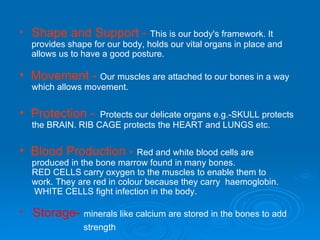
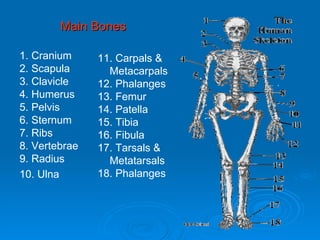
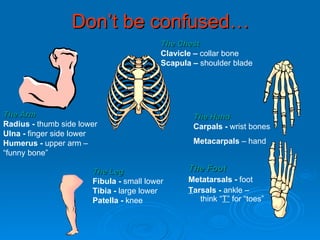
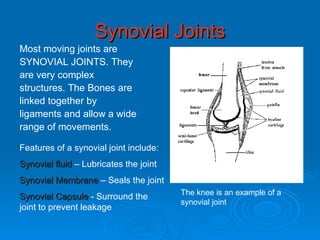
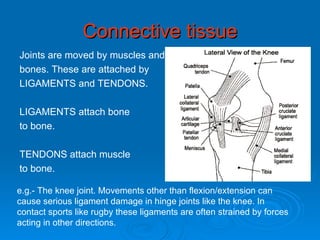
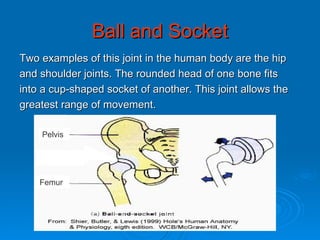
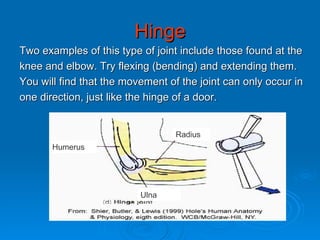
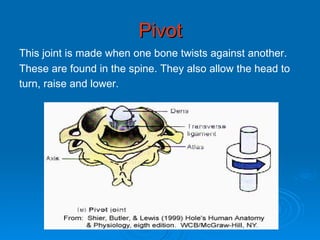
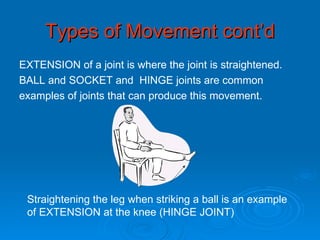
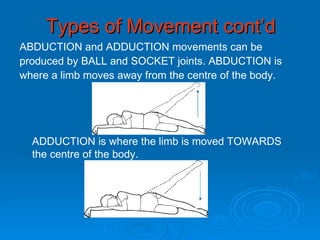
The skeletal system has five main functions: providing shape and support, enabling movement, protecting organs, producing blood cells, and storing minerals. It is made up of bones and joints, with three types of joints - fibrous, cartilaginous, and synovial. Synovial joints allow the greatest range of movement and are found at joints like the knee. Bones and muscles are connected by ligaments and tendons, with different joint types - ball and socket, hinge, gliding, and pivot - enabling various movements like flexion, extension, and rotation. Injuries can result from overuse, incorrect movement, or impacts and twisting.