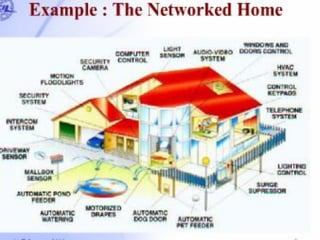
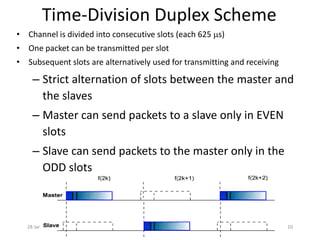
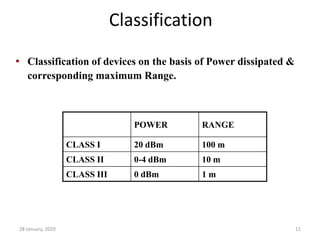
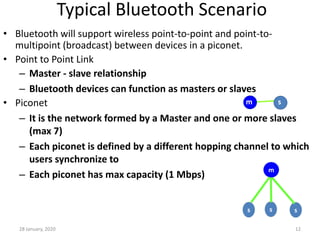
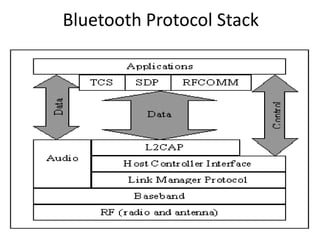
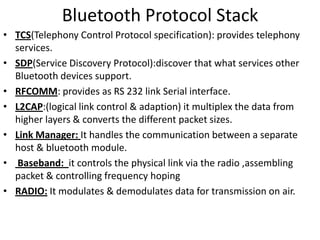
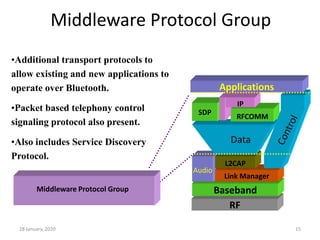
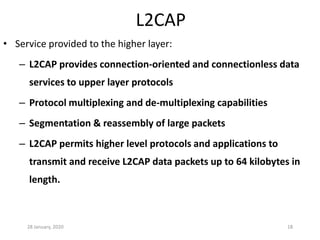
Here is a short note on Bluetooth technology:
Bluetooth is a wireless technology standard for exchanging data over short distances between devices like mobile phones, laptops, personal computers, printers, digital cameras, and video game consoles. It was developed in 1994 by telecom vendor Ericsson and was originally conceived as a wireless alternative to RS-232 data cables.
Some key aspects of Bluetooth technology:
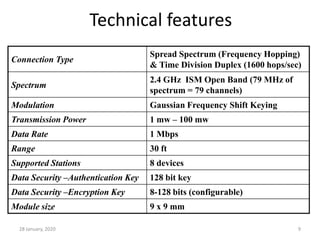
- It operates in the unlicensed 2.4 GHz short-range radio frequency band, allowing devices to connect within a range of around 30 feet.
- It uses a frequency-hopping spread spectrum technique to change between 79 designated frequencies in the 2.4 GHz band, avoiding interference and jamming.