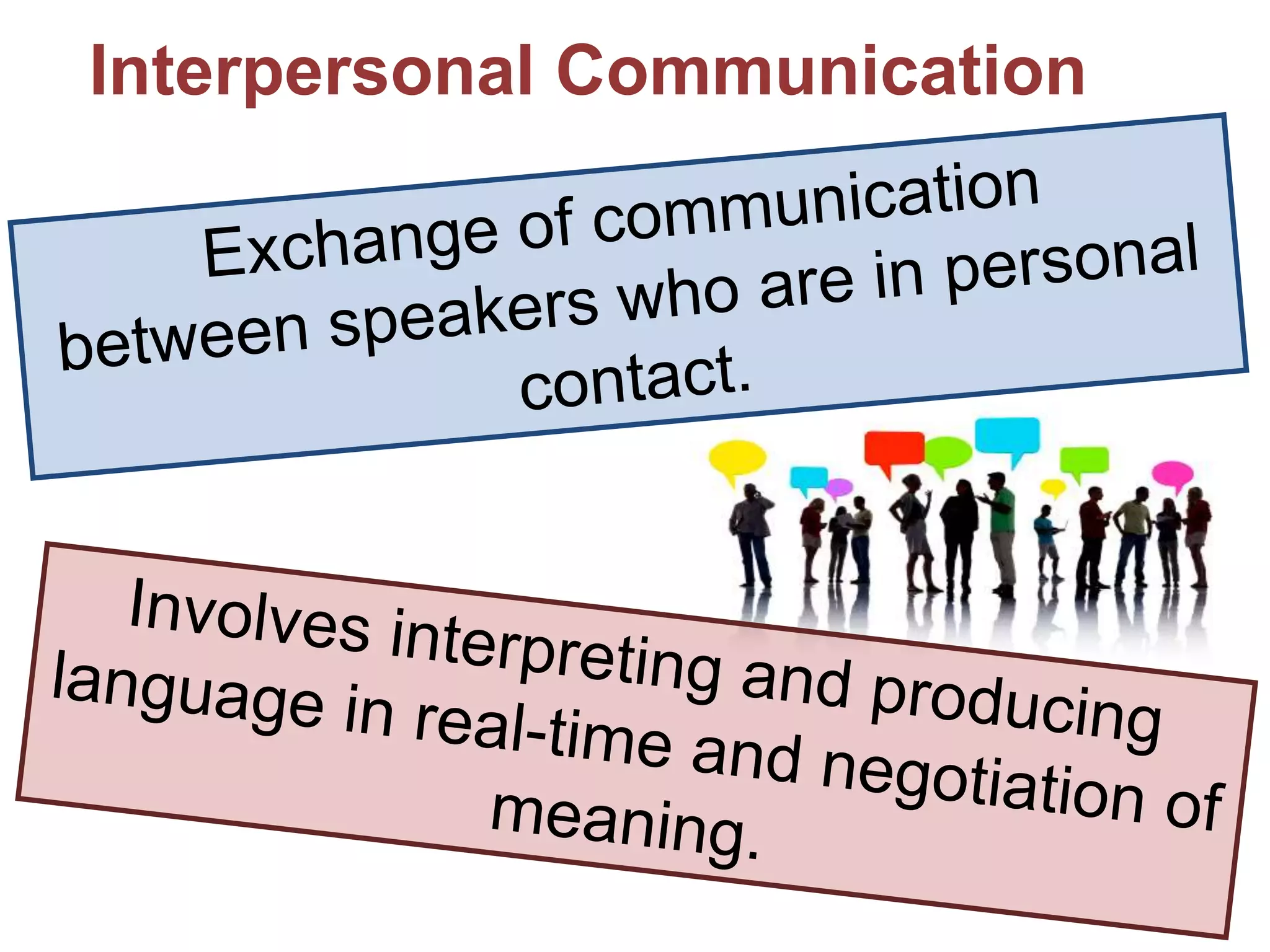
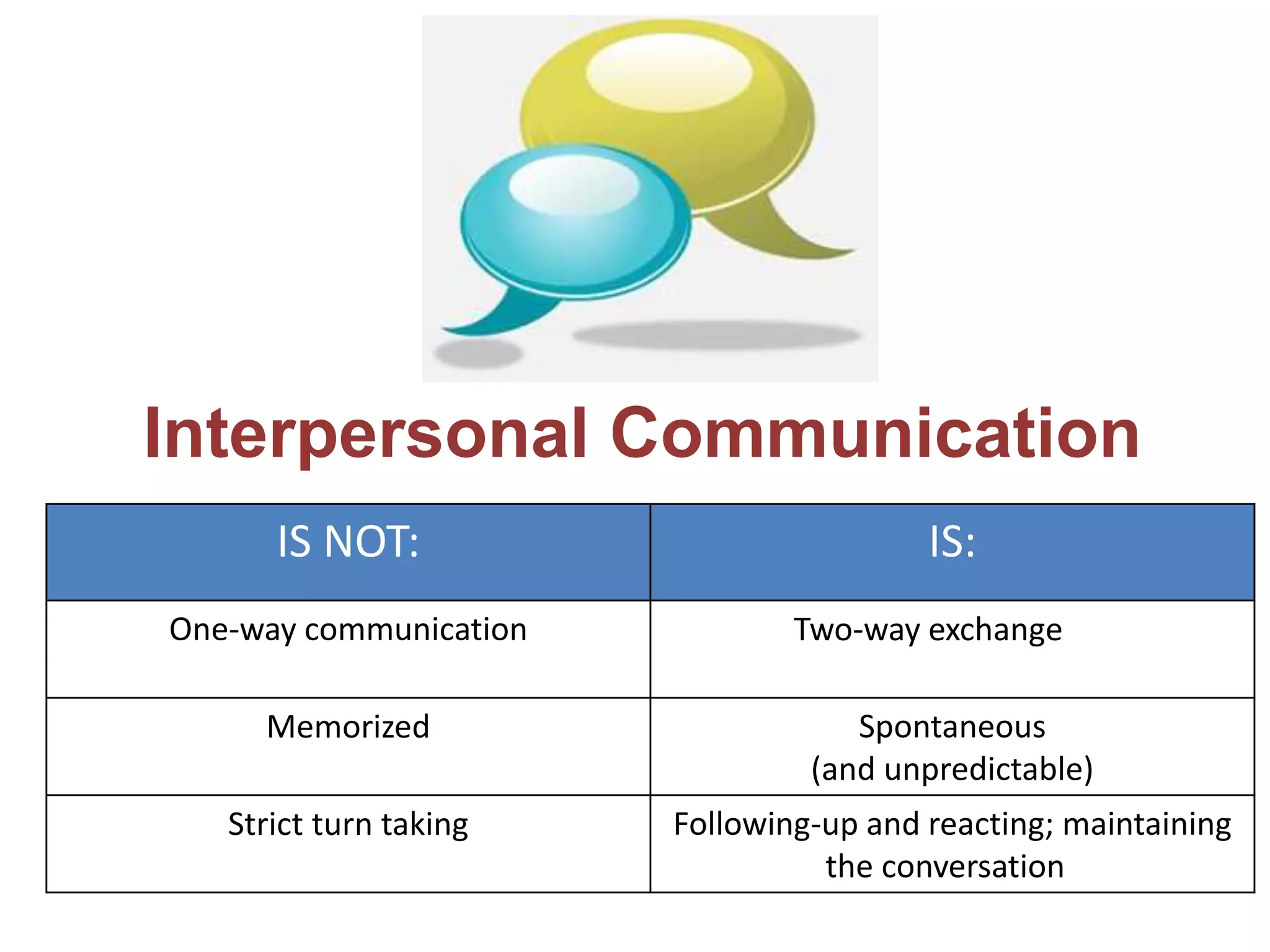
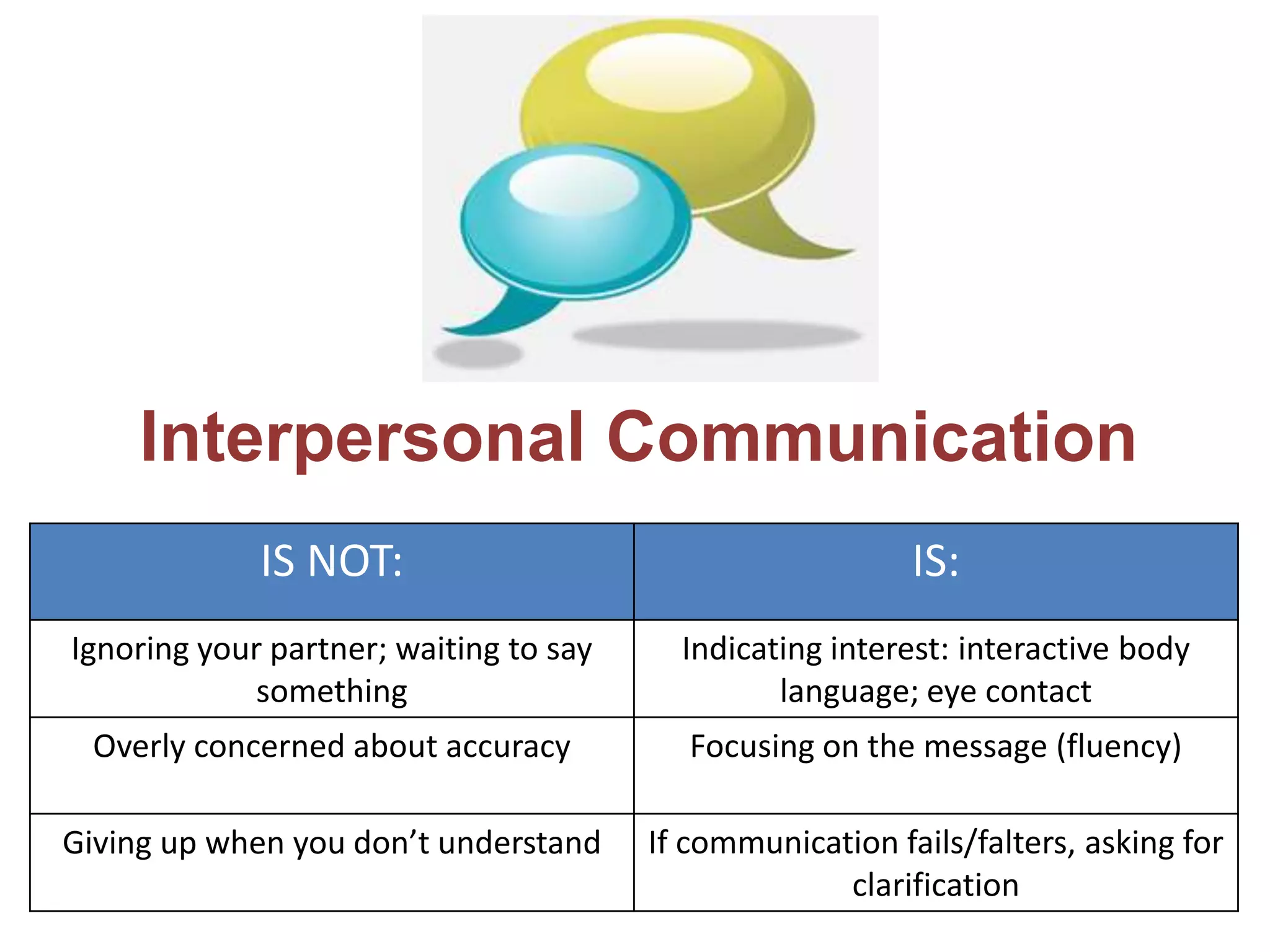
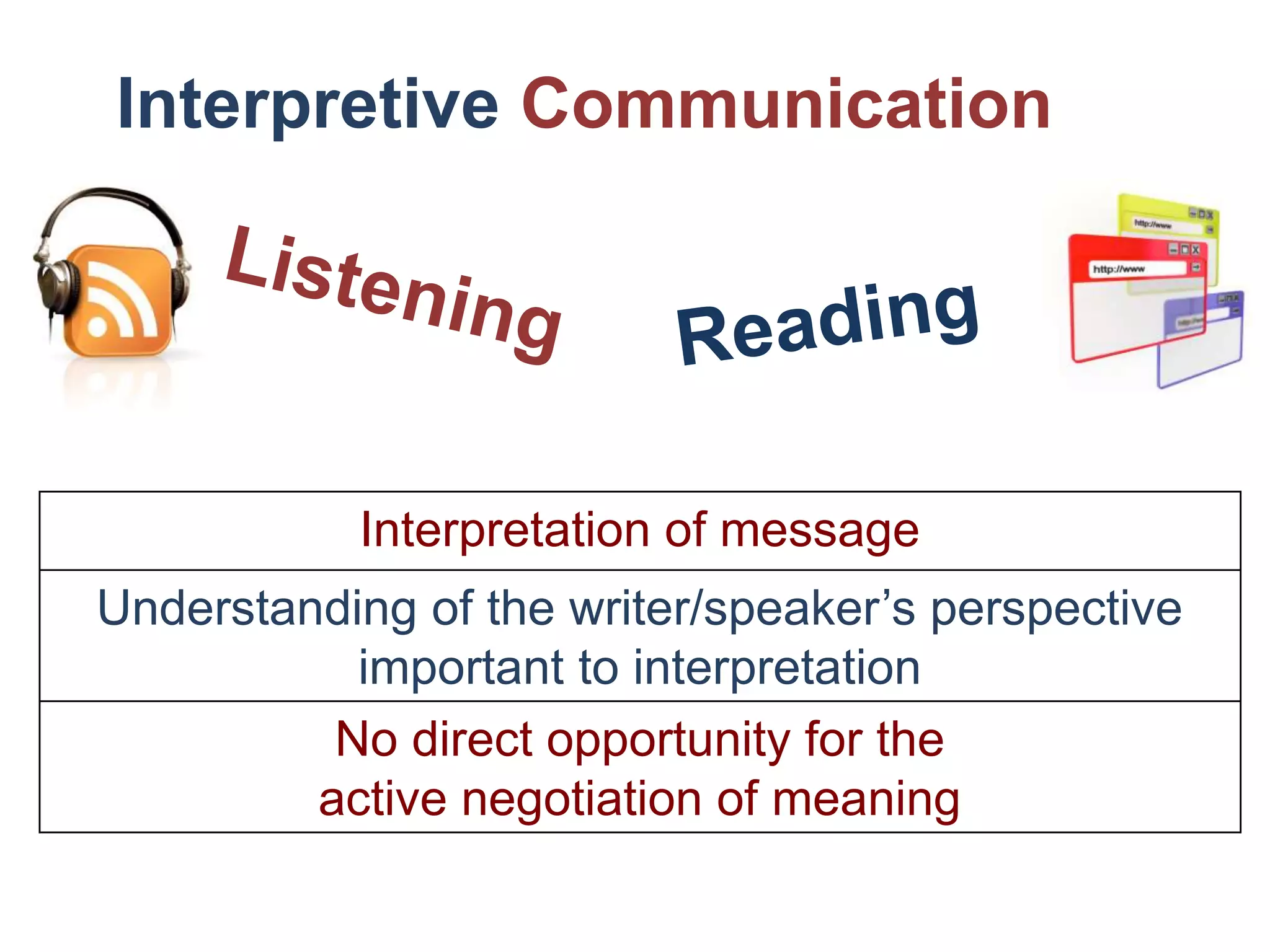
The document outlines tips, tools, and resources to enhance students' proficiency in three modes of communication: presentational, interpretive, and interpersonal. It emphasizes the differences between these modes, particularly highlighting that interpersonal communication is characterized by a two-way exchange and the importance of maintaining engagement through interactive body language. The content encourages focusing on fluency and understanding in communication rather than strict accuracy.