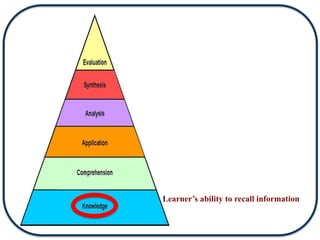
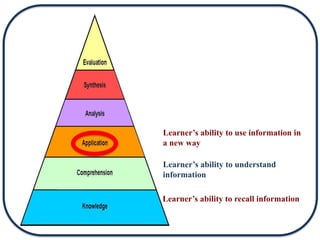
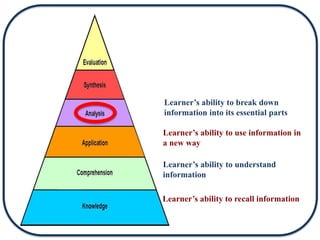
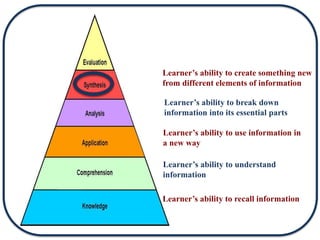
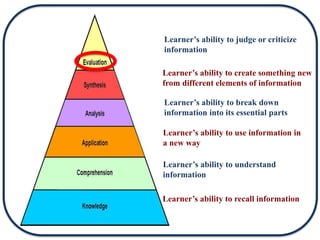
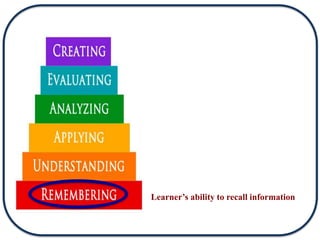
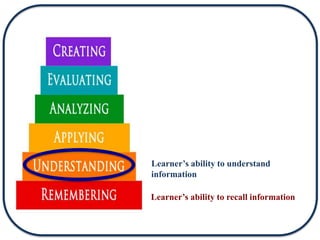
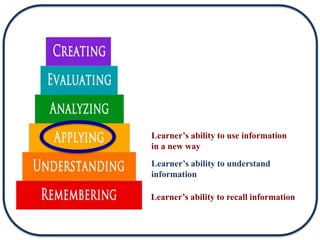
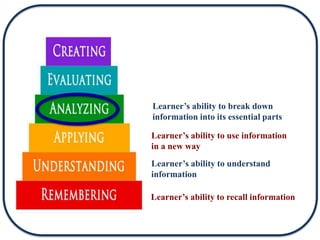
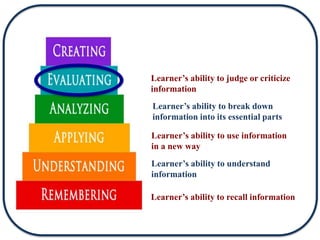
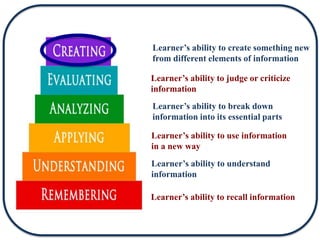
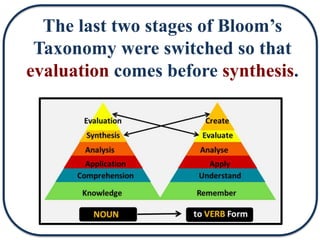
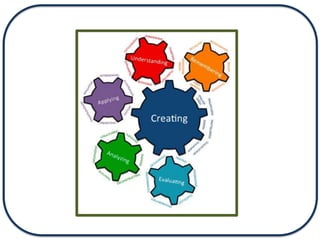
The document discusses Bloom's Taxonomy in the foreign language classroom, emphasizing its updated version and practical applications for enhancing student proficiency. Key changes include revising category names from nouns to verbs and switching the evaluation and synthesis stages. It provides guiding questions for assessing students at various cognitive levels while promoting interrelated learning skills.