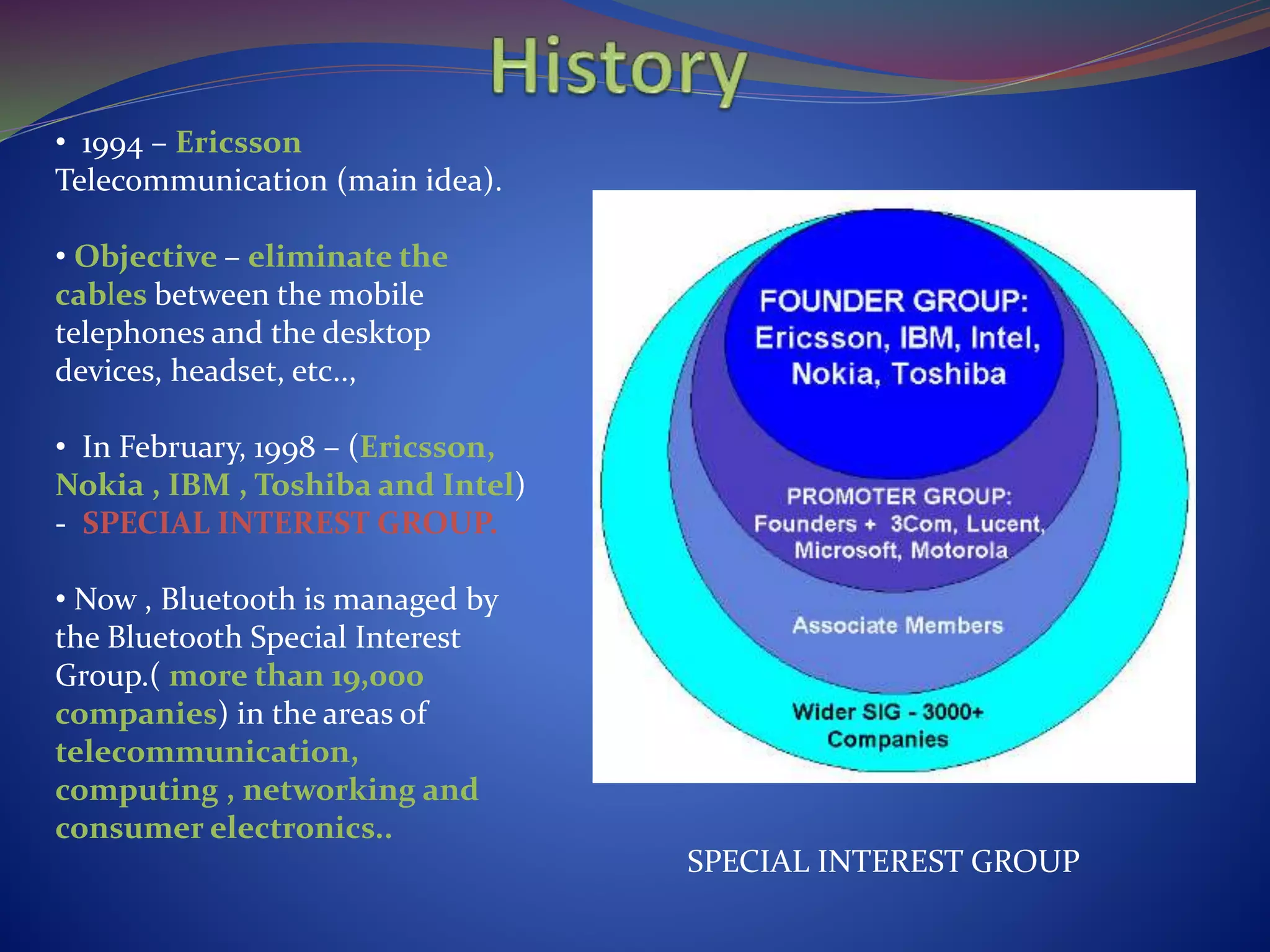
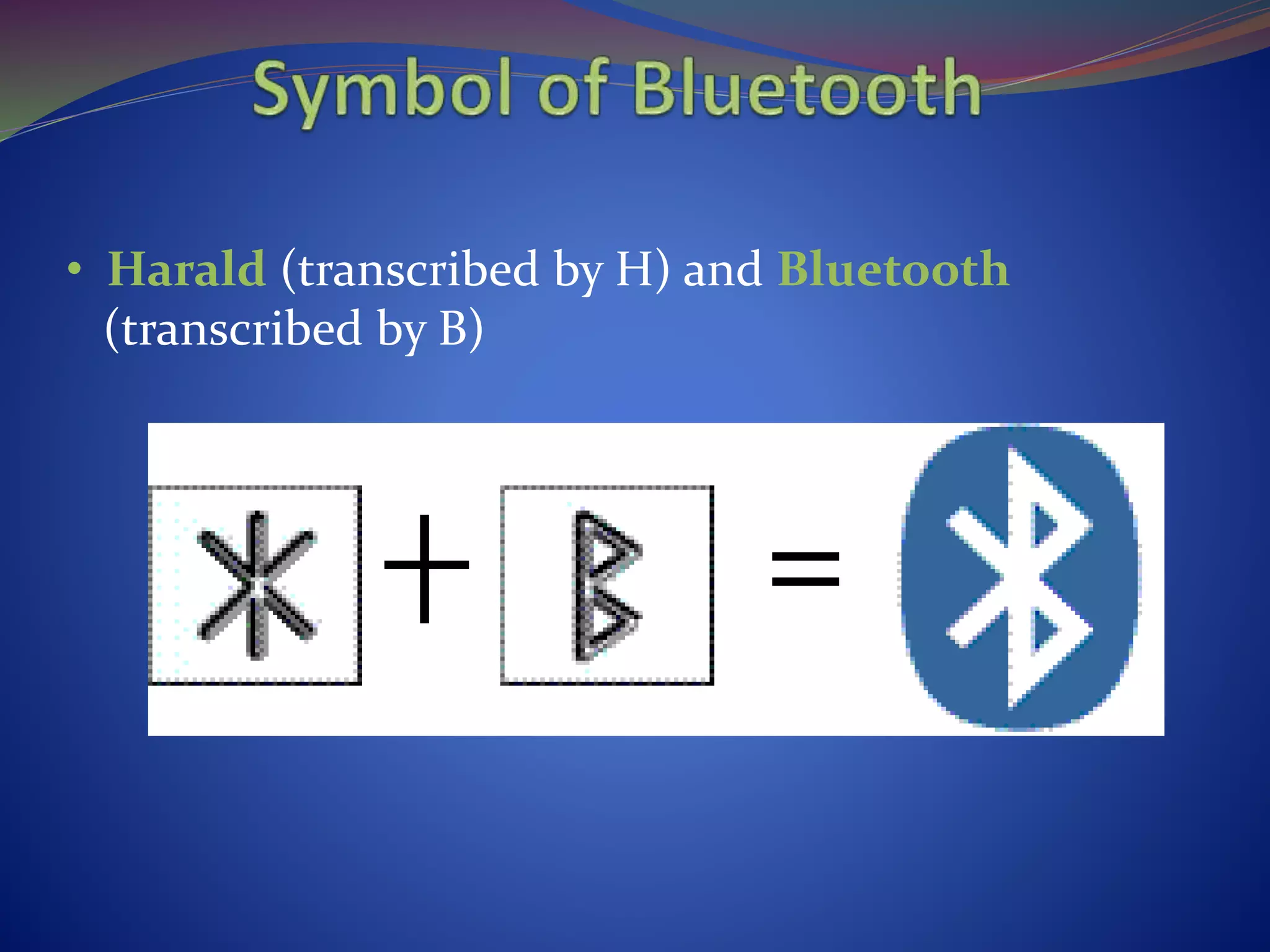
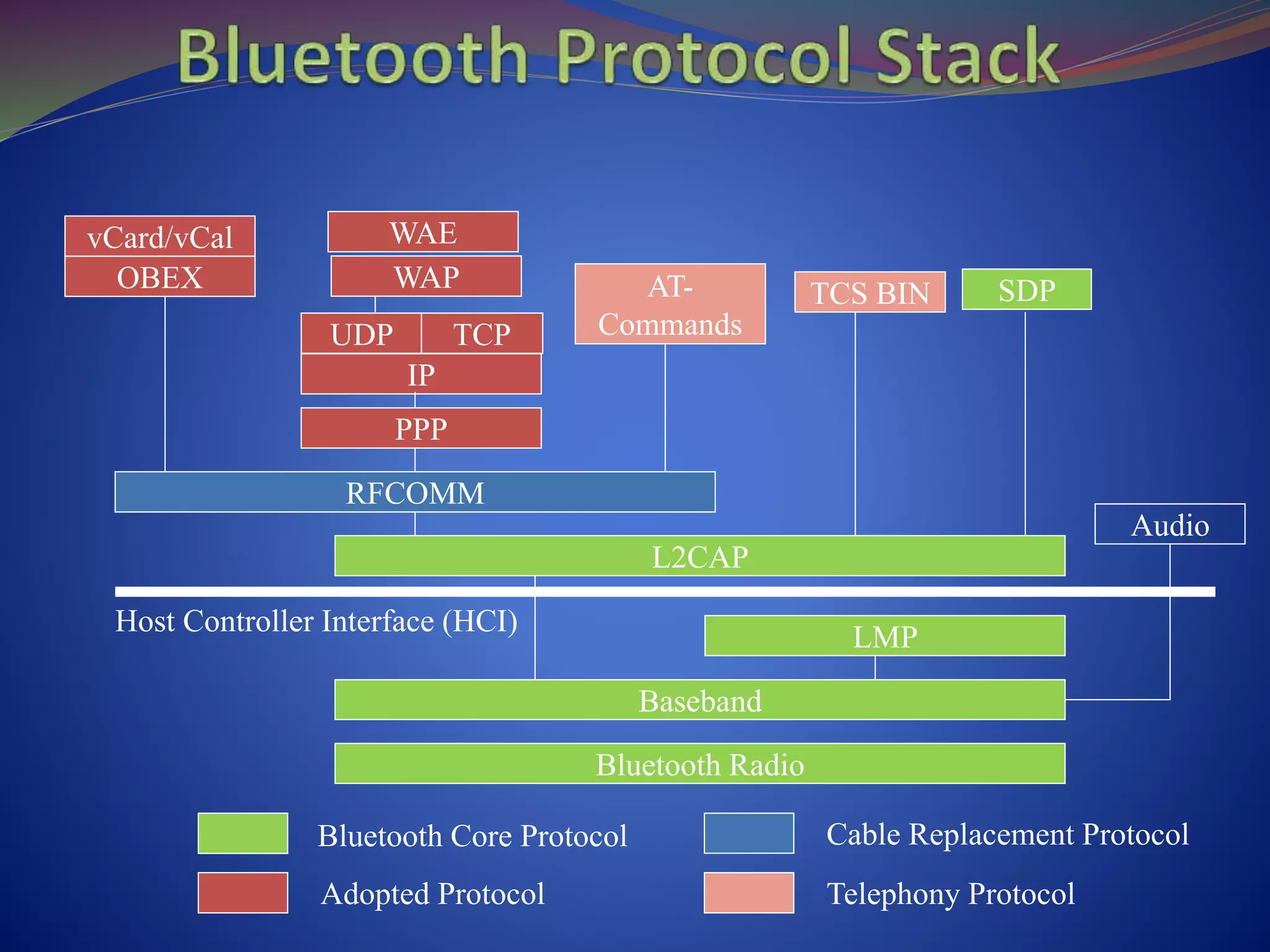
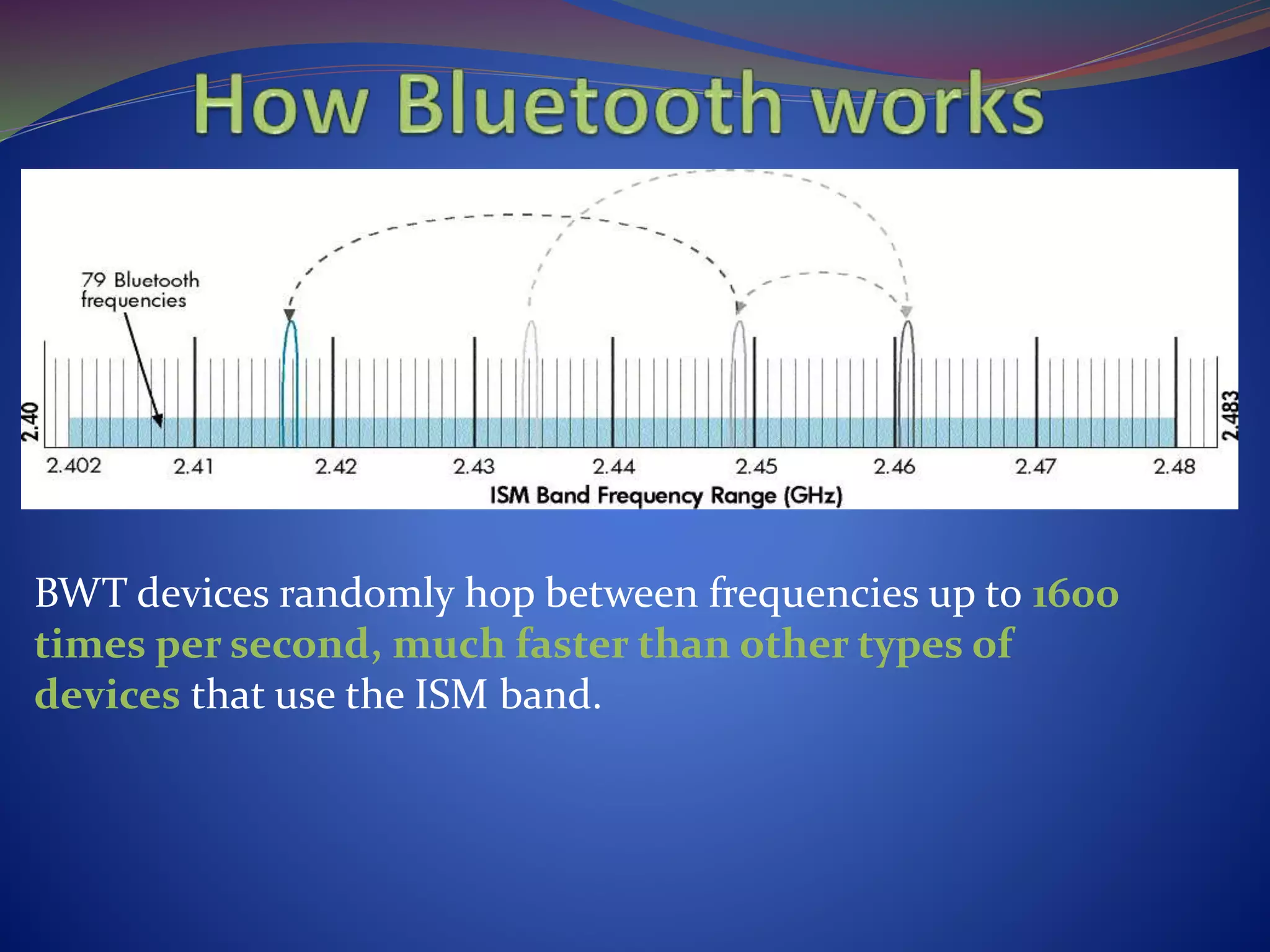
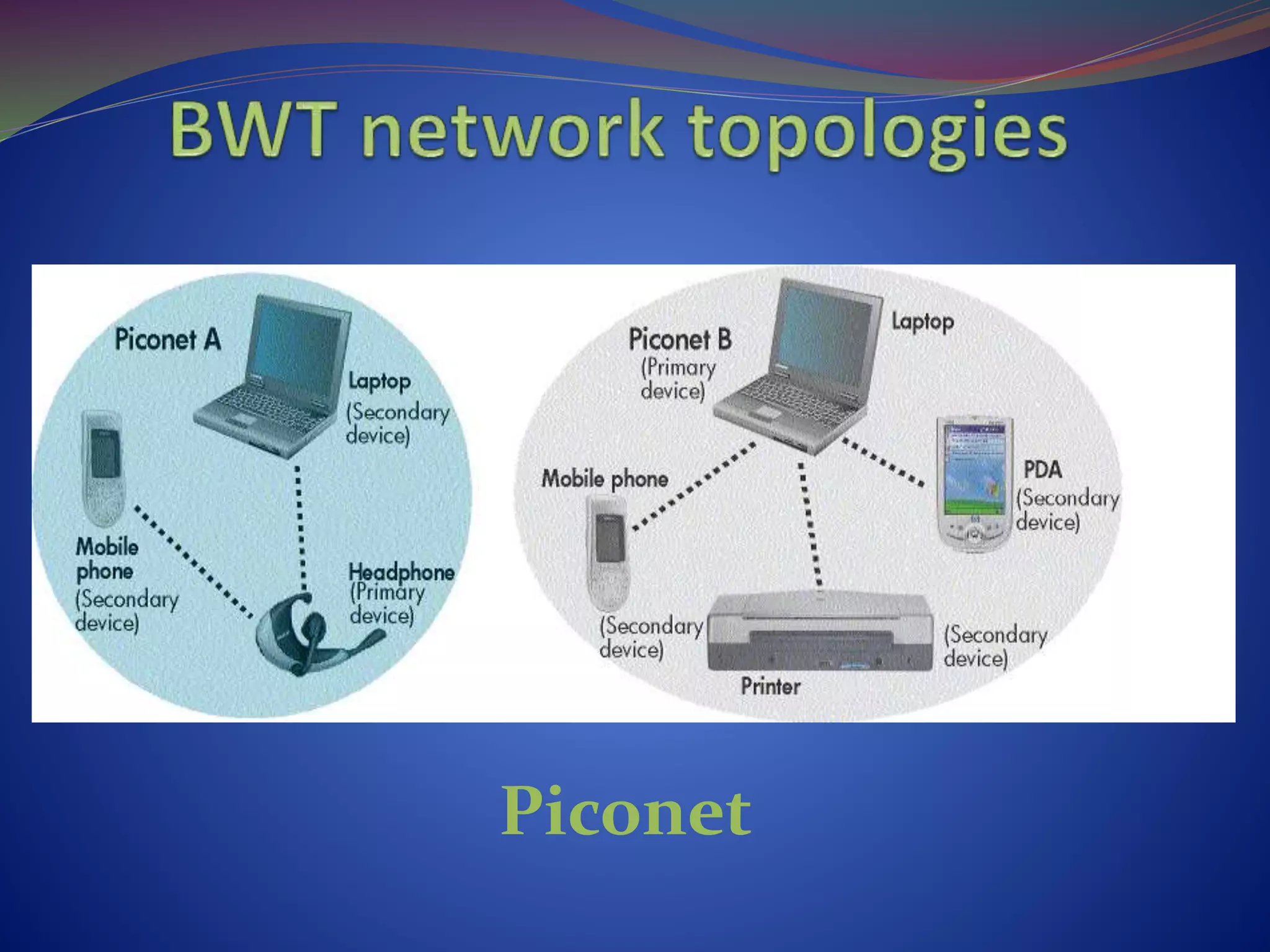
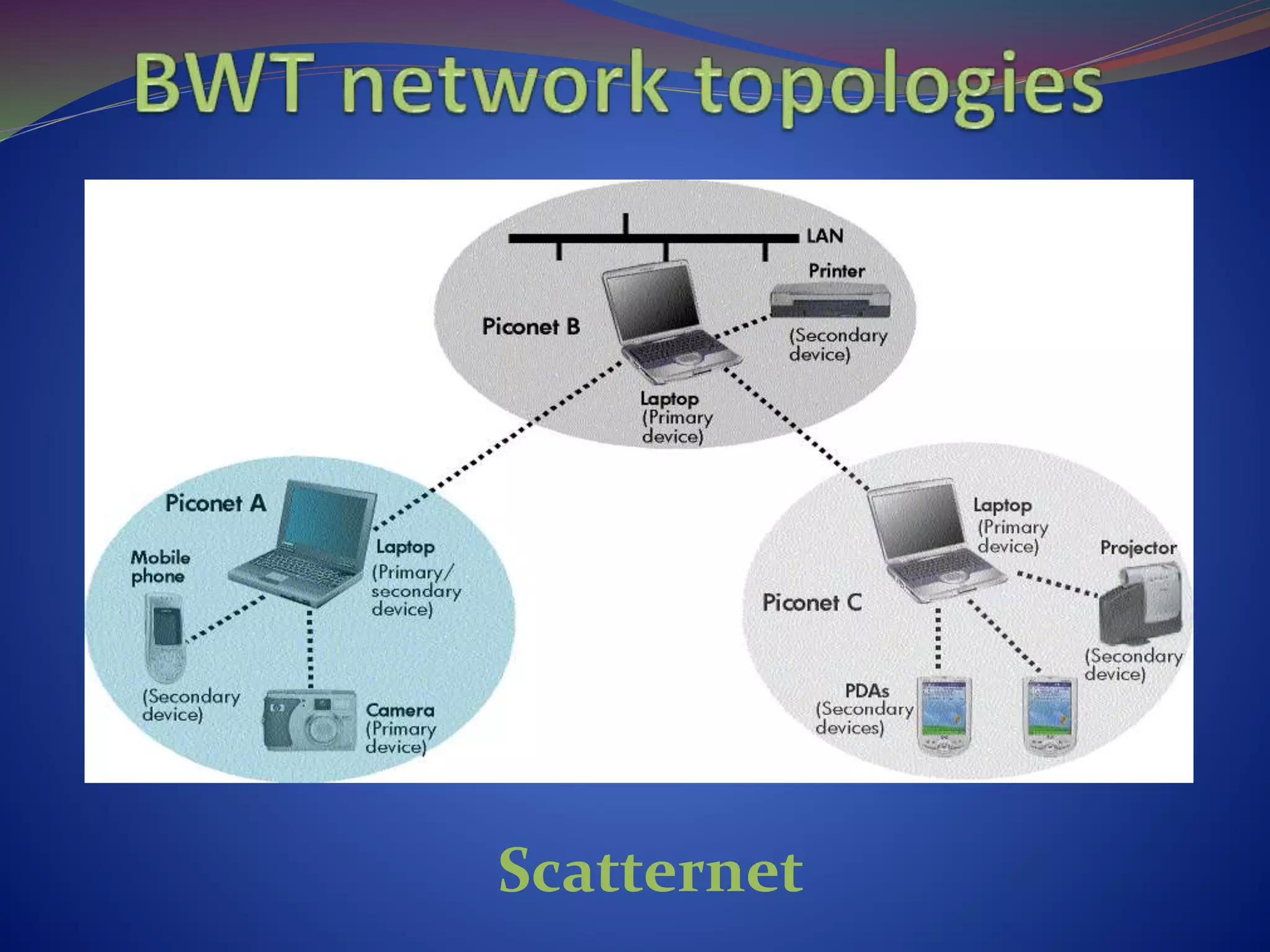
This document discusses the history and technical aspects of Bluetooth technology. It describes how Bluetooth was created in 1994 by Ericsson to eliminate cables between mobile devices. The technology standard is now managed by the Bluetooth Special Interest Group consisting of over 19,000 companies. The name "Bluetooth" comes from the 10th century Danish king Harald Bluetooth who united Scandinavia, just as Bluetooth aims to unite various electronic devices. The document outlines Bluetooth's protocol stack and topology including piconets and scatternets. It notes advantages like being wireless and inexpensive, as well as disadvantages like low data rates compared to infrared. It concludes that Bluetooth is a simple choice for convenient short-range communication between devices.