types of joints - fixed, slightly movable, and freely movable - and provides examples like the ball and socket hip joint. The skeletal system includes bones and cartilage that provide structure, shape, protection and movement. Key bones are discussed like the skull, spine, ribs, limbs and girdles. The muscular system works with tendons and ligaments to contract muscles and enable locomotion. Examples show how different animals like earthworms, birds and fish move using alternative structures and locomotion methods besides bones.